Gene expression
Recent articles
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
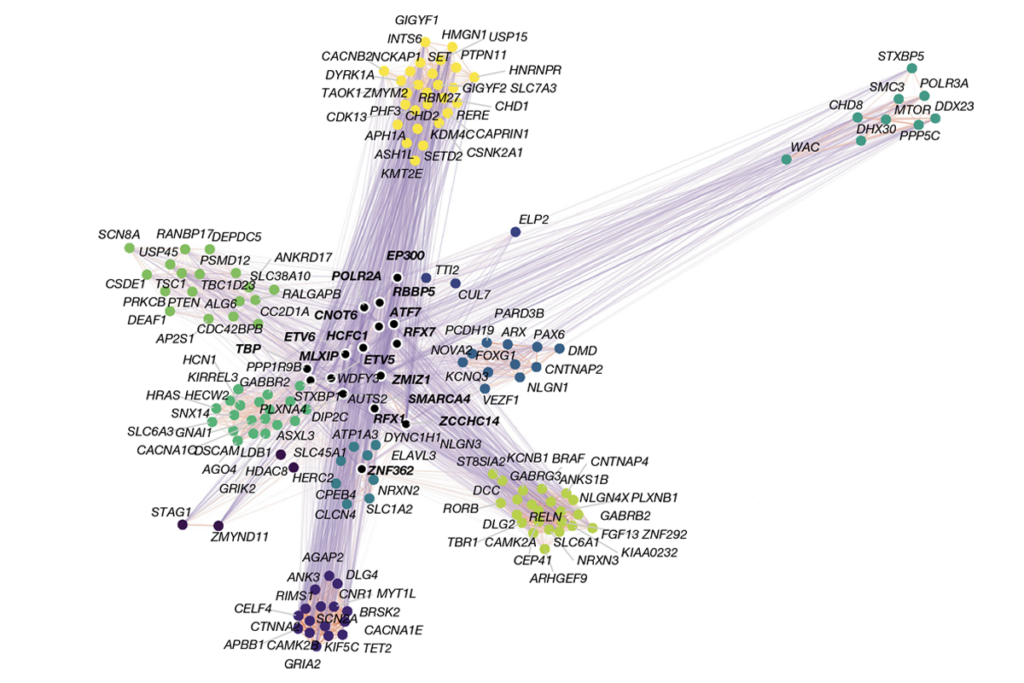
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Constellation of studies charts brain development, offers ‘dramatic revision’
The atlases could pinpoint pathways that determine the fate of cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions.
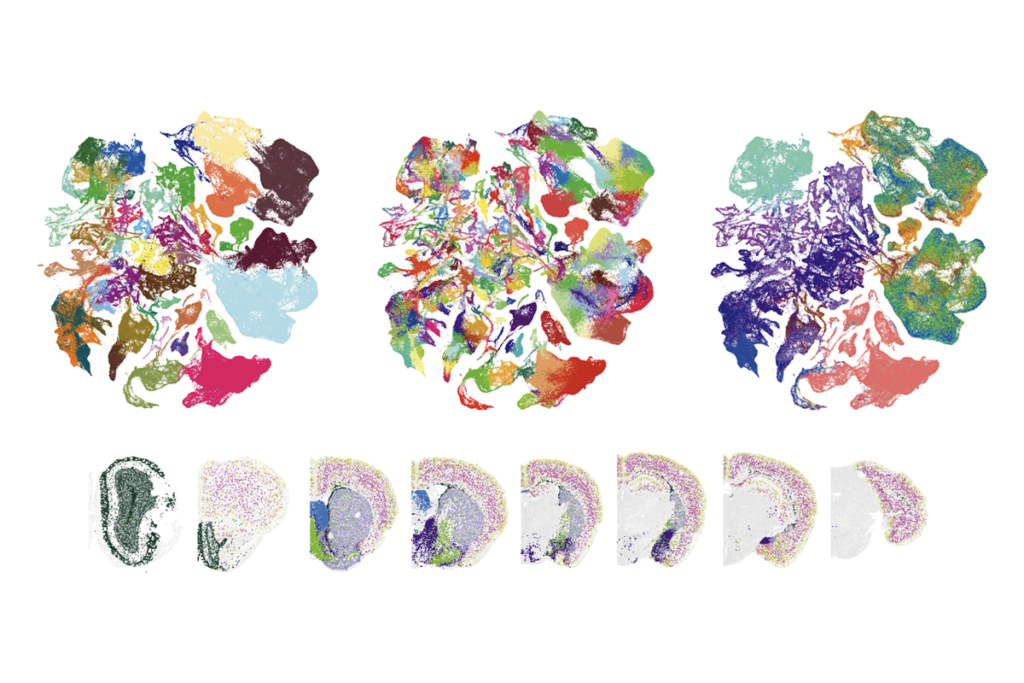

Constellation of studies charts brain development, offers ‘dramatic revision’
The atlases could pinpoint pathways that determine the fate of cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions.
Gene-activity map of developing brain reveals new clues about autism’s sex bias
Boys and girls may be vulnerable to different genetic changes, which could help explain why the condition is more common in boys despite linked variants appearing more often in girls.
Gene-activity map of developing brain reveals new clues about autism’s sex bias
Boys and girls may be vulnerable to different genetic changes, which could help explain why the condition is more common in boys despite linked variants appearing more often in girls.
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
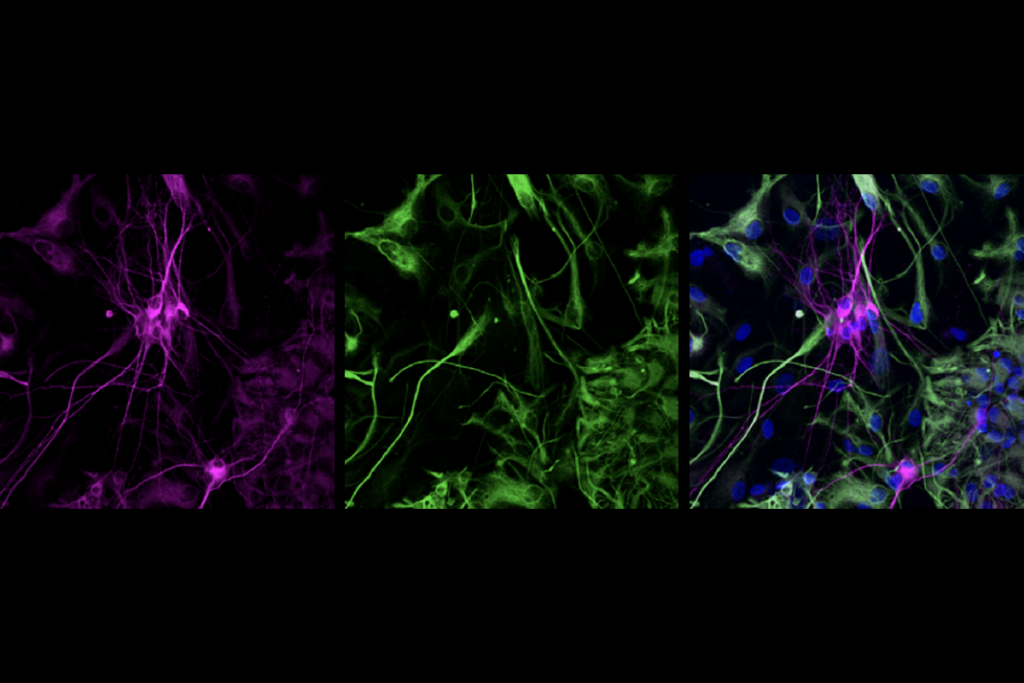
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Four autism subtypes map onto distinct genes, traits
An analysis of more than 5,000 autistic children and their siblings underscores the idea that autism can be understood as multiple conditions with distinct trajectories.

Four autism subtypes map onto distinct genes, traits
An analysis of more than 5,000 autistic children and their siblings underscores the idea that autism can be understood as multiple conditions with distinct trajectories.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.

Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.
Unexpected astrocyte gene flips image of brain’s ‘stalwart sentinels’
The genetic marker upends the accepted orientation of non-star-like astrocytes in the glia limitans superficialis.
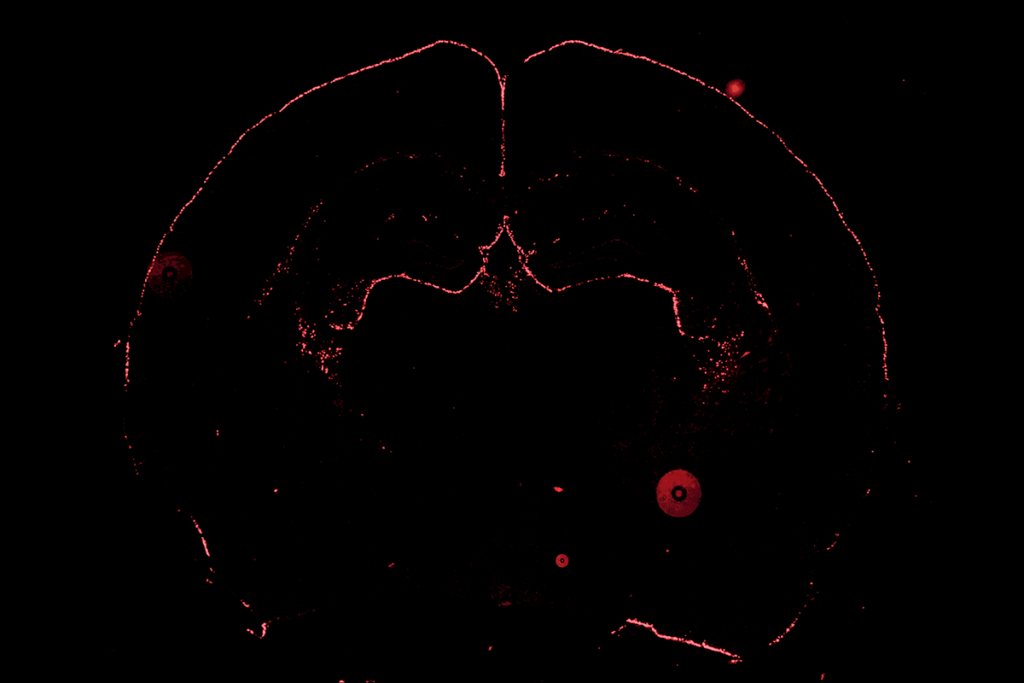
Unexpected astrocyte gene flips image of brain’s ‘stalwart sentinels’
The genetic marker upends the accepted orientation of non-star-like astrocytes in the glia limitans superficialis.
New tool may help untangle downstream effects of autism-linked genes
The statistical approach helps scientists better control for both measured and unmeasured confounders in gene-expression data, revealing causal relationships between autism-linked genetic variants and downstream cellular effects, such as impaired neuron development.
