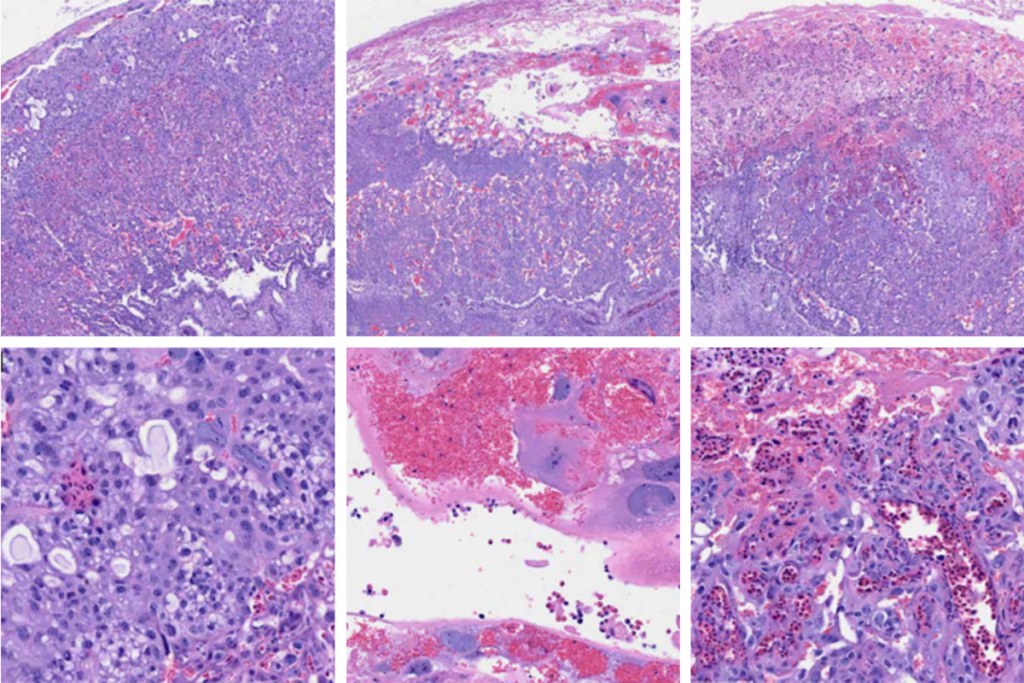
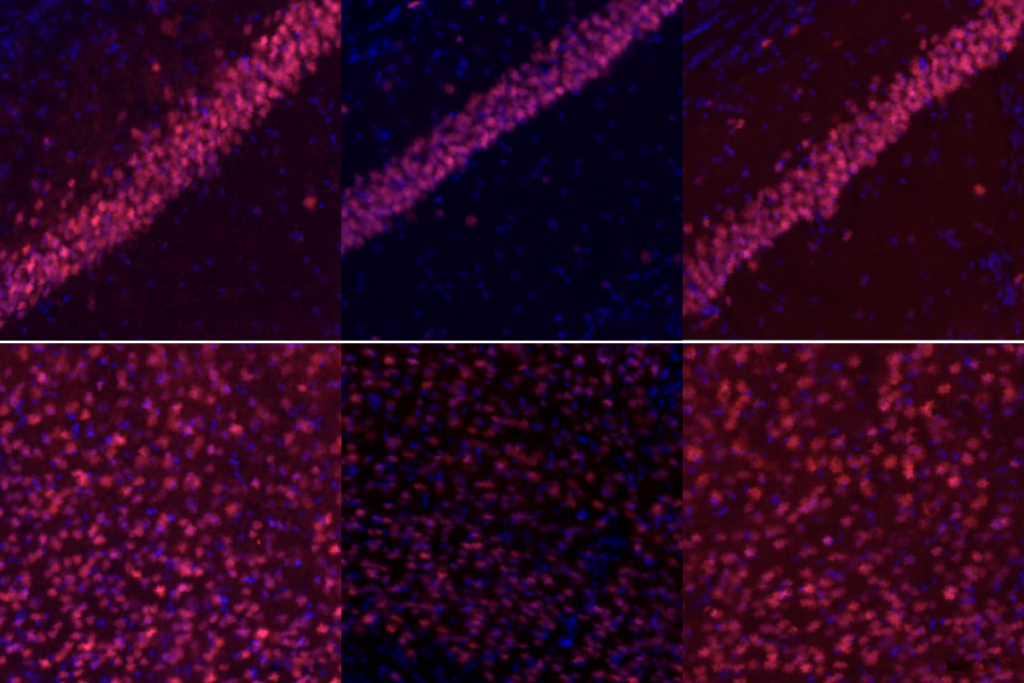
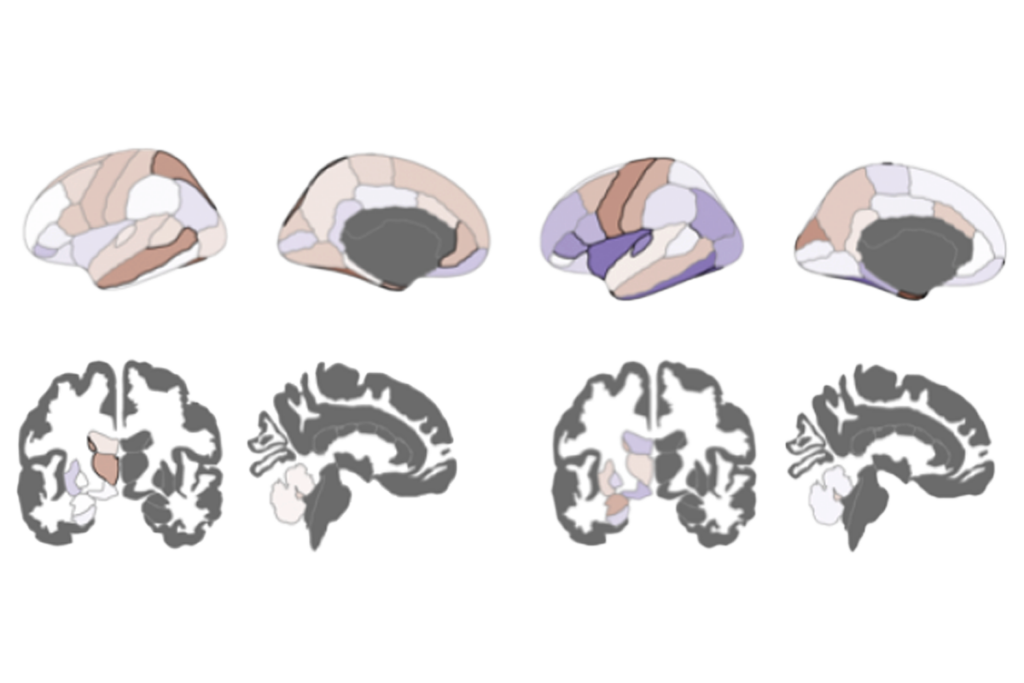
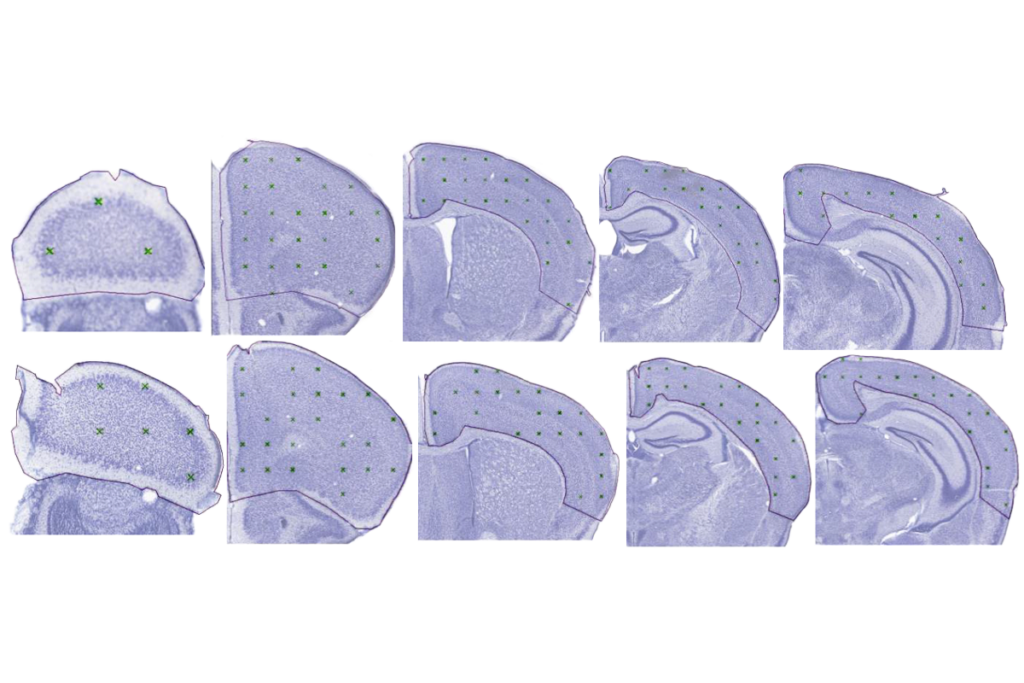
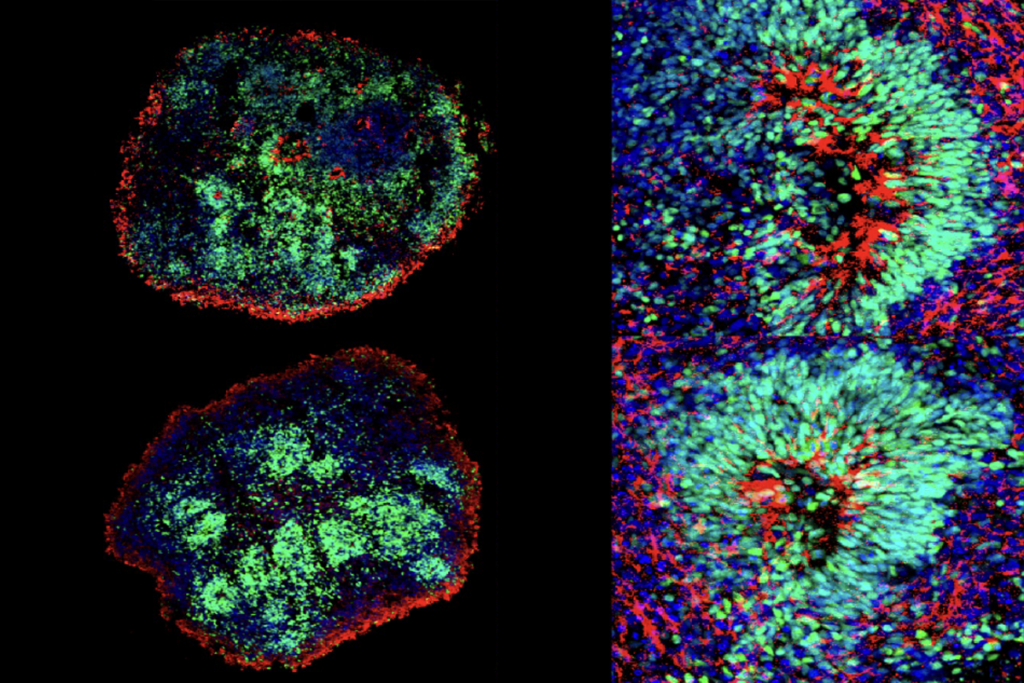
Upstream movers: Mice deficient in the autism-linked gene CHD8 have altered structure and function of excitatory neurons, synapses and circuits, according to a new study. The animals developed atypically large heads, consistent with a similar effect observed in humans with CHD8 variants. But this macroencephaly was not accompanied by more or bigger neurons. Still, glutamate-containing neurons displayed altered spine density and decreased second-messenger activity. The investigators write that their results are consistent with a framework for neurodevelopmental conditions that converges on “excitatory neuron dysfunction at the level of cortical excitatory synapses and circuits.” Research Square
More autism research we spotted:
- “Testing the auditory steady-state response (ASSR) to 40-Hz and 27-Hz click trains in children with autism spectrum disorder and their first-degree biological relatives: A high-density electroencephalographic (EEG) study” bioRxiv
- “Iron deposition and functional connectivity alterations in the right substantia nigra of adult males with autism” Cerebral Cortex
- “Autism-associated SCN2A haploinsufficiency disrupts in vivo dendritic signaling and impairs flexible decision-making” bioRxiv
See also: “Microglial overreaction to atypical neurons may drive autism” - “Neurobehavioral profile of individuals with pathogenic variants in CHD3” European Journal of Human Genetics
- “RFK Jr. vowed to find the environmental causes of autism. Then he shut down research trying to do just that.” ProPublica