Mouse models
Recent articles
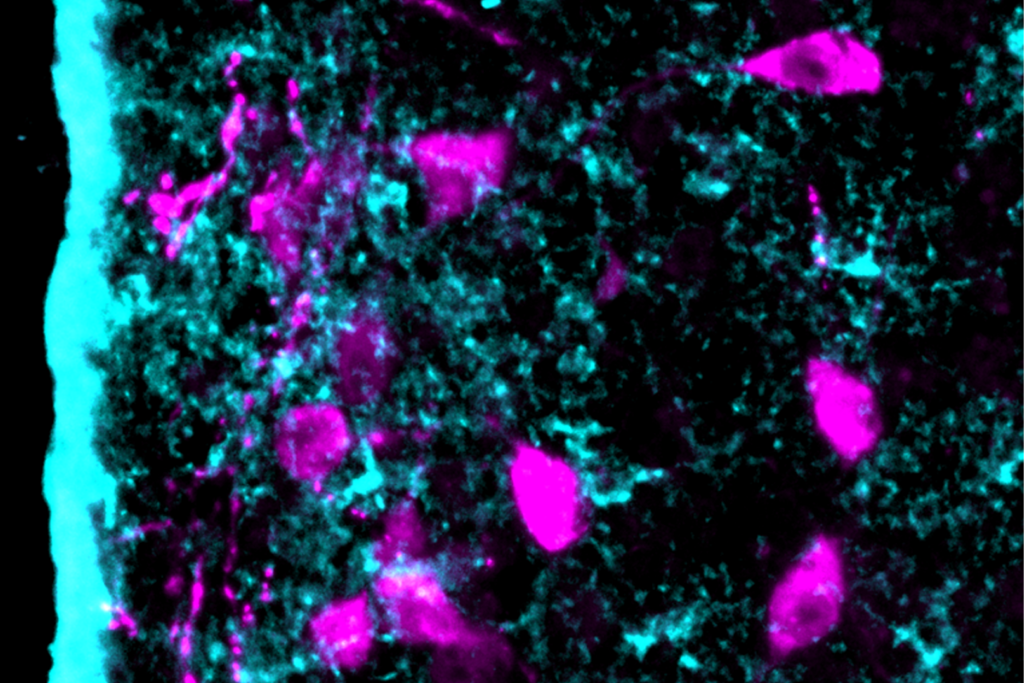
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
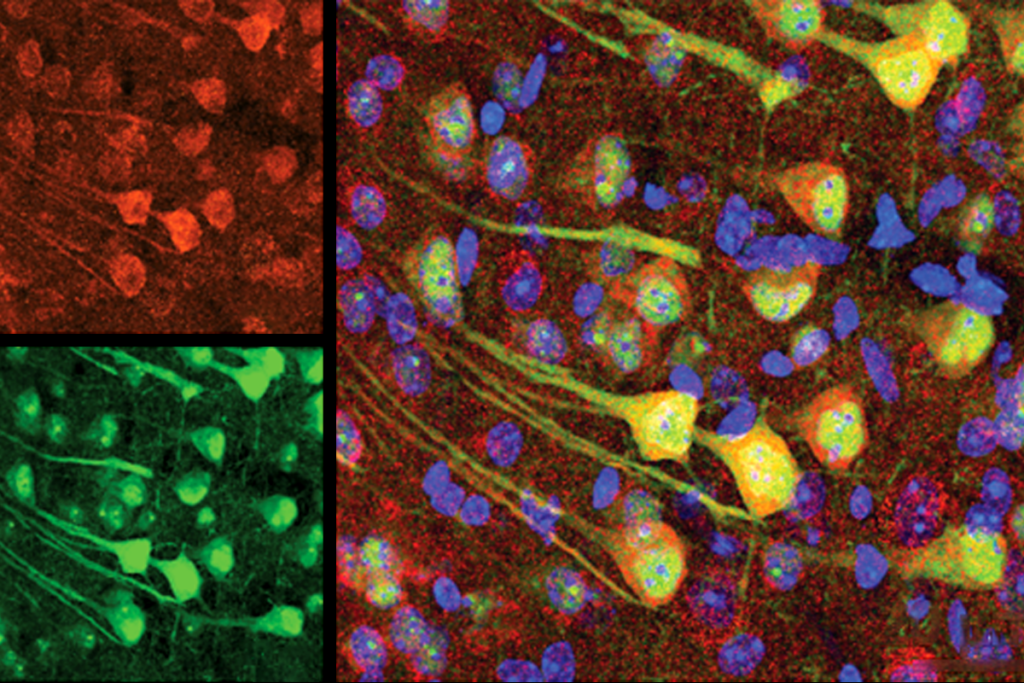
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
Snoozing dragons stir up ancient evidence of sleep’s dual nature
Deep-sleep cycling between brain waves of higher and lower amplitude dates far back on the evolutionary tree, according to a new comparative study of mammals and reptiles.
