Emma Yasinski is a freelance writer covering biology, neuroscience and medicine. Her stories have appeared in The Scientist, Discover Magazine, Smithsonian Magazine, Kaiser Health News and other publications. Yasinski has an M.Sc. in science and medical journalism from Boston University and a B.S. in neuroscience from Lafayette College in Easton, Pennsylvania.

Emma Yasinski
Contributing writer
From this contributor
Parental care may sculpt brain development in prairie voles
Voles reared primarily by their fathers show altered synapse density.

Parental care may sculpt brain development in prairie voles
Social-pragmatic difficulties common with autism, other diagnoses
A standard questionnaire can help identify social (pragmatic) communication disorder more readily in school-age children.

Social-pragmatic difficulties common with autism, other diagnoses
Fragile X neurons develop atypically in chimeric mice
After a brain transplant of reprogrammed human cells, the animals can for the first time recapitulate some neuronal changes seen in people with fragile X syndrome.
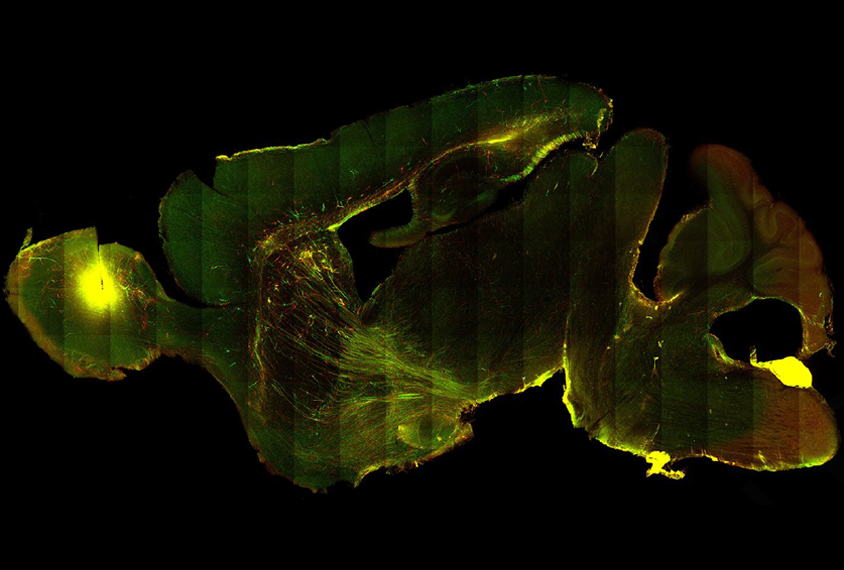
Fragile X neurons develop atypically in chimeric mice
Inflexible thinking in adolescence linked to emotional, behavioral issues in adulthood
Treating cognitive inflexibility — for example, by practicing problem-solving — might help ease anxiety and depression in autistic people.

Inflexible thinking in adolescence linked to emotional, behavioral issues in adulthood
Mutations linked to autism may be detectable in men’s sperm
An advanced DNA-sequencing technique has identified gene-damaging mutations, some with ties to autism, in about 1 in 15 men.

Mutations linked to autism may be detectable in men’s sperm
Explore more from The Transmitter
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.

This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.