Dendrites
Recent articles
Modern AI is simply no match for the complexity likely required for harboring consciousness, says Jaan Aru
He argues that our brain’s computations are of a completely different nature than any artificial intelligence because they take place across many spatial and temporal scales and are inextricably entwined with biological materials.
Modern AI is simply no match for the complexity likely required for harboring consciousness, says Jaan Aru
He argues that our brain’s computations are of a completely different nature than any artificial intelligence because they take place across many spatial and temporal scales and are inextricably entwined with biological materials.
Spatial learning circuitry fluctuates in step with estrous cycle in mice
Cyclic shifts in estradiol levels coincide with changes in dendritic spine density and the activity of place cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a new study shows.
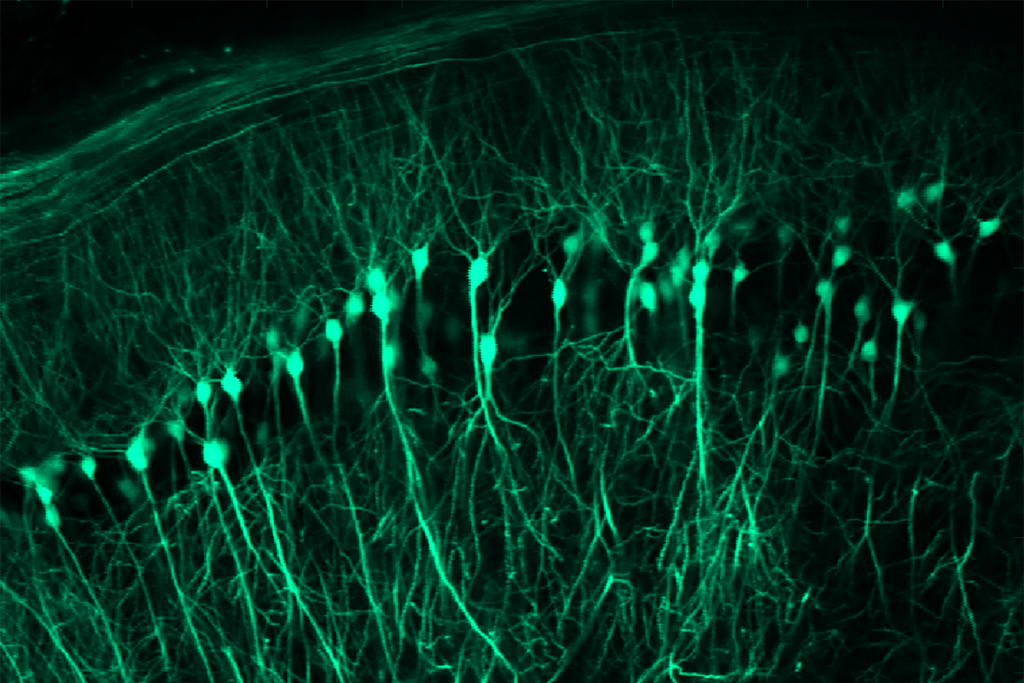
Spatial learning circuitry fluctuates in step with estrous cycle in mice
Cyclic shifts in estradiol levels coincide with changes in dendritic spine density and the activity of place cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a new study shows.
Sounding the alarm on pseudoreplication: Q&A with Constantinos Eleftheriou and Peter Kind
Most studies of neurological disorders in mice erroneously treat multiple samples from a single animal as independent replicates, according to a new analysis. But scientists and journals can take steps to curb this practice.
Sounding the alarm on pseudoreplication: Q&A with Constantinos Eleftheriou and Peter Kind
Most studies of neurological disorders in mice erroneously treat multiple samples from a single animal as independent replicates, according to a new analysis. But scientists and journals can take steps to curb this practice.