Snoozing dragons stir up ancient evidence of sleep’s dual nature
Deep-sleep cycling between brain waves of higher and lower amplitude dates far back on the evolutionary tree, according to a new comparative study of mammals and reptiles.
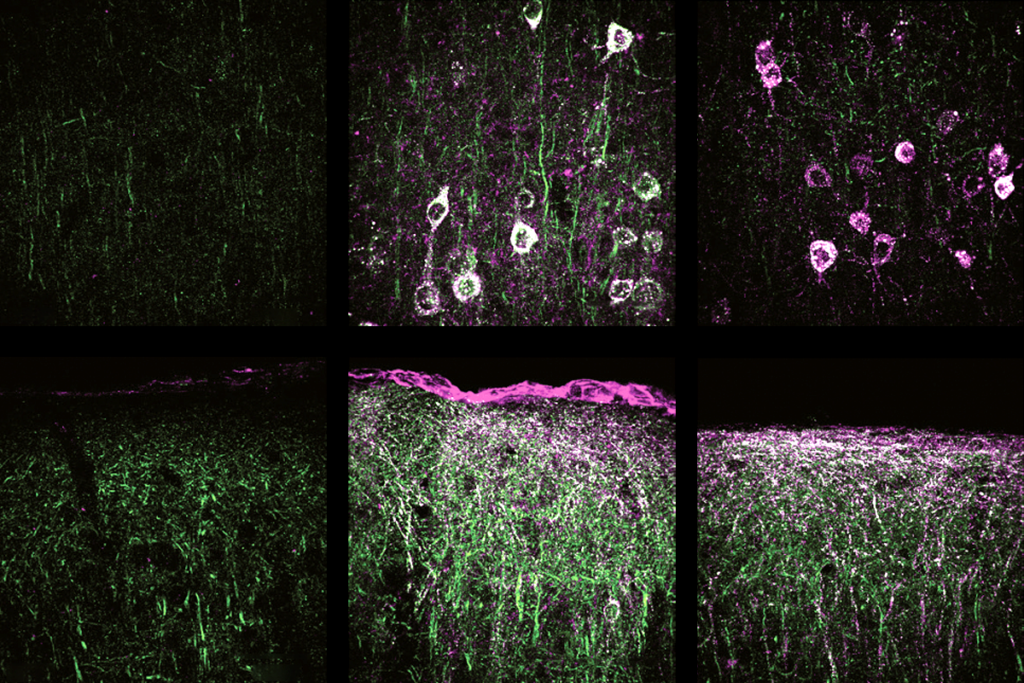
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Constellation of studies charts brain development, offers ‘dramatic revision’
The atlases could pinpoint pathways that determine the fate of cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions.
