Alysson Muotri is professor of pediatrics and of cellular and molecular medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He also co-directs the Stem Cell Program at the university’s Moores Cancer Center.

Alysson Muotri
Associate professor
University of California, San Diego
From this contributor
With tweaks, brains in a dish may yield clear clues to autism
‘Mini-brains’ created in a dish may reveal autism’s roots and point to treatments, but they do not yet mirror some critical features of a human brain.
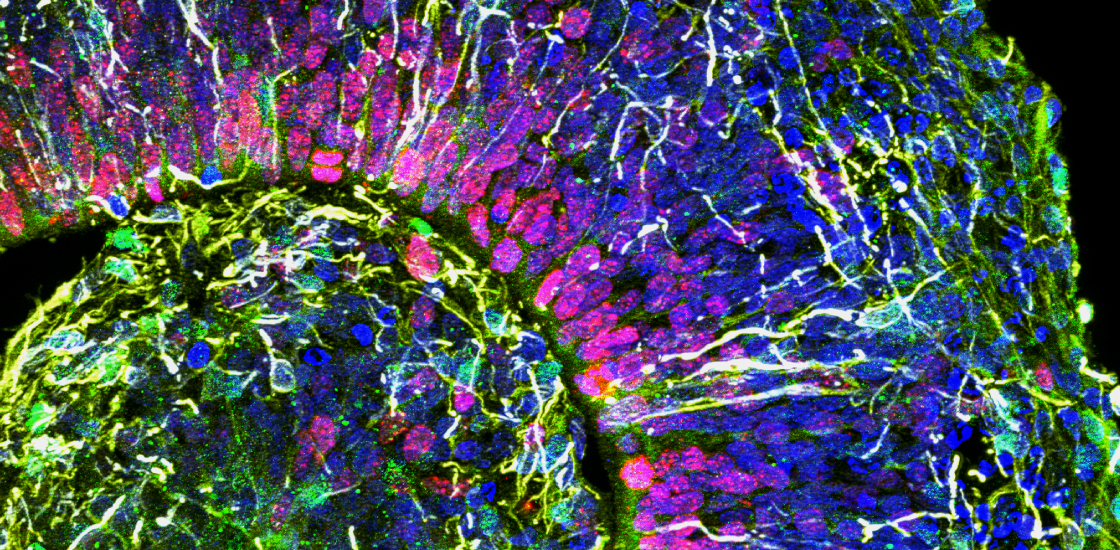
With tweaks, brains in a dish may yield clear clues to autism
Questions for Alysson Muotri: Applying autism tools to Zika
Mini-brains grown from stem cells in culture can reveal the effects of both autism and the Zika virus on early development.

Questions for Alysson Muotri: Applying autism tools to Zika
Explore more from The Transmitter
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
In-vivo base editing in a mouse model of autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 23 February.
