Striatum
Recent articles
Among brain changes studied in autism, spotlight shifts to subcortex
The striatum and thalamus are more likely than the cerebral cortex to express autism variants or bear transcriptional changes, two unpublished studies find.
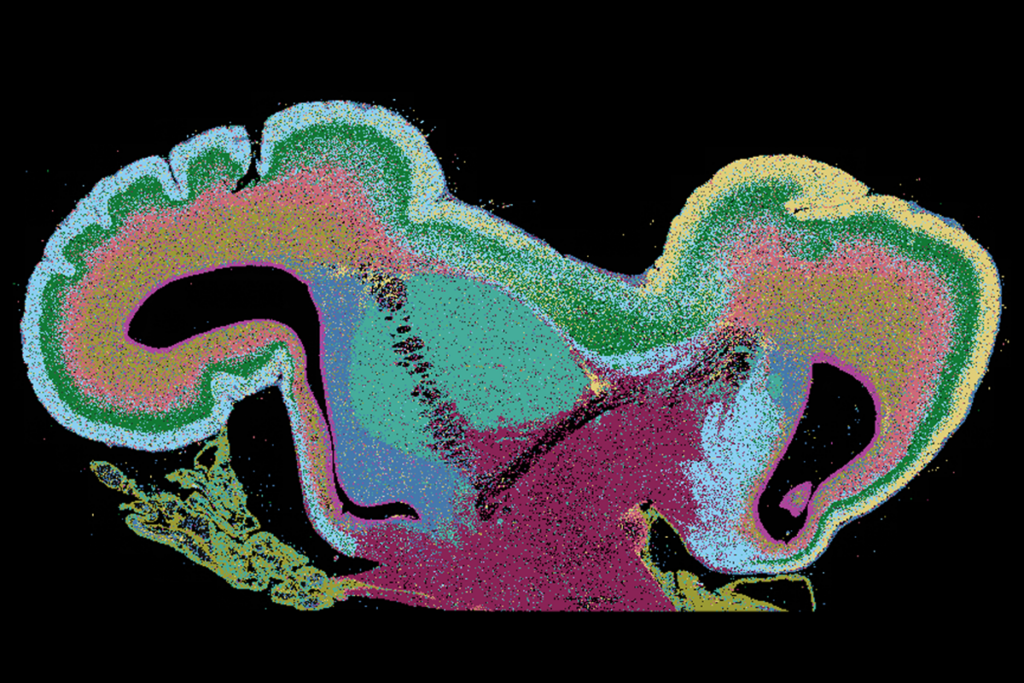

Among brain changes studied in autism, spotlight shifts to subcortex
The striatum and thalamus are more likely than the cerebral cortex to express autism variants or bear transcriptional changes, two unpublished studies find.
Some dopamine neurons signal default behaviors to reinforce habits
Movement-sensing neurons that target the striatum influence a mouse’s choice of action by favoring routine.
Some dopamine neurons signal default behaviors to reinforce habits
Movement-sensing neurons that target the striatum influence a mouse’s choice of action by favoring routine.
‘Ancient’ brainstem structure evolved beyond basic motor control
The human red nucleus may also help coordinate action, reward and motivated behavior, a new study suggests.
‘Ancient’ brainstem structure evolved beyond basic motor control
The human red nucleus may also help coordinate action, reward and motivated behavior, a new study suggests.
Structure of striatum varies by sex in autistic children
The changes could reflect different developmental trajectories between boys and girls with autism, a new study suggests.

Structure of striatum varies by sex in autistic children
The changes could reflect different developmental trajectories between boys and girls with autism, a new study suggests.
Newly characterized striatal circuits add twist to ‘go/no-go’ model of movement control
The two novel pathways control dopamine release in opposing ways and may link motivation and mood to action, a new study shows.
Newly characterized striatal circuits add twist to ‘go/no-go’ model of movement control
The two novel pathways control dopamine release in opposing ways and may link motivation and mood to action, a new study shows.
Reconstructing dopamine’s link to reward
The field is grappling with whether to modify the long-standing theory of reward prediction error—or abandon it entirely.