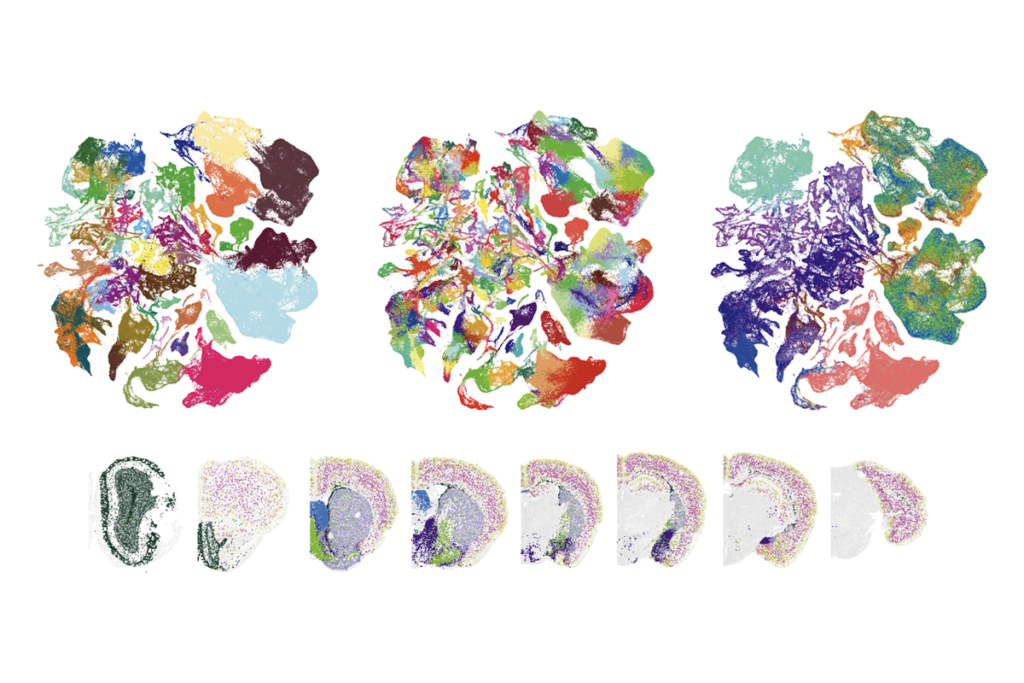

Constellation of studies charts brain development, offers ‘dramatic revision’
The atlases could pinpoint pathways that determine the fate of cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions.
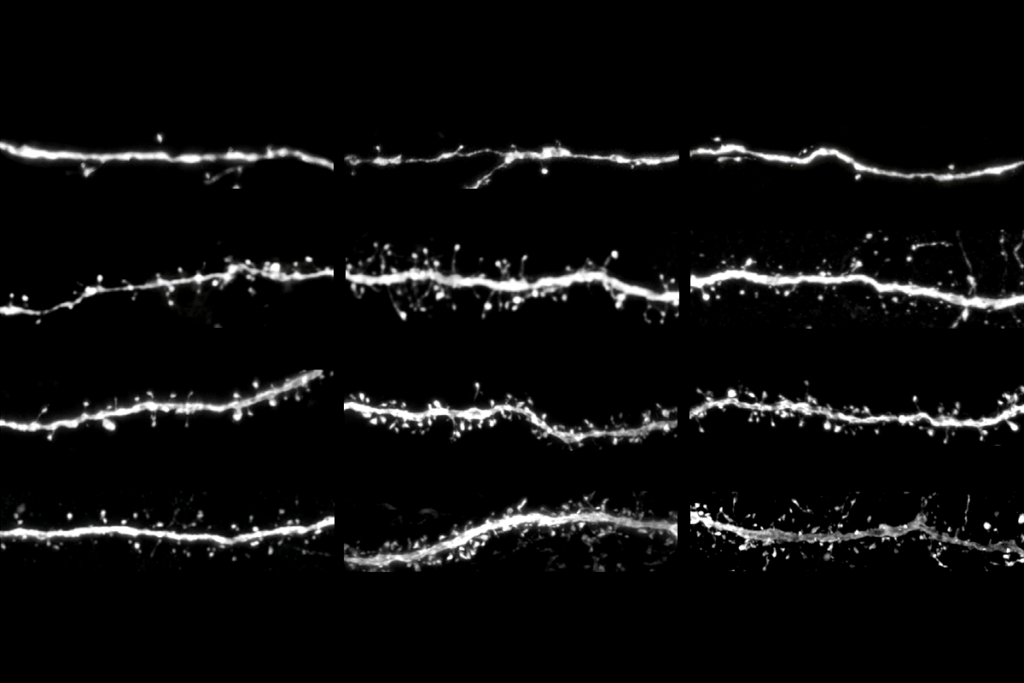
Protein tug-of-war controls pace of synaptic development, sets human brains apart
Human-specific duplicates of SRGAP2 prolong cortical development by manipulating SYNGAP, an autism-linked protein that slows synaptic growth.
Protein tug-of-war controls pace of synaptic development, sets human brains apart
Human-specific duplicates of SRGAP2 prolong cortical development by manipulating SYNGAP, an autism-linked protein that slows synaptic growth.
