Corpus callosum
Recent articles
Brain structures grow differently in boys, men with autism
Autistic boys and men show notable differences in brain development, according to magnetic resonance imaging scans taken over a 16-year period.

Brain structures grow differently in boys, men with autism
Autistic boys and men show notable differences in brain development, according to magnetic resonance imaging scans taken over a 16-year period.
Loss of a top autism gene may alter neuron structure
Mutations in the autism-linked gene ASH1L change how neurons grow and develop.
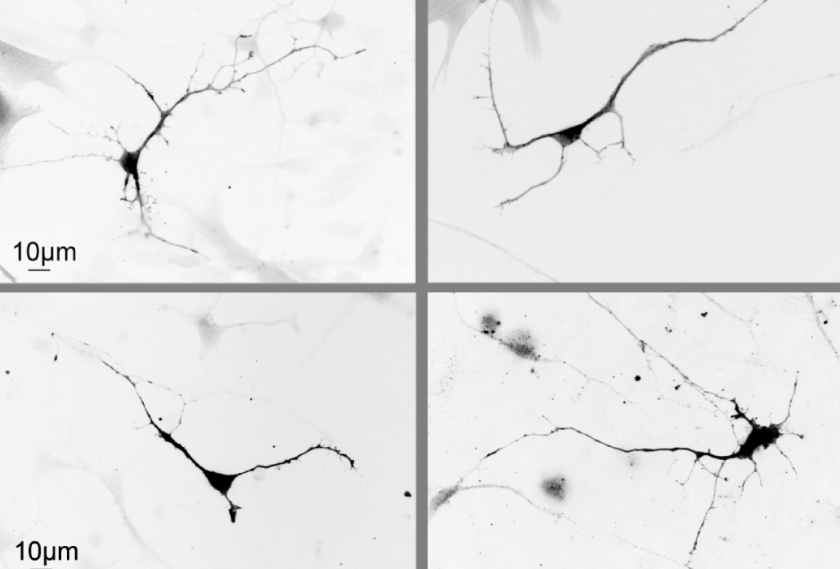
Loss of a top autism gene may alter neuron structure
Mutations in the autism-linked gene ASH1L change how neurons grow and develop.
Brain structure changes in autism, explained
Autistic people have distinct patterns of brain development, which sometimes result in differences in brain structure. Here's what we know about those differences.
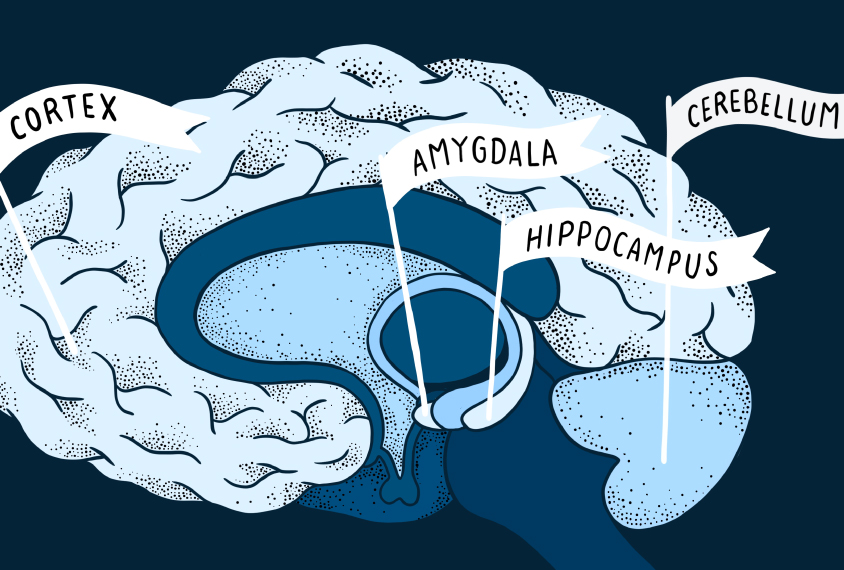
Brain structure changes in autism, explained
Autistic people have distinct patterns of brain development, which sometimes result in differences in brain structure. Here's what we know about those differences.
Study links gene to inherited form of autism
Mutations in both copies of a gene called ACTL6B lead to autism, epilepsy and intellectual disability.
