SFARI Gene
Recent articles
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Sequencing study spotlights tight web of genes tied to autism
The findings, shared in a preprint, help to illuminate how a large and heterogeneous group of genes could be involved in autism.
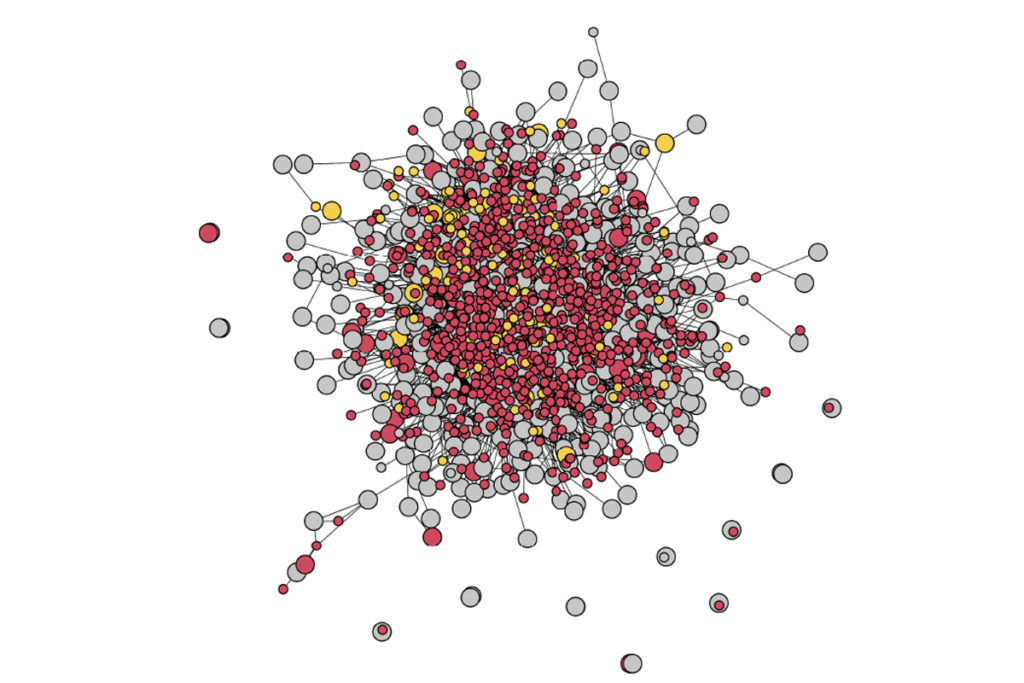
Sequencing study spotlights tight web of genes tied to autism
The findings, shared in a preprint, help to illuminate how a large and heterogeneous group of genes could be involved in autism.
‘VIP’ interneurons may drive autism traits in Dravet syndrome
The inhibitory cells misfire and contribute to social difficulties in mice that model the syndrome.

‘VIP’ interneurons may drive autism traits in Dravet syndrome
The inhibitory cells misfire and contribute to social difficulties in mice that model the syndrome.
Plethora of protein-making machines in neurons may underlie fragile X
An overabundance of ribosomes drives an imbalance of proteins produced from long and short genetic transcripts in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.
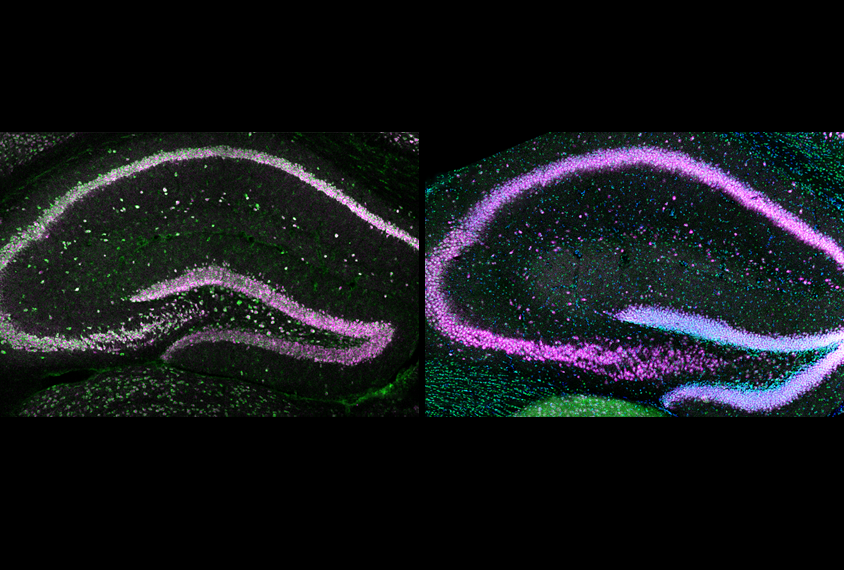
Plethora of protein-making machines in neurons may underlie fragile X
An overabundance of ribosomes drives an imbalance of proteins produced from long and short genetic transcripts in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.
Evolutionary approach reveals impact of missense variants in autism
Cross-species comparisons can help make sense of subtle genetic variants in people with autism and identify hundreds of new genes that may contribute to the condition.