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
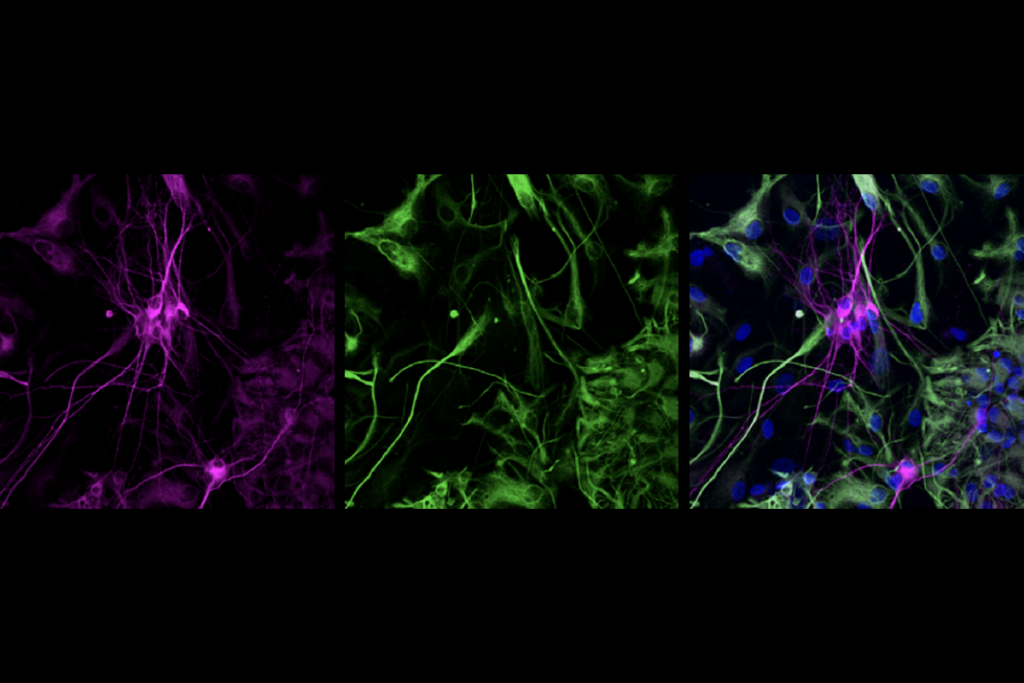
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
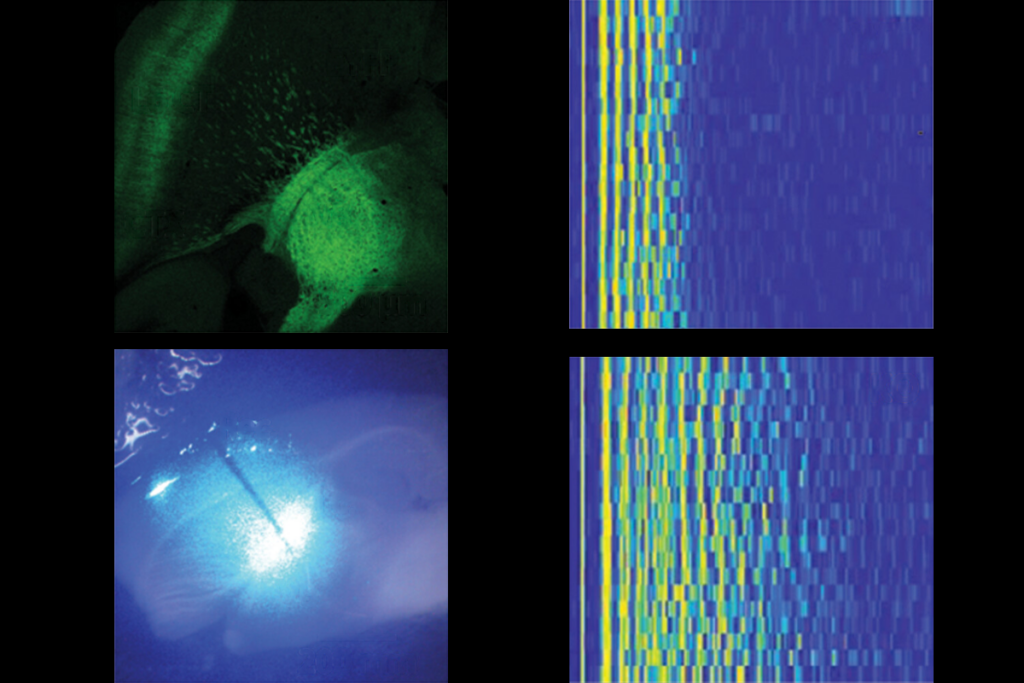
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
Up and out with Peggy Mason
Mason helped define the rodent prosocial behavior field, but now she’s changing course.
