Research roundup
- People with developmental or intellectual disabilities say their mental health has worsened during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatric Services
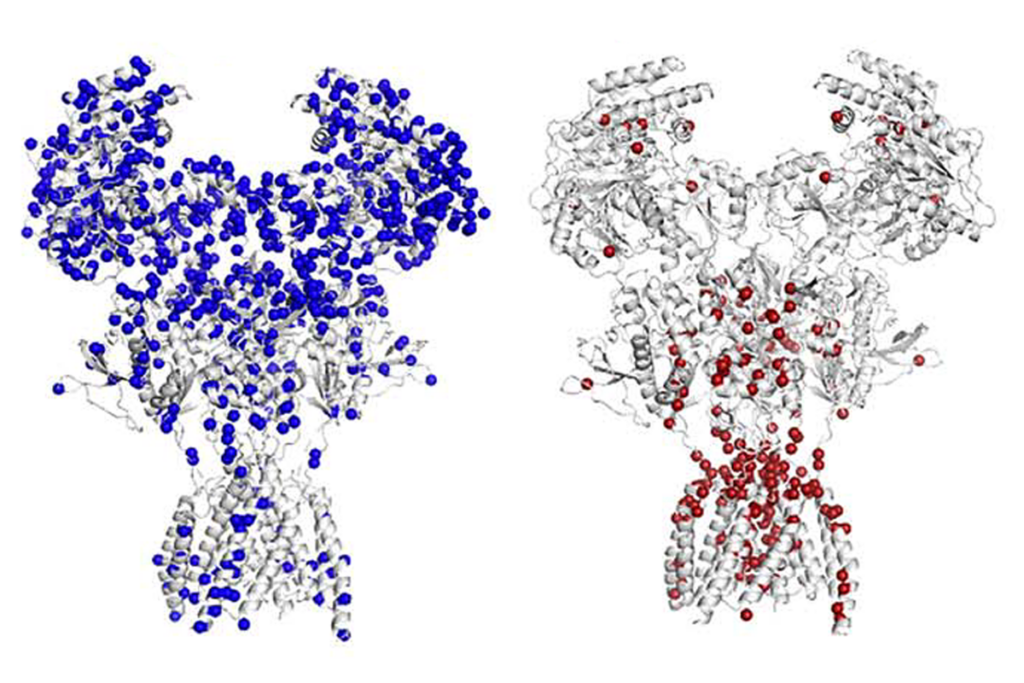
- Molecular analysis of NLGN2, a protein that supports synaptic structure and is linked to autism, reveals that a protein kinase is the go-between for NLGN2 influence on GABA receptors and inhibitory neurotransmission. Science Signaling
- A range of interdependent factors contribute to interpersonal synchrony — the coordination of behaviors between people interacting socially — including multisensory processing, attention and predictive abilities, any of which may be altered when autistic people socialize. Frontiers in Psychology
- Developmental specialists may have less training and fewer strategies for addressing challenging behavior in autistic children than speech pathologists do, according to a survey of 87 early-intervention providers. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities
- Among 41 single-nucleotide polymorphisms across 9 autism-linked genes, 12 stood out as significant in an umbrella review of 28 meta-analyses. Translational Psychiatry
- Mutations in the autism-linked gene WDFY3 appear to cause altered neuronal migration during development, according to a study in mice. Molecular Autism
- Deleting the chromosomal region 22q11.2 in human stem cells affects the expression of genes on other chromosomes, many of which are also linked to autism. Nature Communications
- Less frequent canonical babbling — speech that has both consonant and vowel sounds — by 12-month-old infants is associated with later language delay, with or without an autism diagnosis. Molecular Autism
- Eleven percent of autistic children in Tunisia have copy number variants associated with autism, a result similar to those found in children from other countries. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
- Elevated blood levels of serotonin, which are associated with autism, appear to be linked to the immune system via intestinal T-lymphocytes. Spectrum has reported on the continuing mystery of elevated serotonin in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- Autism researchers are making progress in bringing diagnosis and treatment to underserved populations around the world, according to a short review. Autism
- The FMRP protein, which is deficient in fragile X syndrome, functions to initiate RNA translation of long proteins in mammals. Spectrum covered previous research on this mechanism in fly eggs. Genetics
Science and society
- Yuh-Line Niou, a New York State legislator, is running for a seat in the U.S. Congress and could become the first openly autistic Congress member. Insider
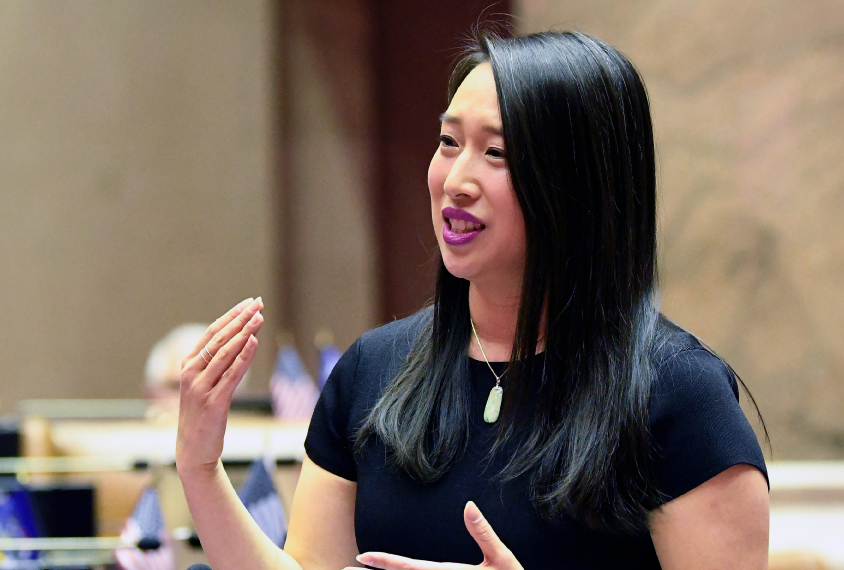

Autistic lawmaker: New York assemblymember Yuh-Line Niou seeks national seat in Congress.
- The parent of an autistic child and spouse of a city employee is calling on Tuscaloosa, Alabama’s city council to include autism therapies in its health insurance policy. Patch
- Scientists, including discoverer Jennifer Doudna, reflect on CRISPR and the decade since the gene-editing tool was developed. The New York Times and STAT
- Researchers are using a suite of new techniques to map RNA species in intact tissues, in a method known as spatial transcriptomics. Nature