Evolutionary approach reveals impact of missense variants in autism
Cross-species comparisons can help make sense of subtle genetic variants in people with autism and identify hundreds of new genes that may contribute to the condition.
New ranking system flags clinically relevant ‘autism genes’
A novel method to evaluate the strength of the evidence linking autism to specific genes could reveal which ones are most useful to screen for.

New ranking system flags clinically relevant ‘autism genes’
A novel method to evaluate the strength of the evidence linking autism to specific genes could reveal which ones are most useful to screen for.
‘Antisocial’ bees point to ancient roots for some autism genes
Honey bees that fail certain social tests have genetic profiles similar to those of people with autism.

‘Antisocial’ bees point to ancient roots for some autism genes
Honey bees that fail certain social tests have genetic profiles similar to those of people with autism.
Family groups play key role in advancing autism research
Families need more support from researchers in order for their heroic efforts to be optimally effective.
Family groups play key role in advancing autism research
Families need more support from researchers in order for their heroic efforts to be optimally effective.
Control centers for genes rife with autism-linked DNA blips
DNA sequences called enhancers — which boost the expression of genes from within or outside them — are enriched for genetic variants linked to autism, suggests a new study. The finding may help researchers understand how variants outside genes contribute to autism.

Control centers for genes rife with autism-linked DNA blips
DNA sequences called enhancers — which boost the expression of genes from within or outside them — are enriched for genetic variants linked to autism, suggests a new study. The finding may help researchers understand how variants outside genes contribute to autism.
Gene networks offer entry point to unraveling autism
By mapping the connections between autism genes, researchers are finding clues to the disorder’s origins. The key, they say, is to begin without bias.

Gene networks offer entry point to unraveling autism
By mapping the connections between autism genes, researchers are finding clues to the disorder’s origins. The key, they say, is to begin without bias.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
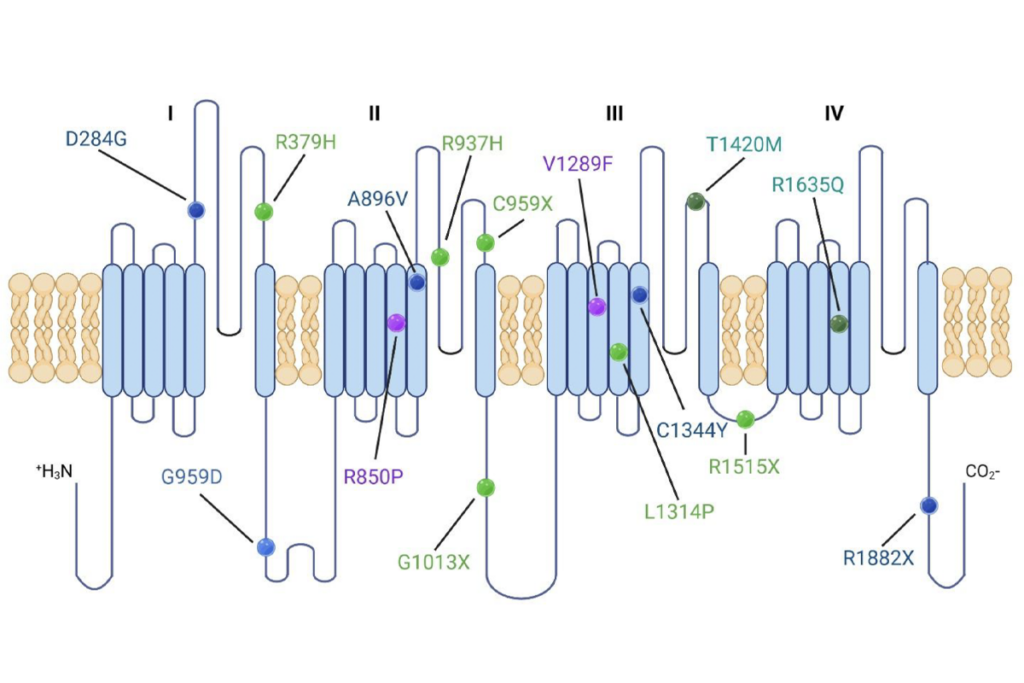
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.