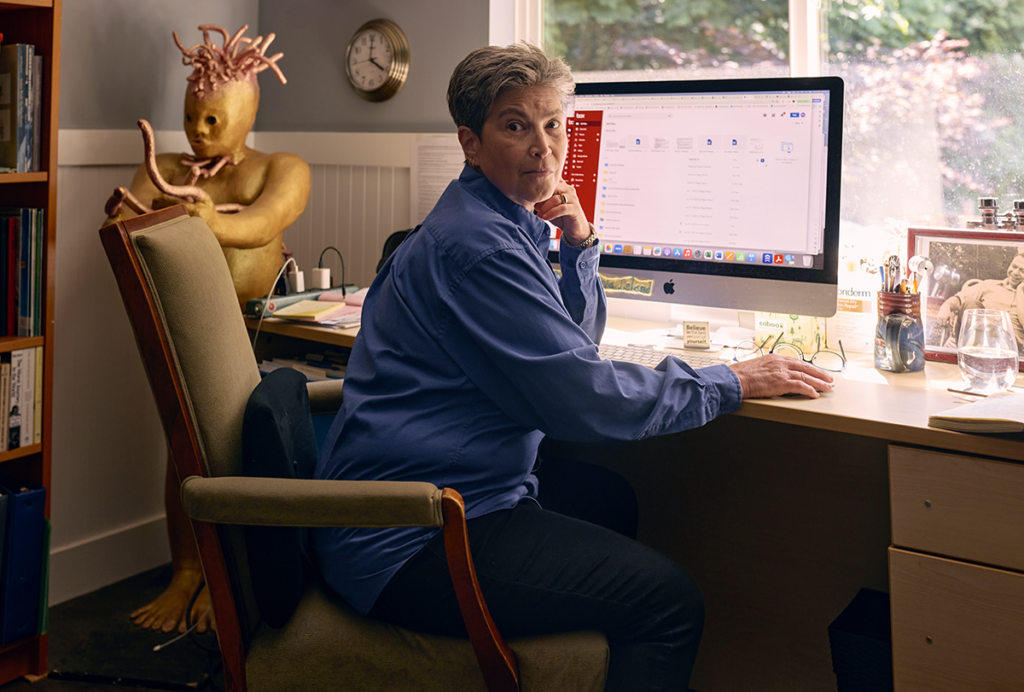

Up and out with Peggy Mason
Mason helped define the rodent prosocial behavior field, but now she’s changing course.
This paper changed my life: Victoria Abraira on a tasty link between circuits and behavior
The findings from Charles Zuker’s lab put the taste system on the map, revealing that some fundamental principles of behavior are hardwired.