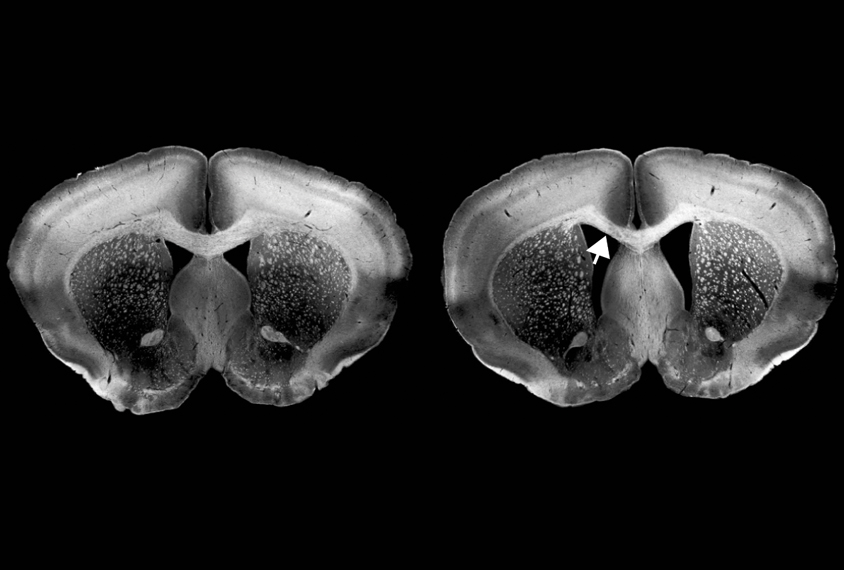
Study links gene to inherited form of autism
Mutations in both copies of a gene called ACTL6B lead to autism, epilepsy and intellectual disability.
Structure of brain matter in young autistic children may show distinct patterns
The long fibers of neurons in the brains of young children with autism are structured differently from those of their neurotypical peers — and from those of older children with the condition.
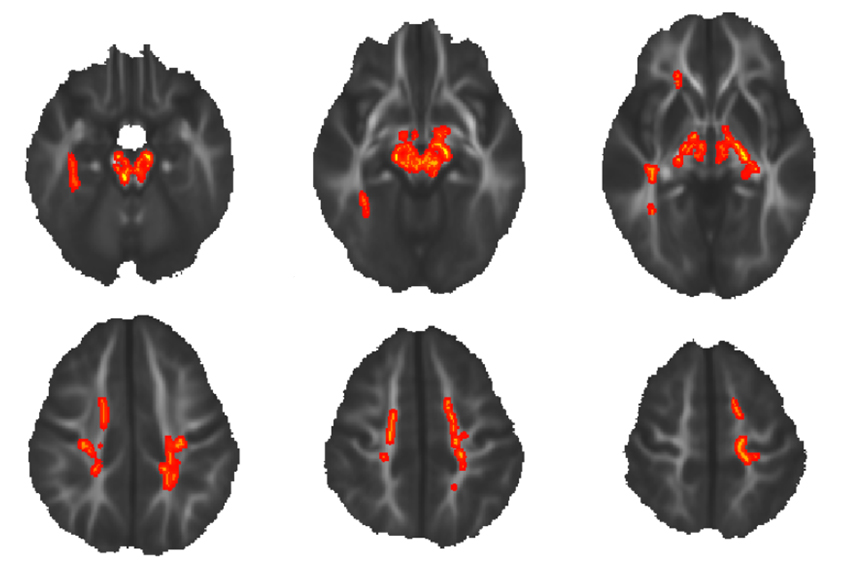
Structure of brain matter in young autistic children may show distinct patterns
The long fibers of neurons in the brains of young children with autism are structured differently from those of their neurotypical peers — and from those of older children with the condition.
In new device, brain organoids ‘talk’ to each other
A novel cell culture device enables researchers to grow bundles of nerve fibers from stem cells, mimicking the tissue that connects distant parts of the brain.
