Hypothalamus
Recent articles
Cracking the neural code for emotional states
Rather than act as a simple switchboard for innate behaviors, the hypothalamus encodes an animal's internal state, which influences behavior.

Cracking the neural code for emotional states
Rather than act as a simple switchboard for innate behaviors, the hypothalamus encodes an animal's internal state, which influences behavior.
Perimenopause: An important—and understudied—transition for the brain
Many well-known perimenopause symptoms arise in the brain, but we still know little about the specific mechanisms at play. More research—in both animals and humans—is essential.

Perimenopause: An important—and understudied—transition for the brain
Many well-known perimenopause symptoms arise in the brain, but we still know little about the specific mechanisms at play. More research—in both animals and humans—is essential.
Too much or too little brain synchrony may underlie autism subtypes
Functional connectivity differences in autism mouse models point to two subtypes that correspond to patterns seen in some people with the condition.
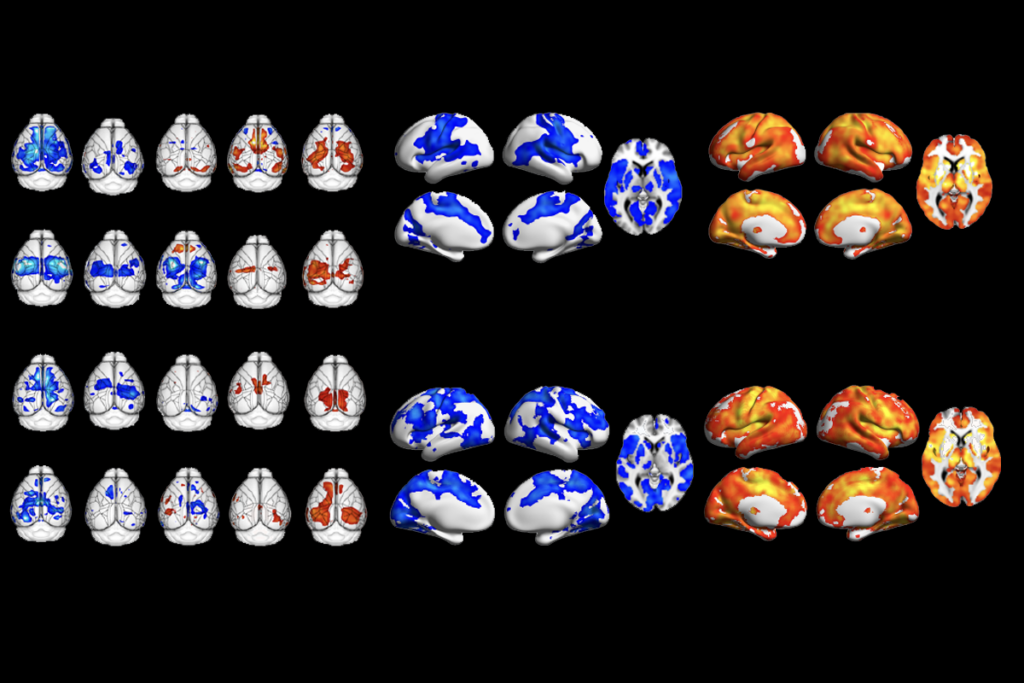

Too much or too little brain synchrony may underlie autism subtypes
Functional connectivity differences in autism mouse models point to two subtypes that correspond to patterns seen in some people with the condition.
Soft touch quells loneliness in mice
Touch modulates one of two dueling types of hypothalamic neurons that, thermostat-like, balance an animal’s drive for social interaction.