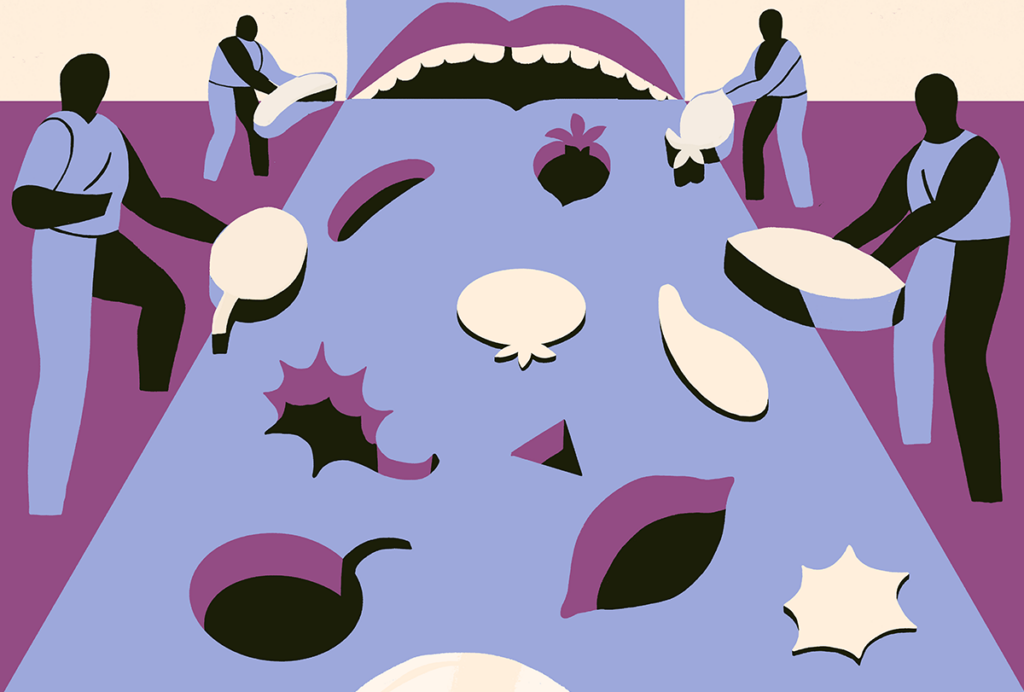

This paper changed my life: Victoria Abraira on a tasty link between circuits and behavior
The findings from Charles Zuker’s lab put the taste system on the map, revealing that some fundamental principles of behavior are hardwired.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.
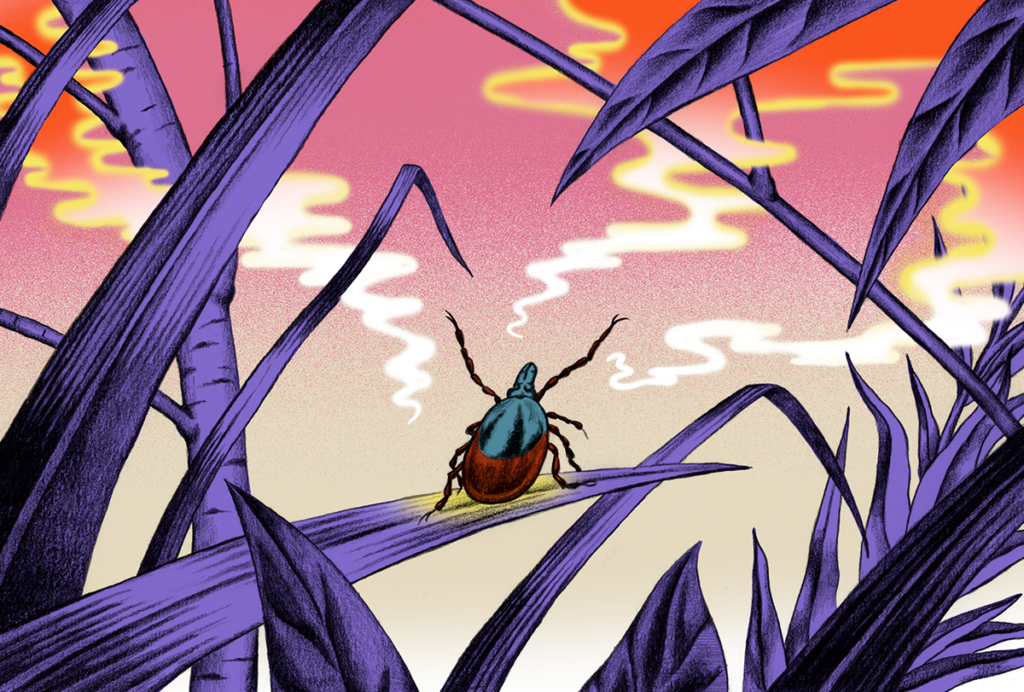

Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
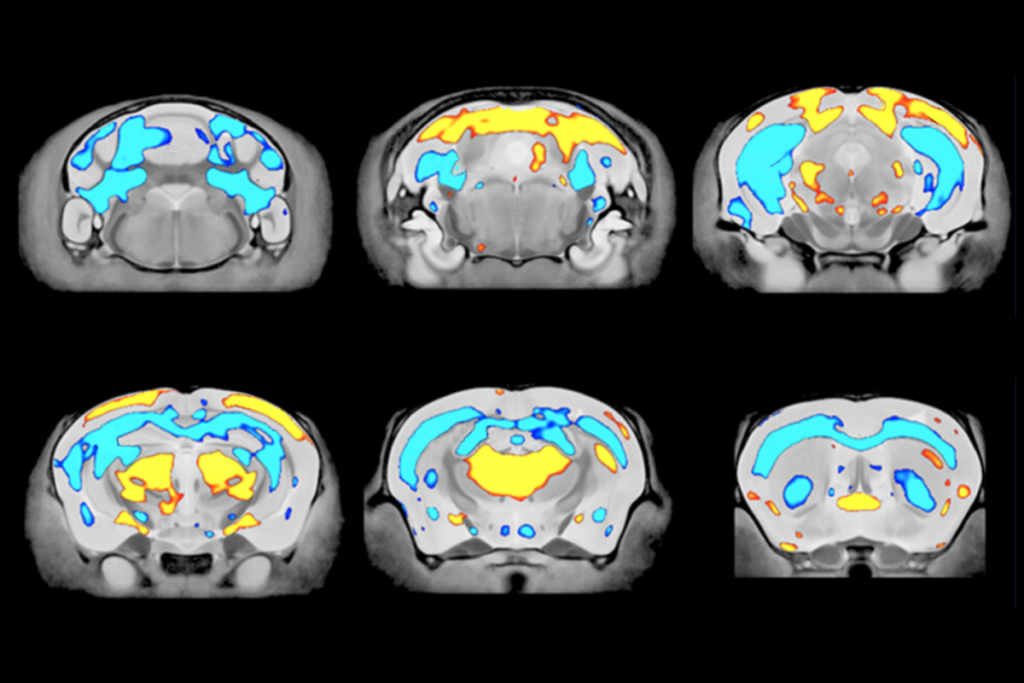
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.
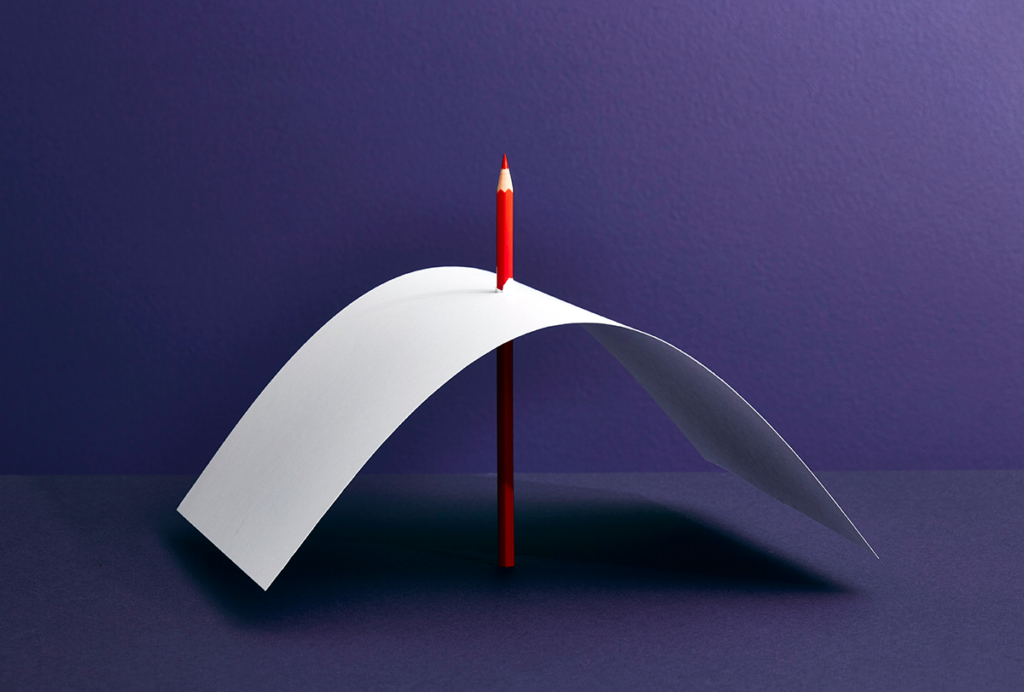

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.