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
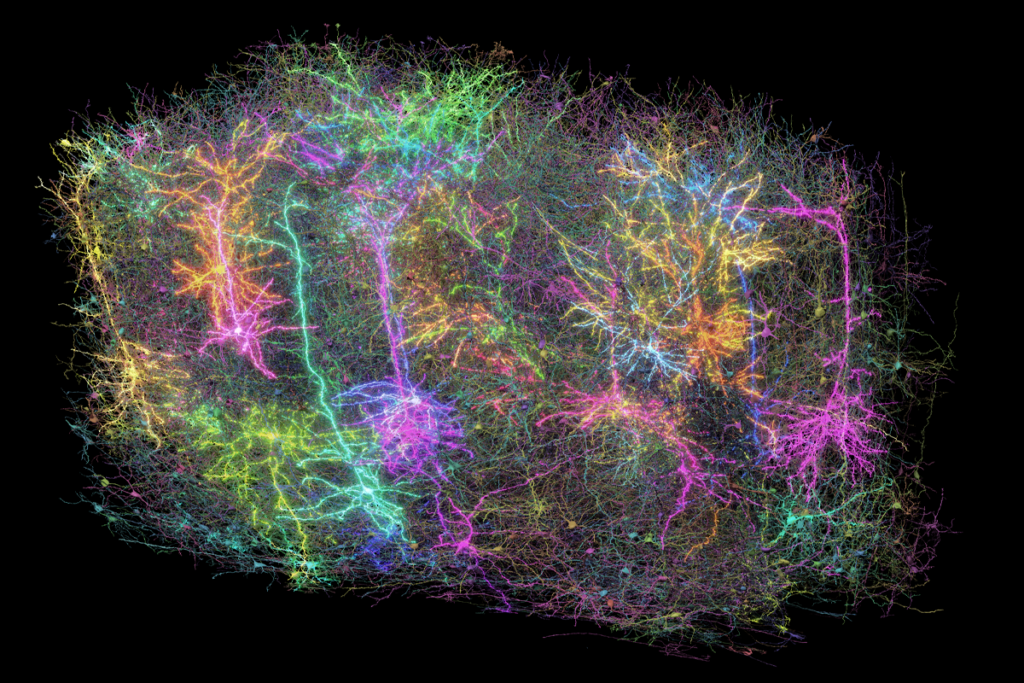
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
Releasing the Hydra with Rafael Yuste
Losing HHMI Investigator status prompted Yuste to study neural networks in a new way.

Releasing the Hydra with Rafael Yuste
Losing HHMI Investigator status prompted Yuste to study neural networks in a new way.
Targeting NMDA receptor subunit reverses fragile X traits in mice
The subunit acts as a “volume control” on signaling that shapes the density of dendritic spines, the new work suggests.
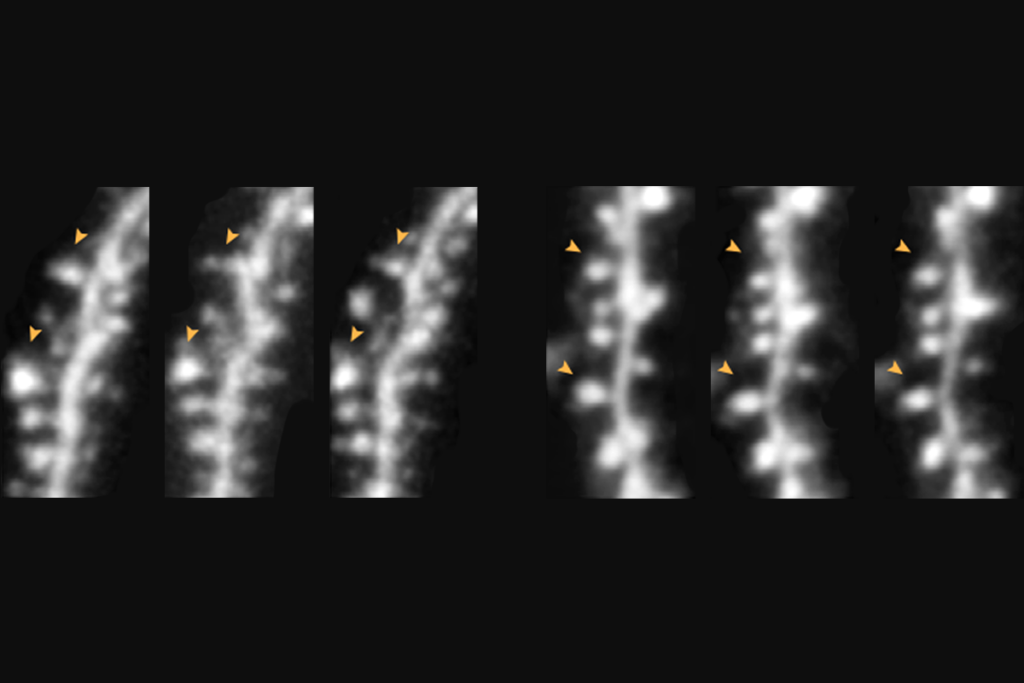
Targeting NMDA receptor subunit reverses fragile X traits in mice
The subunit acts as a “volume control” on signaling that shapes the density of dendritic spines, the new work suggests.