Soft touch quells loneliness in mice
Touch modulates one of two dueling types of hypothalamic neurons that, thermostat-like, balance an animal’s drive for social interaction.
Age-related brain changes in mice strike hypothalamus ‘hot spot’
Neuronal and non-neuronal cells throughout the brain also express genes—particularly those related to neuronal structure and immune function—differently in aged mice, according to a new atlas.
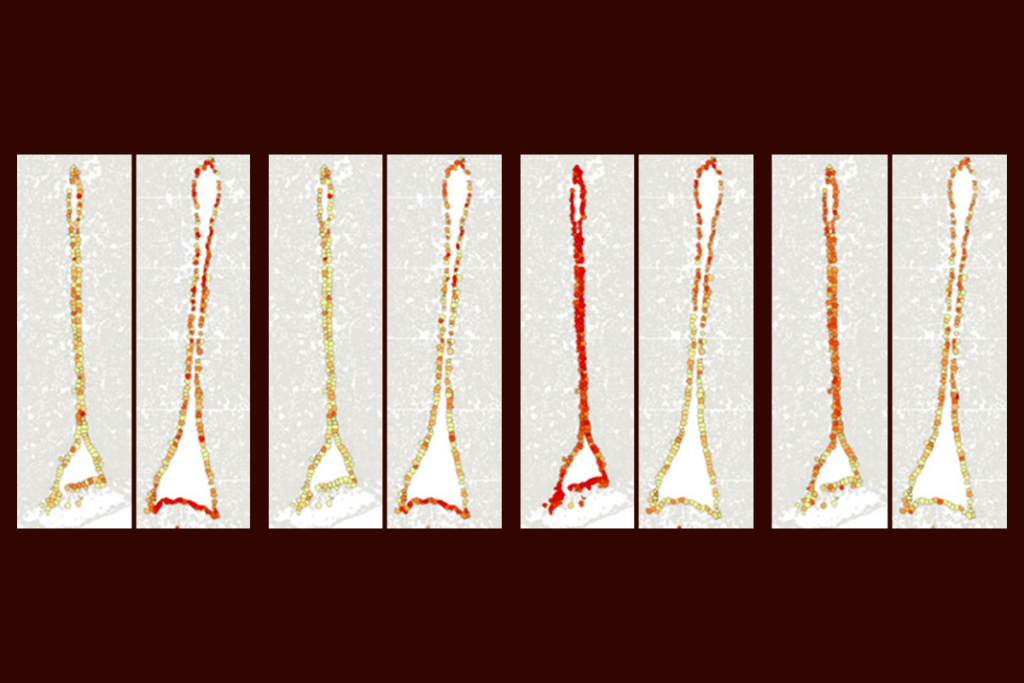
Age-related brain changes in mice strike hypothalamus ‘hot spot’
Neuronal and non-neuronal cells throughout the brain also express genes—particularly those related to neuronal structure and immune function—differently in aged mice, according to a new atlas.
To beat the heat, hypothalamus neurons in mice ramp up their firing
The uptick may help the rodents acclimate to temperature hikes and keep their cool.

To beat the heat, hypothalamus neurons in mice ramp up their firing
The uptick may help the rodents acclimate to temperature hikes and keep their cool.
Novel neurons upend ‘yin-yang’ model of hunger, satiety in brain
The new type of leptin-sensitive cells curb hunger quickly—adding to an increasingly complex picture of brain circuits that control feeding behaviors.
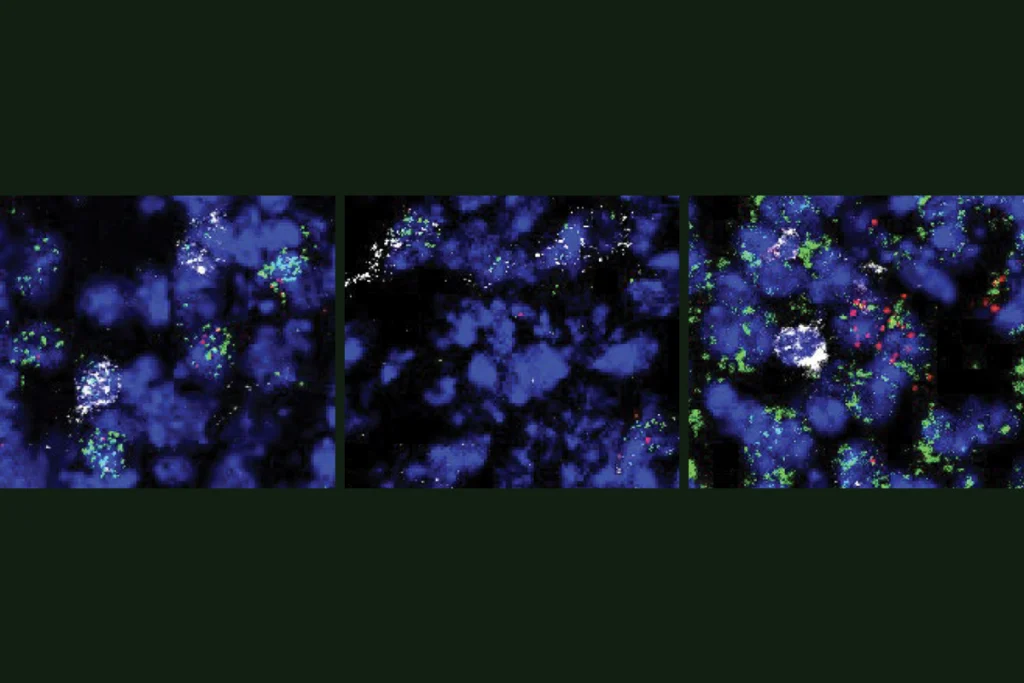
Novel neurons upend ‘yin-yang’ model of hunger, satiety in brain
The new type of leptin-sensitive cells curb hunger quickly—adding to an increasingly complex picture of brain circuits that control feeding behaviors.
Rousing a ‘new era’ of hibernation research
Novel applications of neuroscience tools have enabled researchers to uncover the neural controls of an extreme biological trait.