Reconstructing dopamine’s link to reward
The field is grappling with whether to modify the long-standing theory of reward prediction error—or abandon it entirely.
Skewed signaling in striatum may spawn repetitive behaviors
Synaptic changes in the brain region could drive a core trait of fragile X syndrome, a new mouse study suggests.
Skewed signaling in striatum may spawn repetitive behaviors
Synaptic changes in the brain region could drive a core trait of fragile X syndrome, a new mouse study suggests.
Abundant motor proteins disrupt cries in FOXP2 mice
Knocking down the gene that codes for the proteins normalizes the vocalizations.
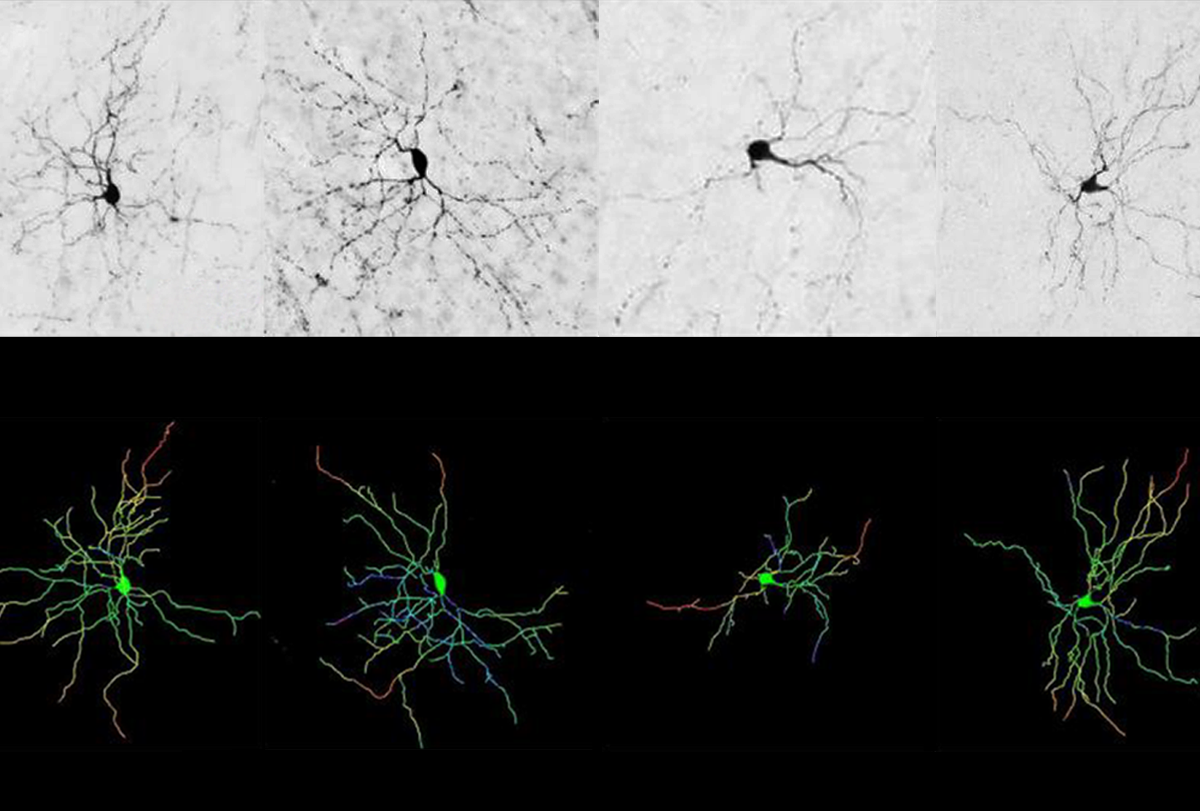
Abundant motor proteins disrupt cries in FOXP2 mice
Knocking down the gene that codes for the proteins normalizes the vocalizations.
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
One-rosette technique grows well-organized organoids
The method yields complex organoids that more closely mimic embryonic brain development than do those cultured in other ways.