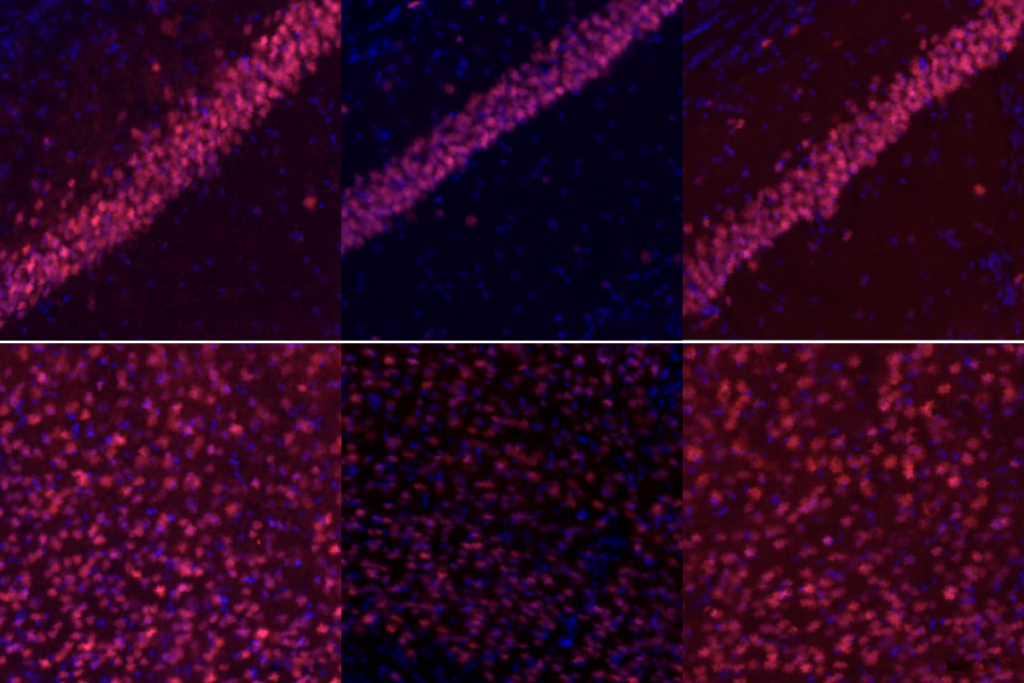
In-vivo base editing in a mouse model of autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 23 February.
Infant visual system categorizes common objects by 2 months of age
Brain activity patterns in the ventral visual cortex appear to distinguish images across 12 categories, including birds and trees, longitudinal functional MRI scans suggest.
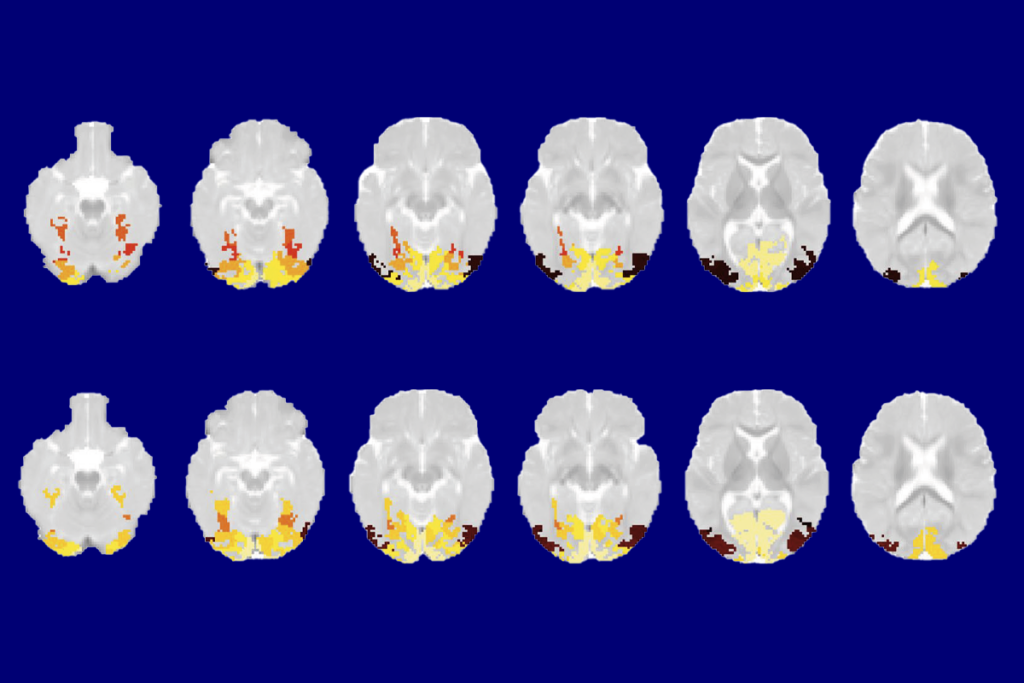
Infant visual system categorizes common objects by 2 months of age
Brain activity patterns in the ventral visual cortex appear to distinguish images across 12 categories, including birds and trees, longitudinal functional MRI scans suggest.