Rousing a ‘new era’ of hibernation research
Novel applications of neuroscience tools have enabled researchers to uncover the neural controls of an extreme biological trait.
Should I stay (and eat) or should I go? How the brain balances hunger with competing drives
Understanding the interplay among rival signals, such as pain, thirst and fear, could provide insights into anxiety and other neuropsychiatric conditions.

Should I stay (and eat) or should I go? How the brain balances hunger with competing drives
Understanding the interplay among rival signals, such as pain, thirst and fear, could provide insights into anxiety and other neuropsychiatric conditions.
Temperature tunes circadian timing in some desert mammals
Light has hogged all the attention in chronobiology research—but now, in camel, goat and mole rat experiments, temperature takes the lead.

Temperature tunes circadian timing in some desert mammals
Light has hogged all the attention in chronobiology research—but now, in camel, goat and mole rat experiments, temperature takes the lead.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.

Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.
This paper changed my life: Ishmail Abdus-Saboor on balancing the study of pain and pleasure
A 2013 Nature paper from David Anderson’s lab revealed a group of sensory neurons involved in pleasurable touch and led Abdus-Saboor down a new research path.
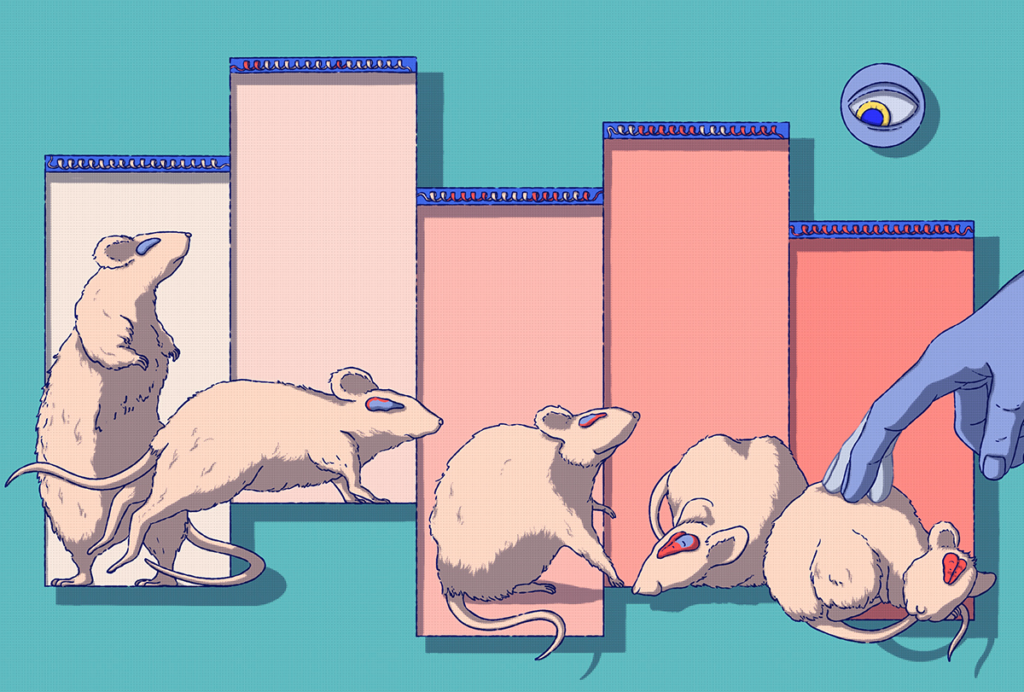
This paper changed my life: Ishmail Abdus-Saboor on balancing the study of pain and pleasure
A 2013 Nature paper from David Anderson’s lab revealed a group of sensory neurons involved in pleasurable touch and led Abdus-Saboor down a new research path.
Sex bias in autism drops as age at diagnosis rises
The disparity begins to level out after age 10, raising questions about why so many autistic girls go undiagnosed earlier in childhood.

Sex bias in autism drops as age at diagnosis rises
The disparity begins to level out after age 10, raising questions about why so many autistic girls go undiagnosed earlier in childhood.