- Cultured neurons carrying an SCN3A gene variant, a model of SCN3A-related neurodevelopmental disorder, show altered sodium conductance, leading to lower action-potential thresholds and aberrant firing patterns. Brain
- Babies born to parents with documented infertility issues have a slightly greater likelihood of having autism, according to an analysis of 1.3 million births in Ontario, Canada. JAMA Network Open
- A new resource contains the gamut of microglia shapes — branched, ameboid, rod-like and hypertrophic — in different brain regions, according to a preprint. bioRxiv
- High-frequency neurotransmission, or “burst firing,” depends on local axonal translation of proteins near the synapse. Neuron
- The PANSS-Autism-Severity-Score screen, used to assess autism traits in people with psychosis, appears to miss those traits in autistic people. Schizophrenia Bulletin
- Brain regions mature at different rates in early childhood, according to a comprehensive analysis of neuroimaging data from 2,000 children under age 7. Nature Neuroscience
- In mice, the hormone leptin appears to mediate weight gain and insulin resistance that occurs with antipsychotic medication; anti-leptin antibodies ameliorate these effects. Science Translational Medicine
- The autism-linked gene KDM5A is essential for establishing hippocampal cell identity, via its role in regulating chromatin. Science Advances
Microglia shapes; SCN3A gene; leptin’s role in antipsychotic-induced weight gain
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 4 December.
By
Jill Adams
5 December 2023 | 2 min read
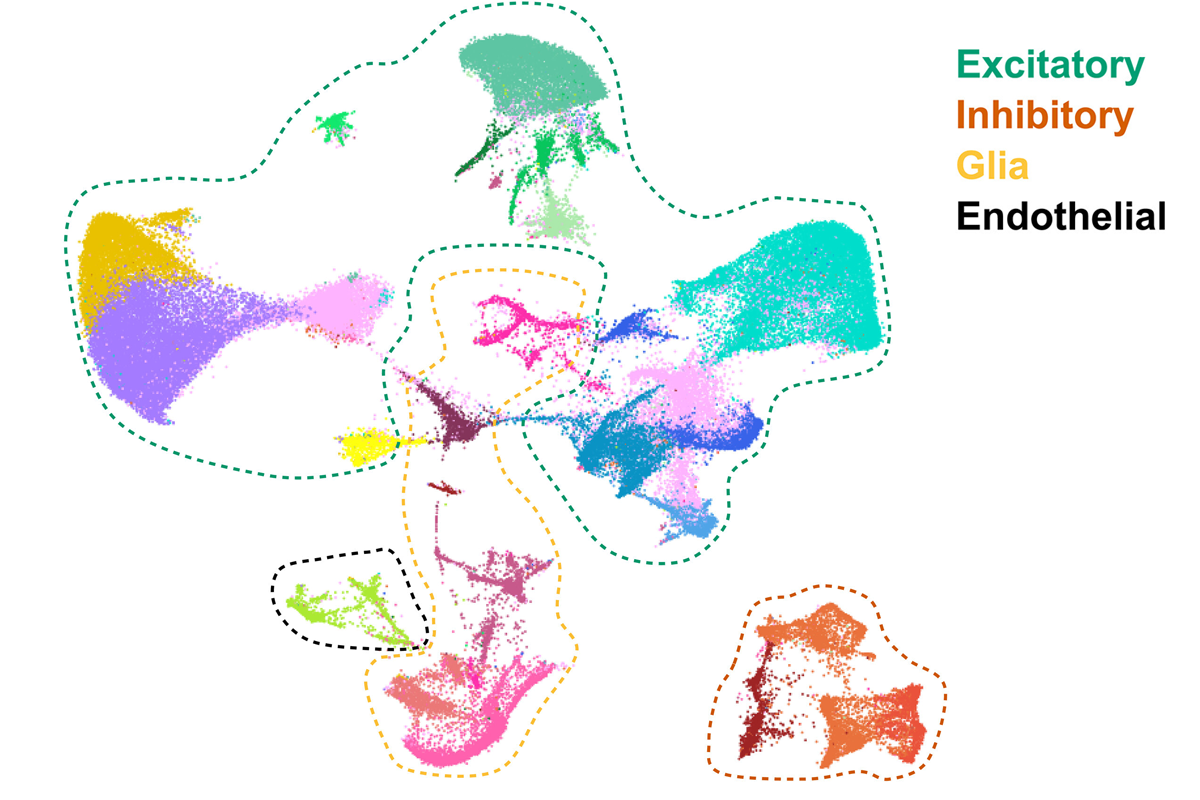
Cell demographics: The autism-linked gene KDM5A is essential to establish hippocampal cell identity, grouped here by type in the mouse hippocampus using UMAP, a dimensionality reduction tool.
- Among girls evaluated for autism, those who are diagnosed tend to be younger and have lower cognitive skills and fewer internalizing or externalizing behaviors. The Clinical Neuropsychologist
- The gaze behavior of autistic children viewing a social interaction — i.e., whether they look at people’s eyes or not — appears to correlate with fractional anisotropy values, a biomarker of nerve myelination, in specific brain areas. Cerebral Cortex
Explore more from The Transmitter

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
By
Michael Eisenstein
13 March 2026 | 7 min read

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
By
Holly Barker
12 March 2026 | 4 min read
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
By
Paul Middlebrooks
11 March 2026 | 100 min listen
Cite this article: