Almost every human cell teems with a potpourri of tiny powerhouses: mitochondria. Up to thousands of them. These organelles use oxygen to convert the nutrients from the food you eat into a form of energy the body can use. The brain consumes a lot of this energy — about 20 percent. Could changes in mitochondria, then, affect how the brain functions and contribute to autism? Read the related article, Meet the ‘mitomaniacs’ who say mitochondria matter in autism.
Mitochondria: An energy explanation for autism
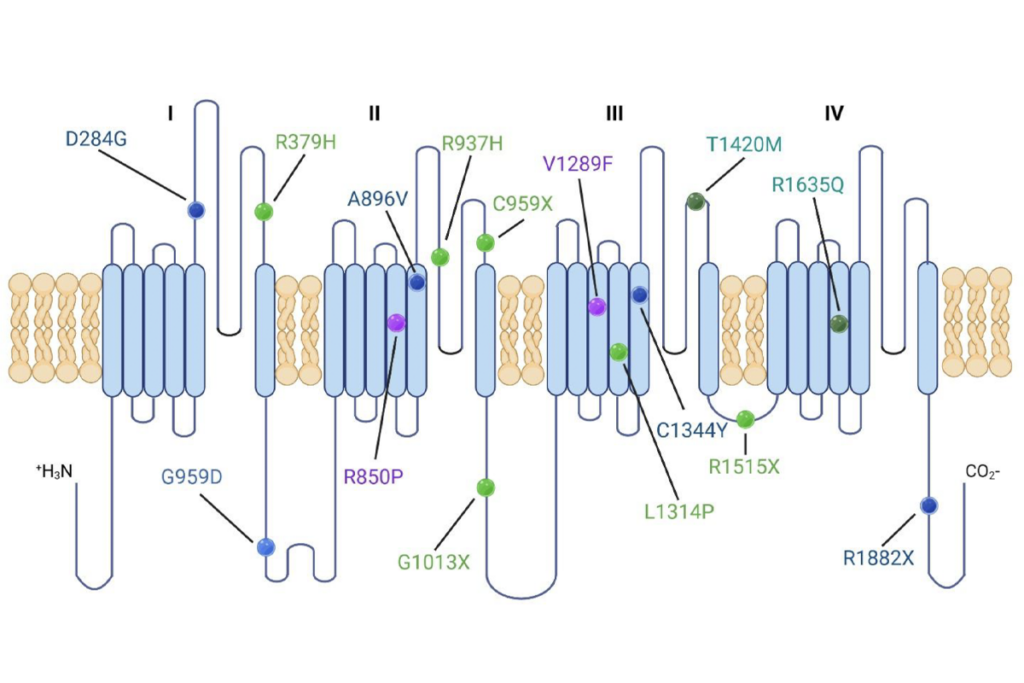
People with autism have more mutations than others do in both mitochondrial DNA and nuclear DNA that affects mitochondrial function.
By
Laura Dattaro
22 November 2021 | 3 min watch
Illustration by Mengxin Li
Recommended reading

