Research roundup
- Autistic adolescents shared their experiences, interests and future plans in structured interviews designed to accommodate a range of verbal and cognitive abilities. Spectrum covered the interview protocol in a video in August. Autism
- Longitudinal studies must consider how best to transfer consent as autistic participants transition from childhood to adulthood. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- An X chromosome analysis uncovers genes linked to cognition, language and seizures, and two genes newly linked to autism: CDK16 and TRPC5. Nature Communications
- A new atlas catalogs adenosine-to-inosine editing sites in RNA, which are functionally linked to brain development, over space and time. Cell Reports
- A group of researchers provides a conceptual framework to move beyond simplistic approaches for classifying microglia states and functions. Neuron
- Singing to babies, which occurs across cultures, entrains social-visual behaviors in infants and reinforces the rhythms of social communication. PNAS
- Sensory integration, such as coordinating tactile, visual and sensorimotor stimuli, may be altered in autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
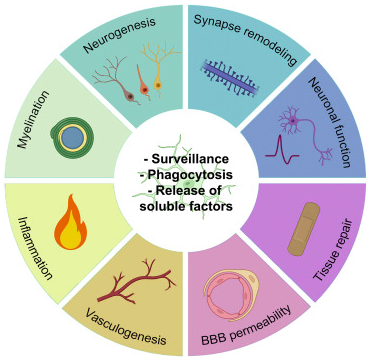 Multitasking pros: Microglia have more than two states and influence a broad set of functions.
Multitasking pros: Microglia have more than two states and influence a broad set of functions. - People with the autism-linked DDX3X syndrome often have a complicated set of neurological, psychological, ophthalmological and gastrointestinal issues, according to a literature review. Spectrum reported on DDX3X in girls and women last year. Pediatric Neurology
- Researchers have built a spatiotemporal atlas of fetal brain development from gestational week 23 to 38 using in utero MRI scans collected in China. Journal of Neuroscience
- Telehealth visits have the potential to make care more accessible, but they introduce new bumps and barriers, autistic people and clinical care providers say. Autism
- The Autism Impact Measure does not appear to assess autism traits differently in boys versus girls. Autism Research
- Left-hemisphere areas of the brain that are active during a language task tend to be mirrored in the right hemisphere during a social task, suggesting a close integration of the two functions. Cell Reports
- Optogenetic functional MRI data, together with computational modeling, may provide a clearer picture of whole-brain circuit functioning in health and disease, according to a review. Science
- Newly identified electroencephalogram metrics may serve as noninvasive biomarkers for imbalanced excitatory and inhibitory brain activity, with potential future use in fine-tuning autism diagnoses. Translational Psychiatry
- Methods to evaluate speech in minimally verbal autistic people vary in strengths and weaknesses, according to a review. Augmentative and Alternative Communication
Science and society
- Gloria Choi, professor of brain and cognitive sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, shares her research on neuroimmune interactions during fetal development in a new Q&A. Neuron
- Researchers across the globe have started turning to alternative social media sites, such as Mastodon, since Elon Musk bought Twitter. Science
- As societal perceptions of autism have shifted, in part by listening to autistic people’s voices, the label ‘profound autism’ has spurred a controversy. Spectrum has covered viewpoints from parent advocates and researchers. The Conversation