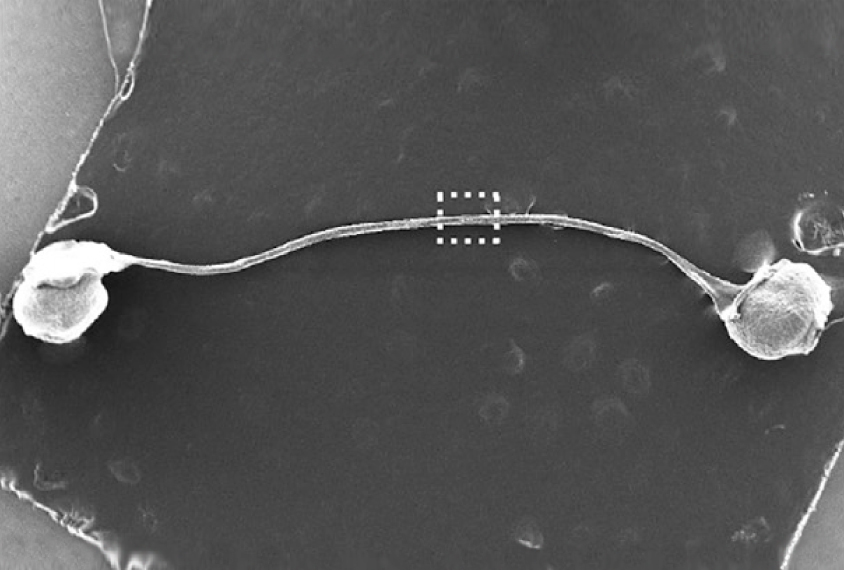
In new device, brain organoids ‘talk’ to each other
A novel cell culture device enables researchers to grow bundles of nerve fibers from stem cells, mimicking the tissue that connects distant parts of the brain.
‘Outmoded’ mouse models of autism may still yield new advances
Many researchers question the value of three early mouse models of autism, but the models have their staunch supporters.

‘Outmoded’ mouse models of autism may still yield new advances
Many researchers question the value of three early mouse models of autism, but the models have their staunch supporters.
Decoding the overlap between autism and ADHD
Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder often coincide, but the search for common biological roots has turned up conflicting evidence.
Decoding the overlap between autism and ADHD
Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder often coincide, but the search for common biological roots has turned up conflicting evidence.
Three autism mouse models marked by defects in same circuit
Problems with social interactions stem from faulty wiring of a single circuit spanning distant brain regions, results from three mouse models of autism suggest.
Three autism mouse models marked by defects in same circuit
Problems with social interactions stem from faulty wiring of a single circuit spanning distant brain regions, results from three mouse models of autism suggest.
Off-key outcomes; visualizing variants; urine indifference and more
Music therapy proves ineffective for autism, brain structures differ with 16p11.2 duplications and deletions, and mice missing NLGN3 may influence the sociability of their littermates.
Off-key outcomes; visualizing variants; urine indifference and more
Music therapy proves ineffective for autism, brain structures differ with 16p11.2 duplications and deletions, and mice missing NLGN3 may influence the sociability of their littermates.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
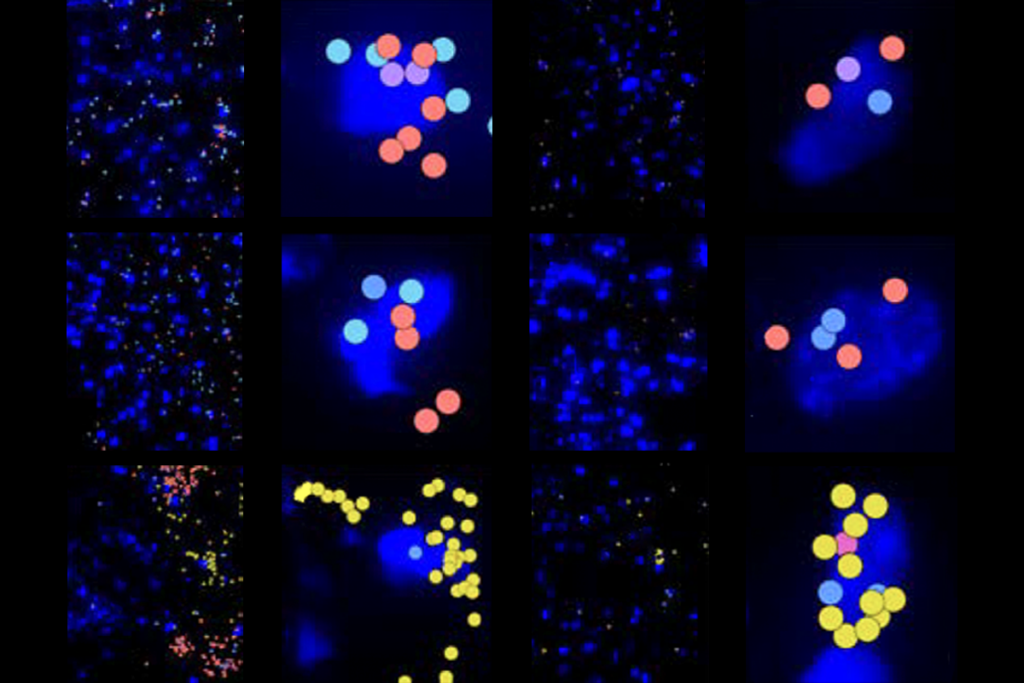
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.