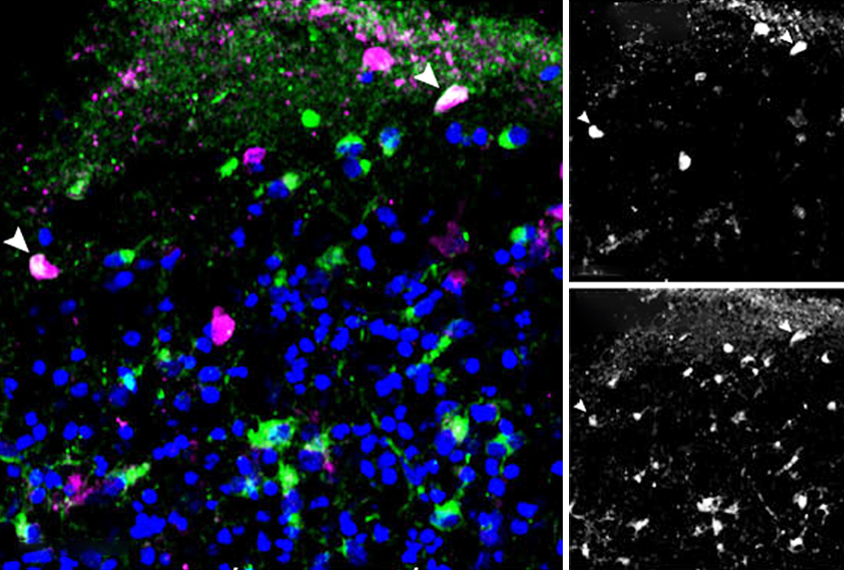
One-rosette technique grows well-organized organoids
The method yields complex organoids that more closely mimic embryonic brain development than do those cultured in other ways.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.

Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
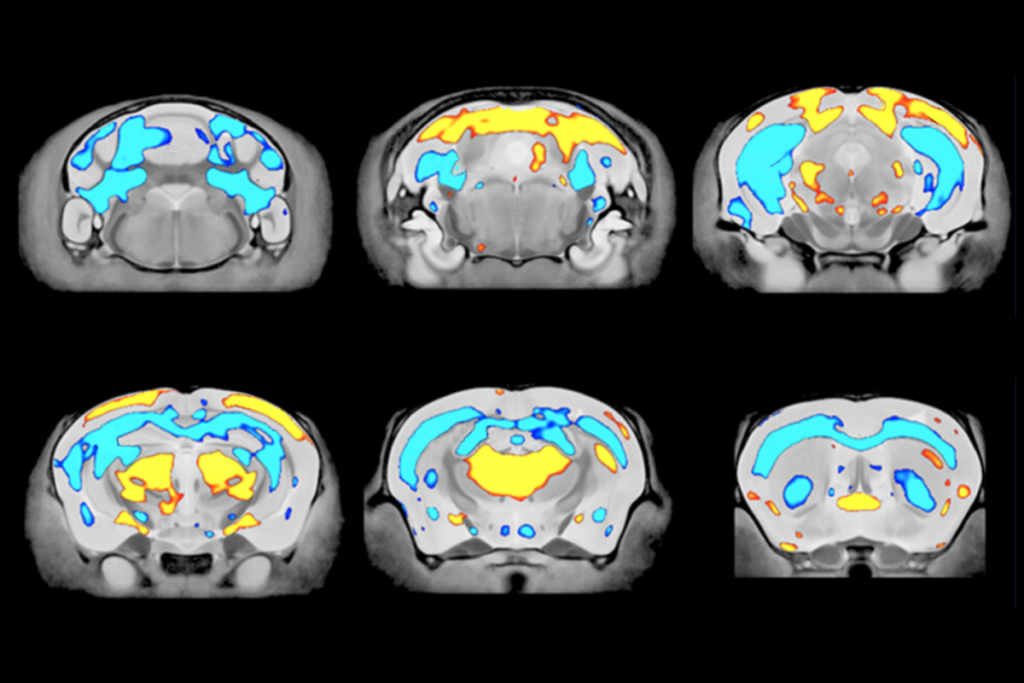
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.