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
By
Angie Voyles Askham
5 March 2026 | 5 min read
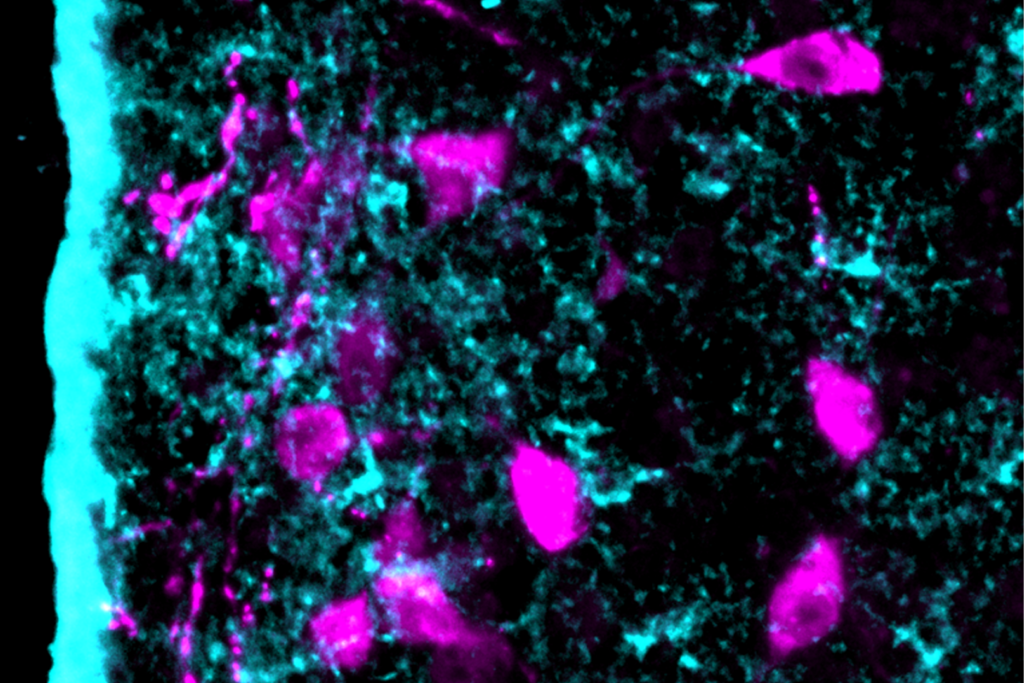
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
By
Holly Barker
4 March 2026 | 5 min read
Explore more from The Transmitter
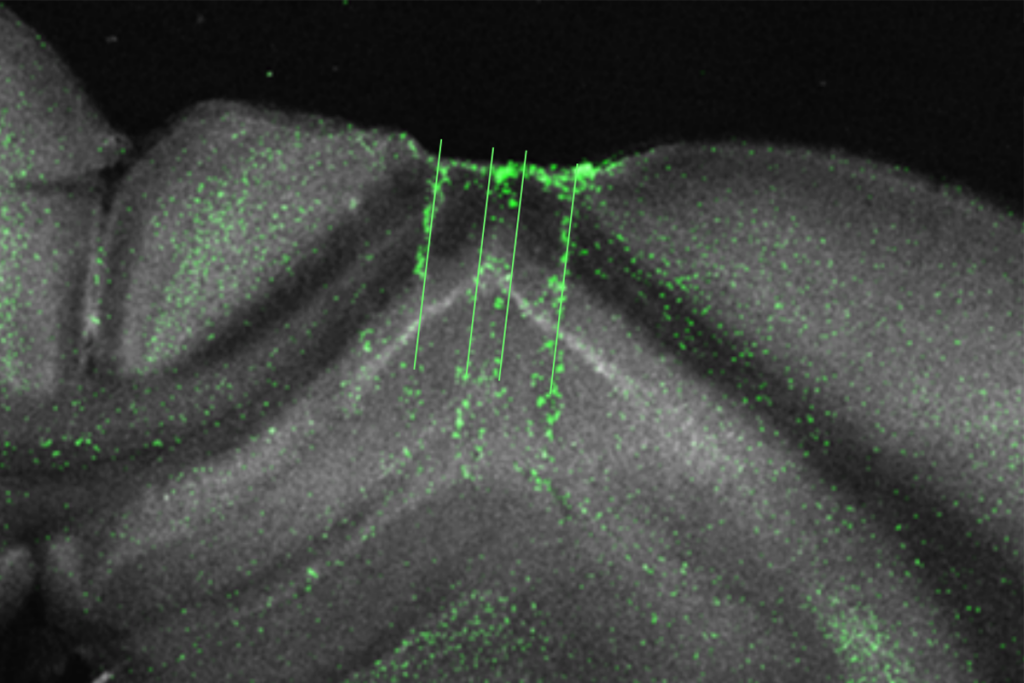
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
By
Natalia Mesa
10 March 2026 | 5 min read

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
By
Rogier Mars
10 March 2026 | 6 min read

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
By
Lucina Q. Uddin
9 March 2026 | 4 min read
Cite this article: