Girls and autism
Recent articles
Structure of striatum varies by sex in autistic children
The changes could reflect different developmental trajectories between boys and girls with autism, a new study suggests.

Structure of striatum varies by sex in autistic children
The changes could reflect different developmental trajectories between boys and girls with autism, a new study suggests.
Extra Y chromosomes are linked to autism
Data from people with more or fewer than two sex chromosomes could help answer questions around genetic protection and vulnerability.
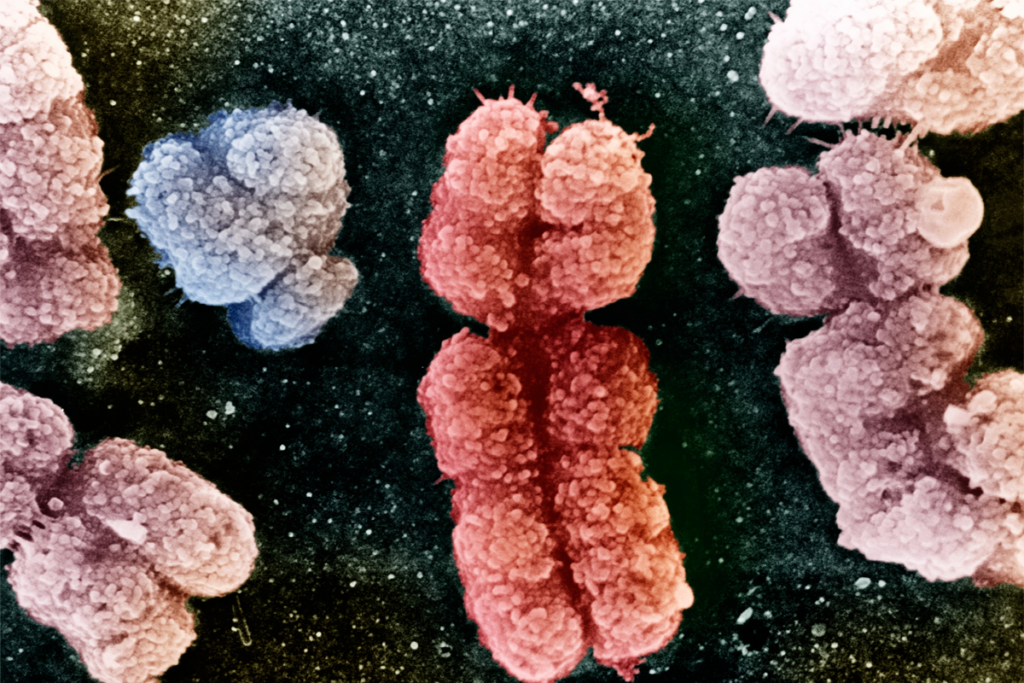
Extra Y chromosomes are linked to autism
Data from people with more or fewer than two sex chromosomes could help answer questions around genetic protection and vulnerability.
Link between autism and transness being misused, scientists say
Some researchers are pushing back — with mixed results.

Link between autism and transness being misused, scientists say
Some researchers are pushing back — with mixed results.
Genetic background sways effects of autism-linked mutation
Experiments offer clues to why certain mutations are associated with autism in some people and not others.
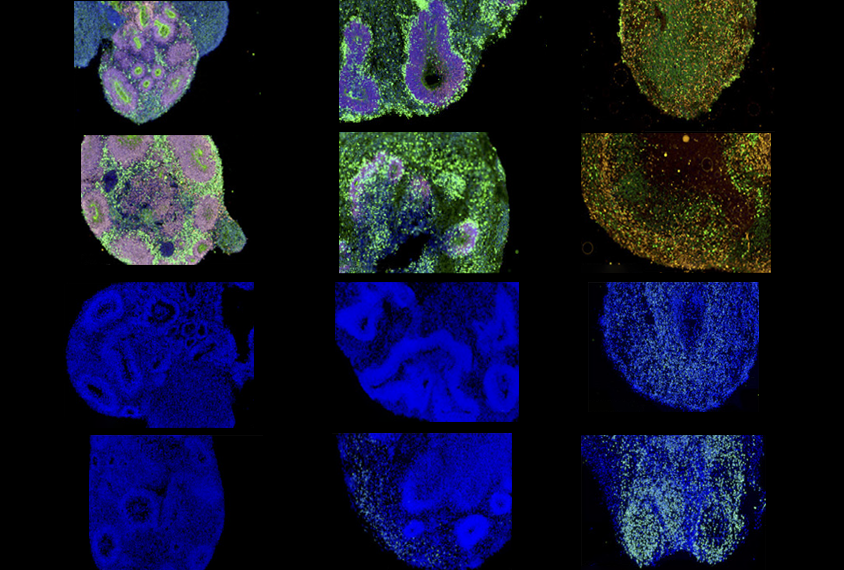
Genetic background sways effects of autism-linked mutation
Experiments offer clues to why certain mutations are associated with autism in some people and not others.