Synaptic anomalies in autistic people support imbalance hypothesis
Increased excitatory and decreased inhibitory synapses in the prefrontal cortex of autistic people suggest broader impacts on brain function and connectivity.
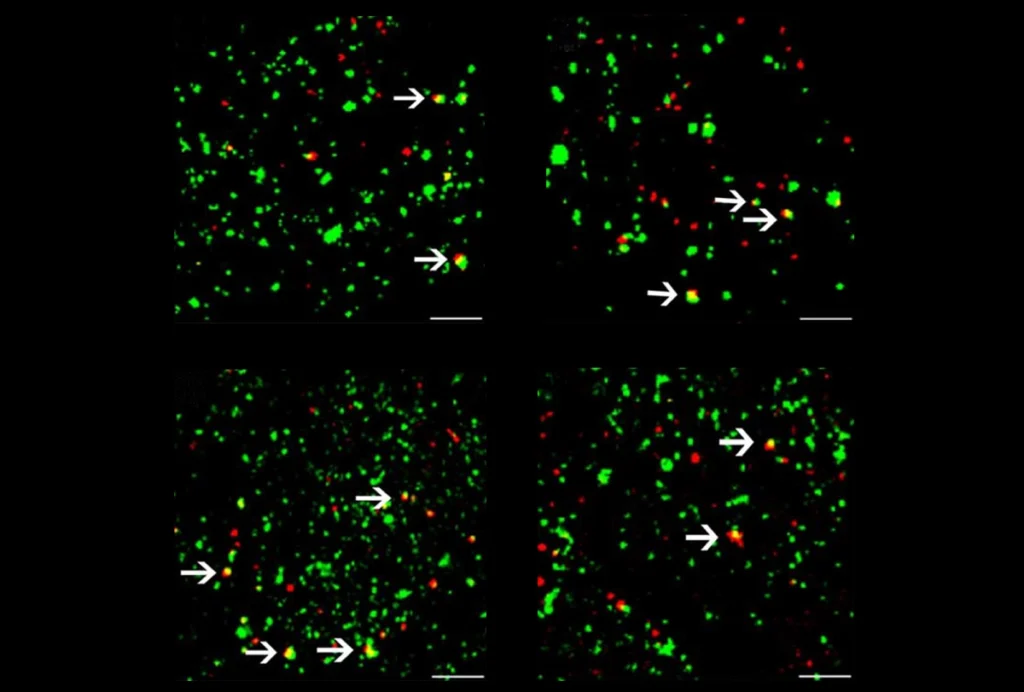
Synaptic anomalies in autistic people support imbalance hypothesis
Increased excitatory and decreased inhibitory synapses in the prefrontal cortex of autistic people suggest broader impacts on brain function and connectivity.
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Faulty mTOR signaling, implicated in syndromic forms of autism, also hinders cells grown from people with idiopathic autism or autism-linked deletions on chromosome 16.
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Faulty mTOR signaling, implicated in syndromic forms of autism, also hinders cells grown from people with idiopathic autism or autism-linked deletions on chromosome 16.
Neurons making memories shush their neighbors
When neurons strengthen their synapses, they “infect” surrounding cells with a virus-like protein to weaken those cells’ excitatory connections, according to a new preprint.
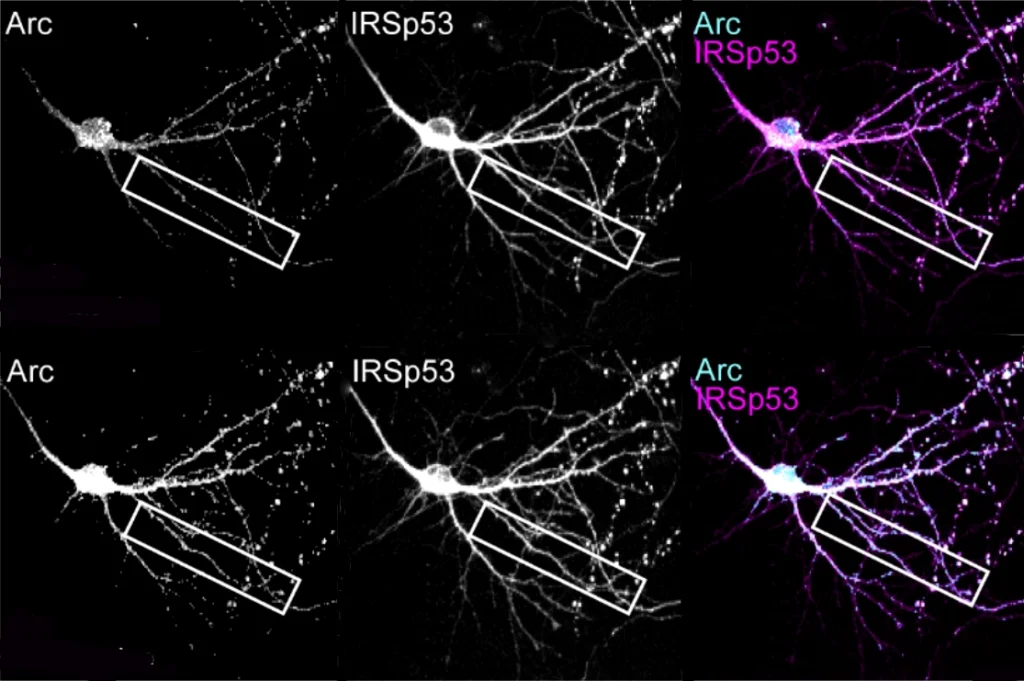
Neurons making memories shush their neighbors
When neurons strengthen their synapses, they “infect” surrounding cells with a virus-like protein to weaken those cells’ excitatory connections, according to a new preprint.
Microglial overreaction to atypical neurons may drive autism
In mice and organoids lacking a neuronal protein, microglia prune synapses to excess.