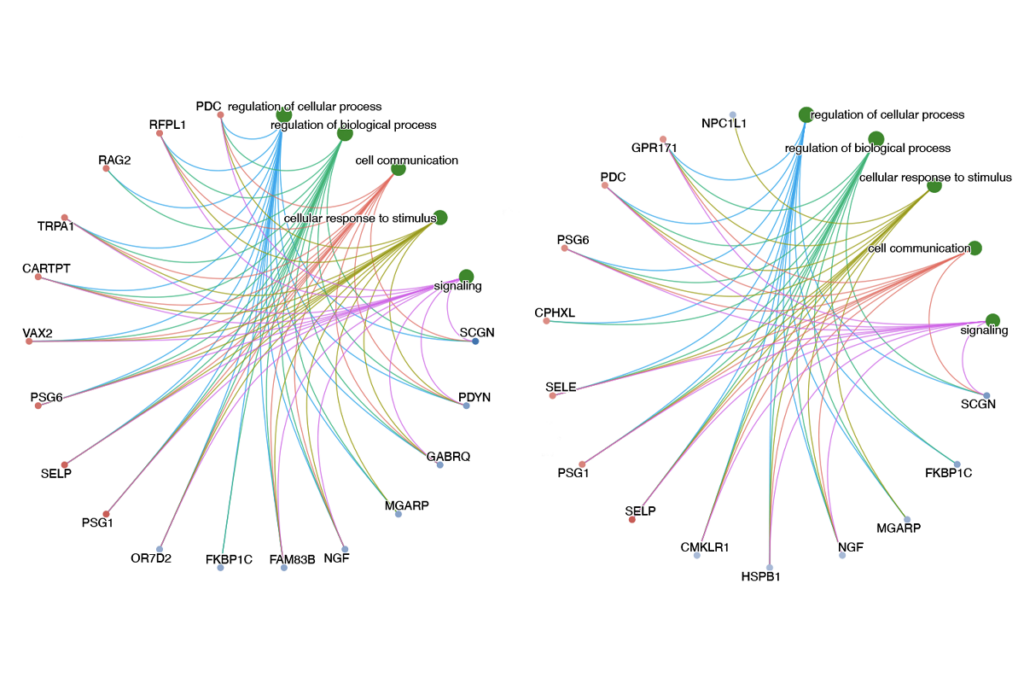
New tool may help untangle downstream effects of autism-linked genes
The statistical approach helps scientists better control for both measured and unmeasured confounders in gene-expression data, revealing causal relationships between autism-linked genetic variants and downstream cellular effects, such as impaired neuron development.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.
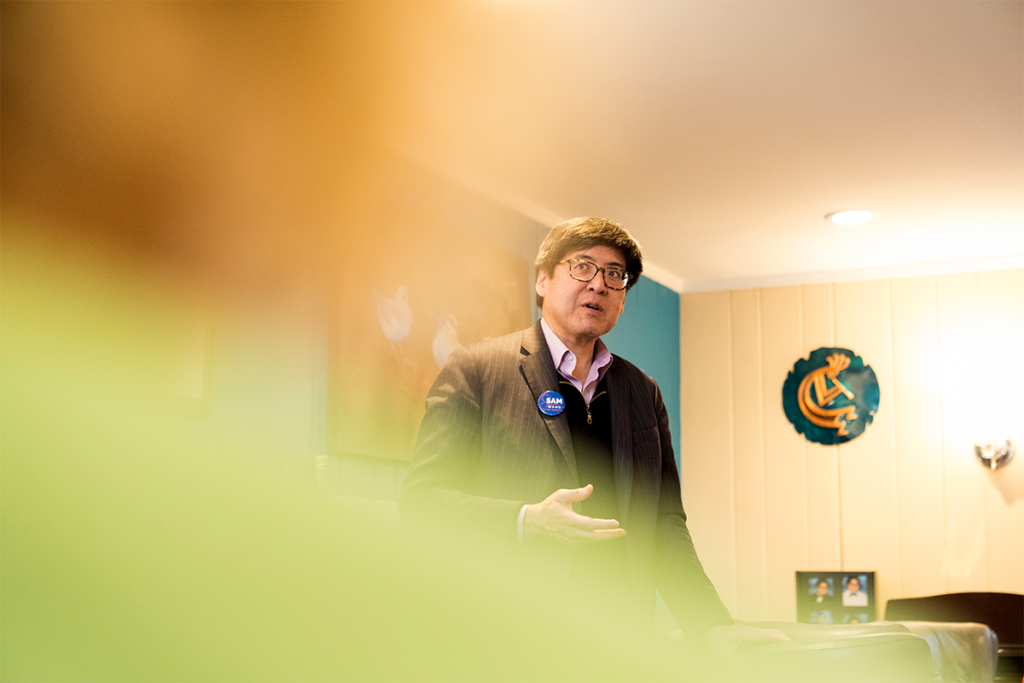

Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.