Diffusion tensor imaging
Recent articles
Mapping genetic influences on the infant brain: A chat with Rebecca Knickmeyer
Researchers know little about the ways genetic variants affect development in the infant brain. Knickmeyer, who launched the Organization for Imaging Genomics in Infancy, has spent the past five years trying to close the gap.
Mapping genetic influences on the infant brain: A chat with Rebecca Knickmeyer
Researchers know little about the ways genetic variants affect development in the infant brain. Knickmeyer, who launched the Organization for Imaging Genomics in Infancy, has spent the past five years trying to close the gap.
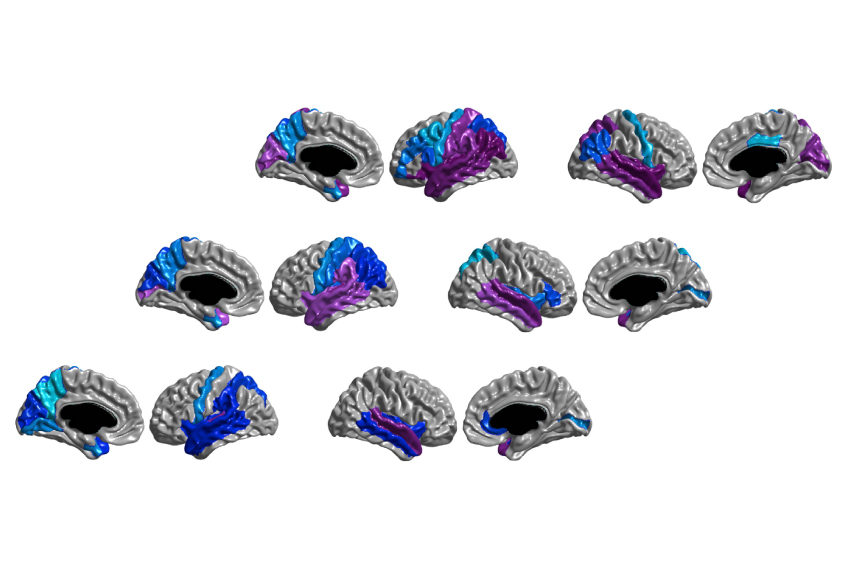
Weak ‘wiring’ in infant brains augurs severe autism features
Babies who are later diagnosed with autism may show aberrant connections between some brain regions in their first year of life.
Weak ‘wiring’ in infant brains augurs severe autism features
Babies who are later diagnosed with autism may show aberrant connections between some brain regions in their first year of life.
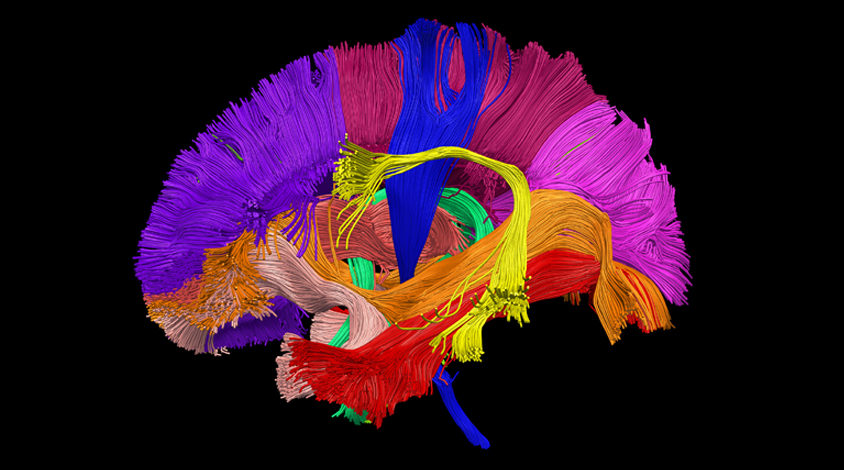
Brain scans of babies reveal how nerve tracts mature
Bundles of nerve fibers that bridge brain areas develop rapidly during the first six months of life. Fibers that connect language regions mature more slowly than those linking motor regions.
Brain scans of babies reveal how nerve tracts mature
Bundles of nerve fibers that bridge brain areas develop rapidly during the first six months of life. Fibers that connect language regions mature more slowly than those linking motor regions.
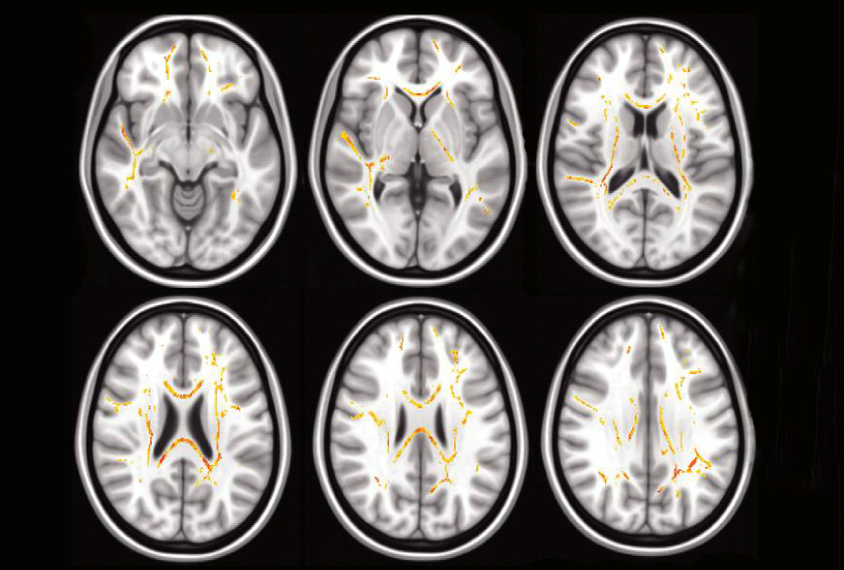
Common brain signature marks autism, attention deficit
Children with autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder all show similar disruptions in brain structure.
Common brain signature marks autism, attention deficit
Children with autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder all show similar disruptions in brain structure.
Motor troubles in Angelman may stem from nerve fiber anomaly
Unusually thin nerve fibers in the brain may underlie the motor difficulties seen in children with Angelman syndrome, an autism-related condition.
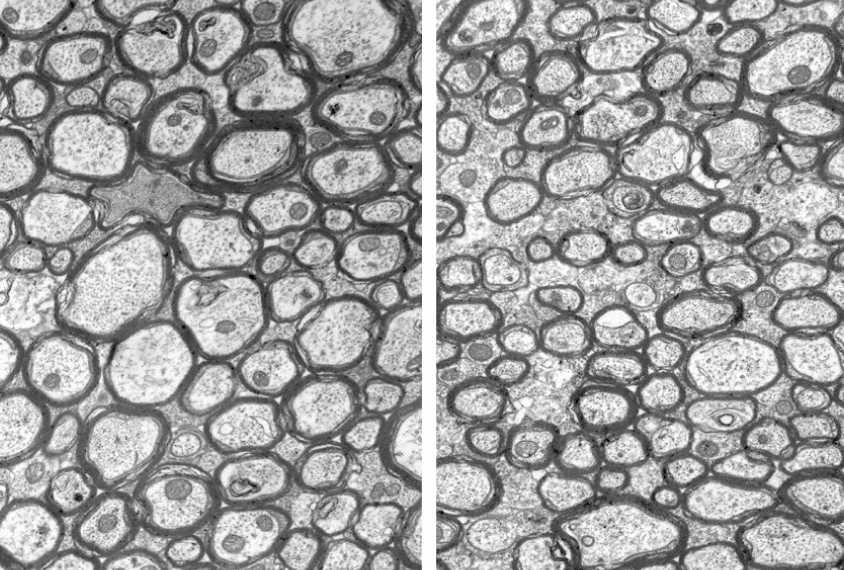
Motor troubles in Angelman may stem from nerve fiber anomaly
Unusually thin nerve fibers in the brain may underlie the motor difficulties seen in children with Angelman syndrome, an autism-related condition.
Tightly folded autism brain tied to dense neural connections
An intricately pleated brain may underlie the highly organized connections between nearby neurons in people with autism.