Immune molecule alters cellular makeup of human brain organoids
The changes may help explain the link between maternal infection and autism, though more research is needed.
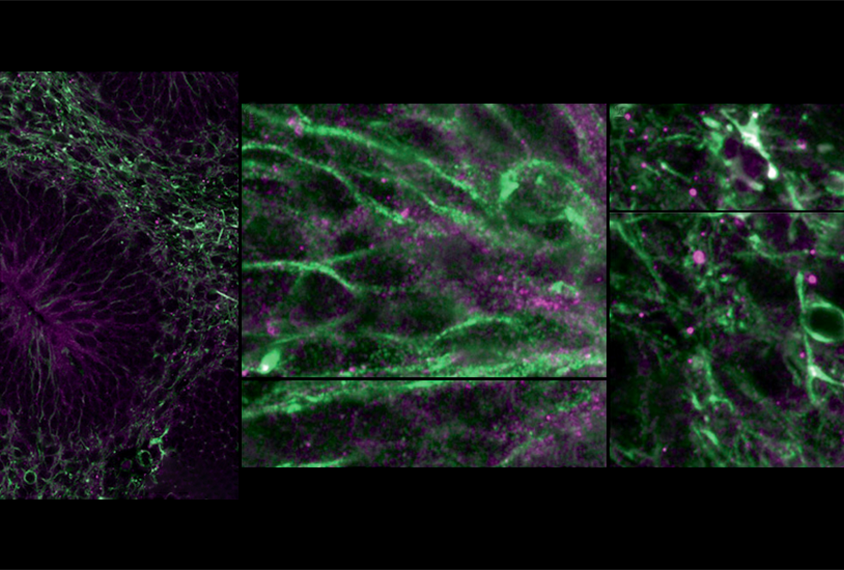
Immune molecule alters cellular makeup of human brain organoids
The changes may help explain the link between maternal infection and autism, though more research is needed.
Autism incidence in England varies by ethnicity, class, location
High rates of autism are linked to lower socioeconomic status and minority ethnic groups, according to the largest-ever autism incidence study.
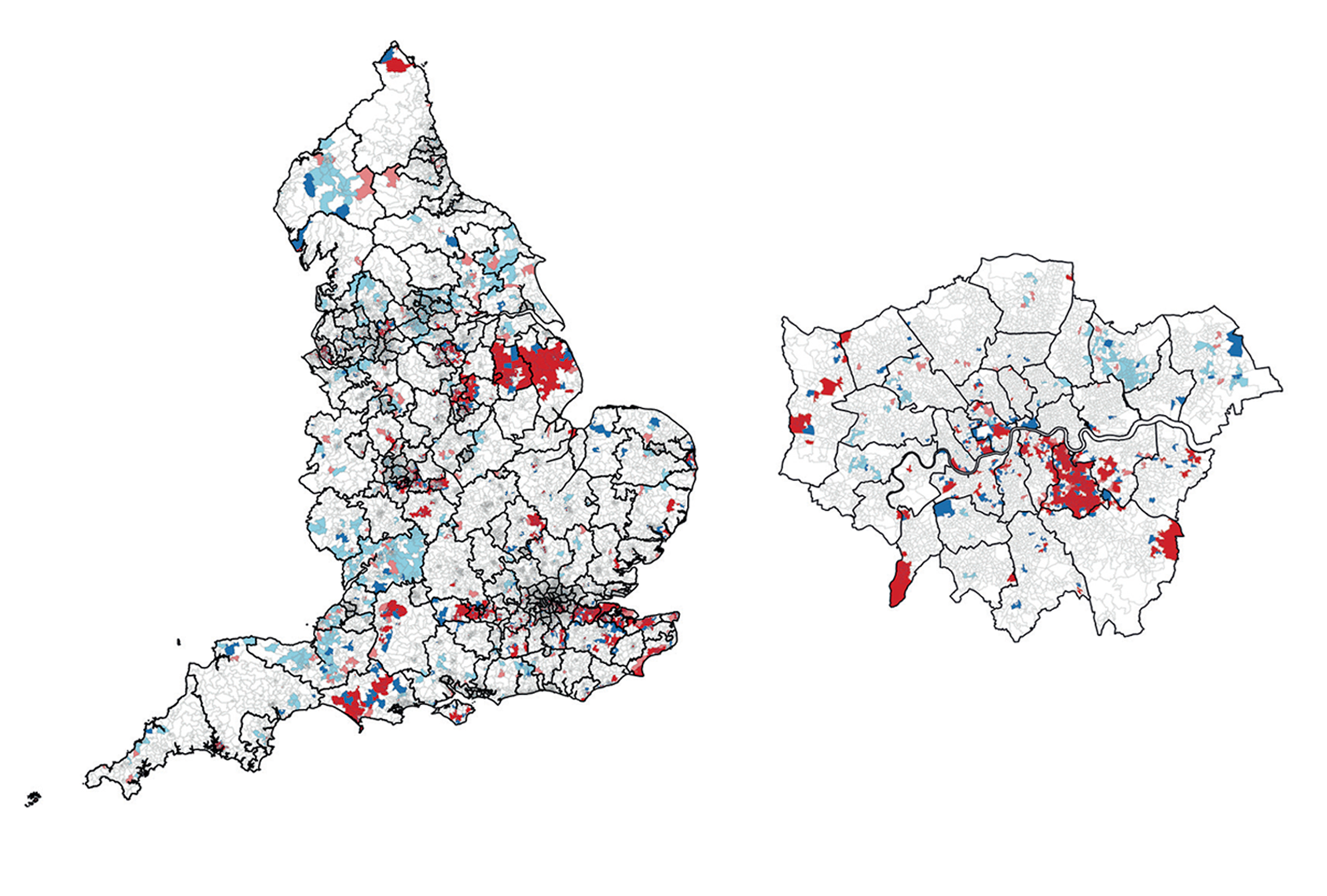
Autism incidence in England varies by ethnicity, class, location
High rates of autism are linked to lower socioeconomic status and minority ethnic groups, according to the largest-ever autism incidence study.
Null and Noteworthy: COVID-19 conclusions; diagnosis duplication; oxytocin again
This month’s newsletter explores the pandemic’s effects on autism rates, trends in co-occurring mental health conditions, and the impact of intranasal oxytocin.
Null and Noteworthy: COVID-19 conclusions; diagnosis duplication; oxytocin again
This month’s newsletter explores the pandemic’s effects on autism rates, trends in co-occurring mental health conditions, and the impact of intranasal oxytocin.
Explore more from The Transmitter
How insights from network theory can boost interdisciplinary efforts
Communication on one interdisciplinary research team improved after the researchers turned an analysis technique used to study the brain on themselves and identified the roles people played in lab meetings.
How insights from network theory can boost interdisciplinary efforts
Communication on one interdisciplinary research team improved after the researchers turned an analysis technique used to study the brain on themselves and identified the roles people played in lab meetings.
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
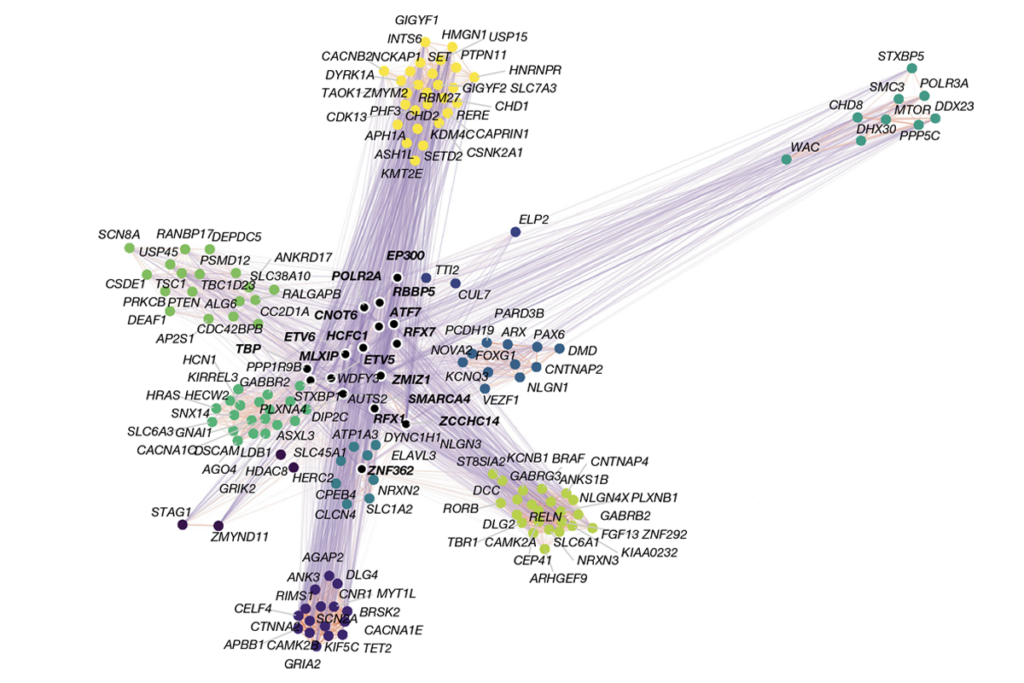
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.