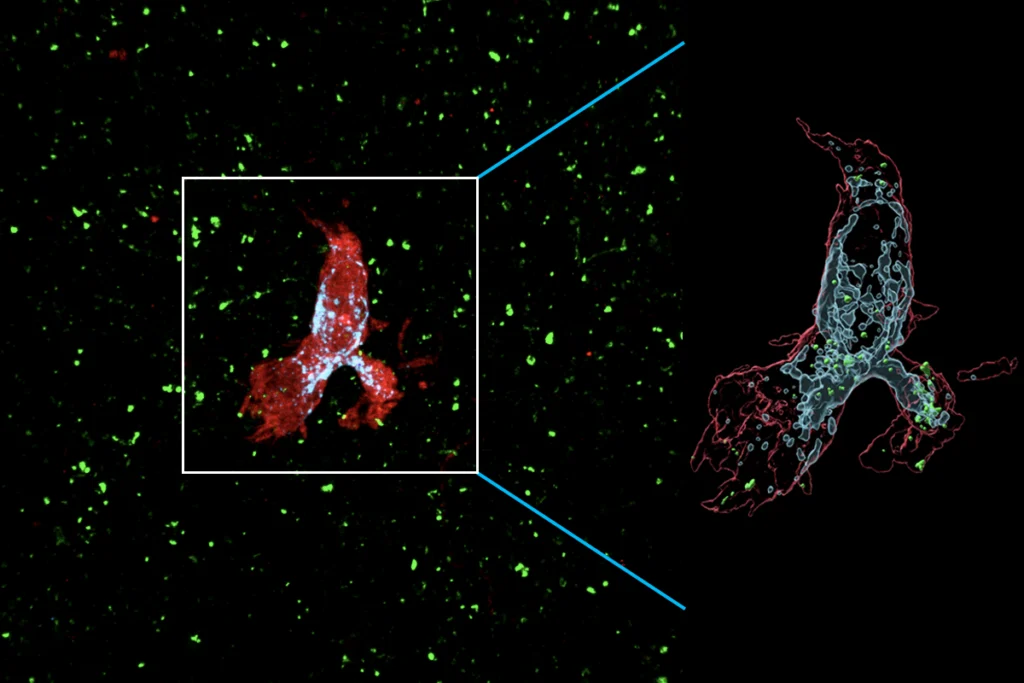
Microglial overreaction to atypical neurons may drive autism
In mice and organoids lacking a neuronal protein, microglia prune synapses to excess.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
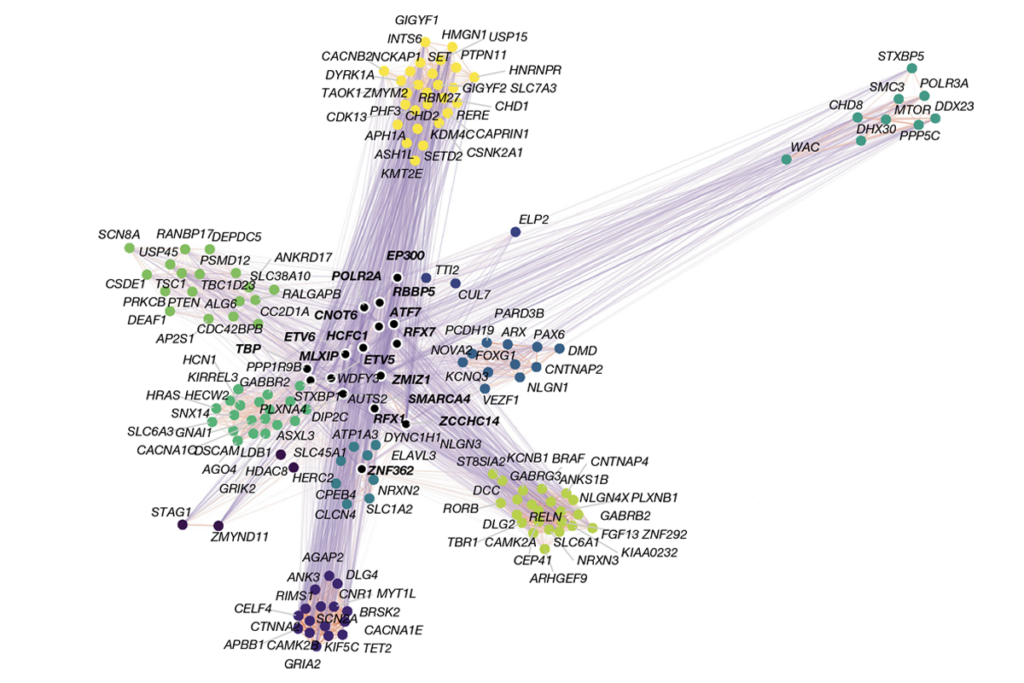
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
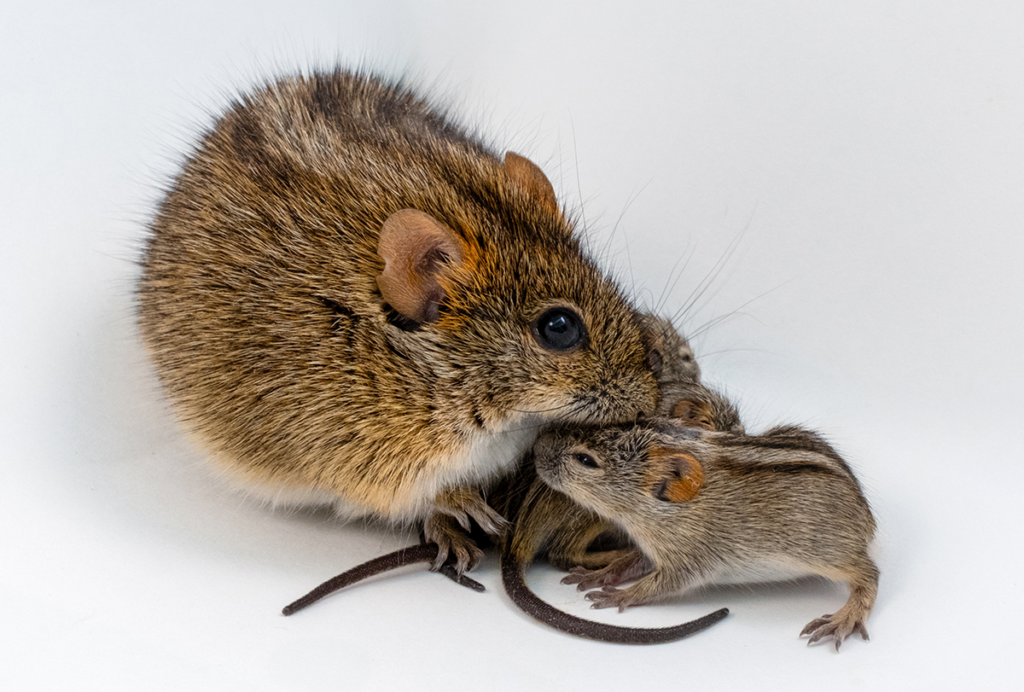

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.