Tightly folded autism brain tied to dense neural connections
An intricately pleated brain may underlie the highly organized connections between nearby neurons in people with autism.
Extra-thick connections mark brains of toddlers with autism
The brains of young children with autism show abnormally dense connections involving the frontal lobe. The excess wiring may disrupt the development of social and language circuits.

Extra-thick connections mark brains of toddlers with autism
The brains of young children with autism show abnormally dense connections involving the frontal lobe. The excess wiring may disrupt the development of social and language circuits.
Thick bridge of nerves may signal autism in infancy
The bundle of nerves that connects the brain’s two hemispheres is abnormally thick in infants who are later diagnosed with autism. The broader the bundle, called the corpus callosum, the more severe a child’s symptoms.

Thick bridge of nerves may signal autism in infancy
The bundle of nerves that connects the brain’s two hemispheres is abnormally thick in infants who are later diagnosed with autism. The broader the bundle, called the corpus callosum, the more severe a child’s symptoms.
Brain structure abnormalities predict repetitive behaviors
Among babies who go on to receive a diagnosis of autism at age 2, alterations in brain structures forecast the severity of repetitive behaviors. The preliminary results were presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Brain structure abnormalities predict repetitive behaviors
Among babies who go on to receive a diagnosis of autism at age 2, alterations in brain structures forecast the severity of repetitive behaviors. The preliminary results were presented Saturday at the 2015 International Meeting for Autism Research in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Head movement in scanners skews brain measurements
Even small movements of the head during magnetic resonance imaging can lead to spurious measurements of brain structures, according to a new study.

Head movement in scanners skews brain measurements
Even small movements of the head during magnetic resonance imaging can lead to spurious measurements of brain structures, according to a new study.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.