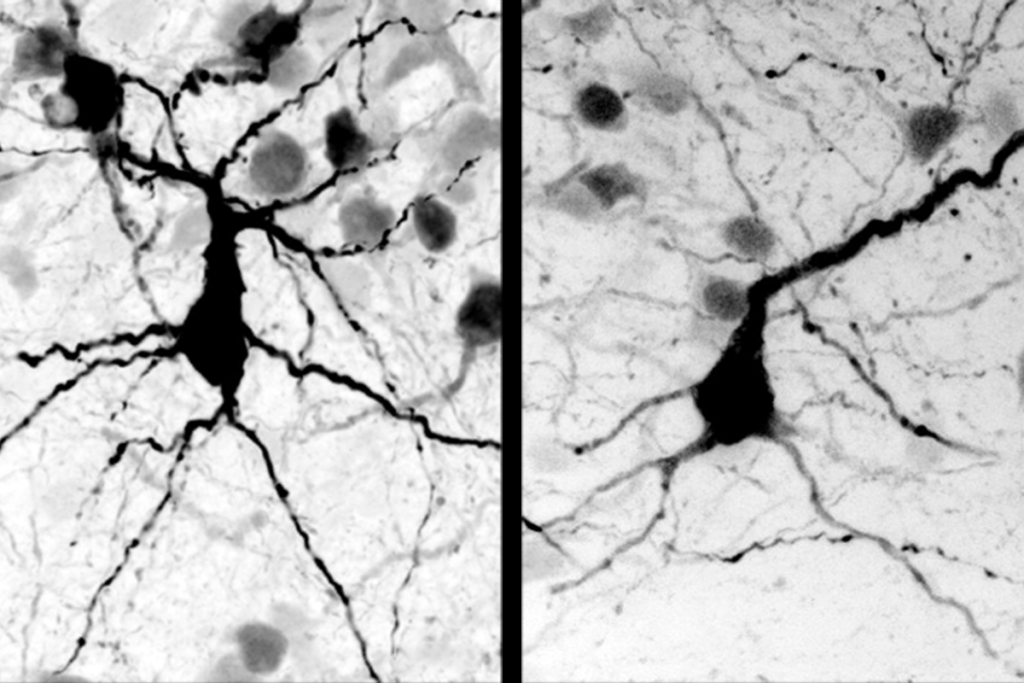
- Children with SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability show elevated levels of autism traits and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) traits, but reduced signs of conduct or oppositional defiant disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- In a mouse model of fragile X syndrome, the variability of single-neuron responses to sensory stimuli appears to be a function of noise in the neuronal networks. Nature Communications
- Infants who are later diagnosed with autism show differences in white-matter tracts, as measured with diffusion-tensor imaging techniques. Frontiers in Neuroscience
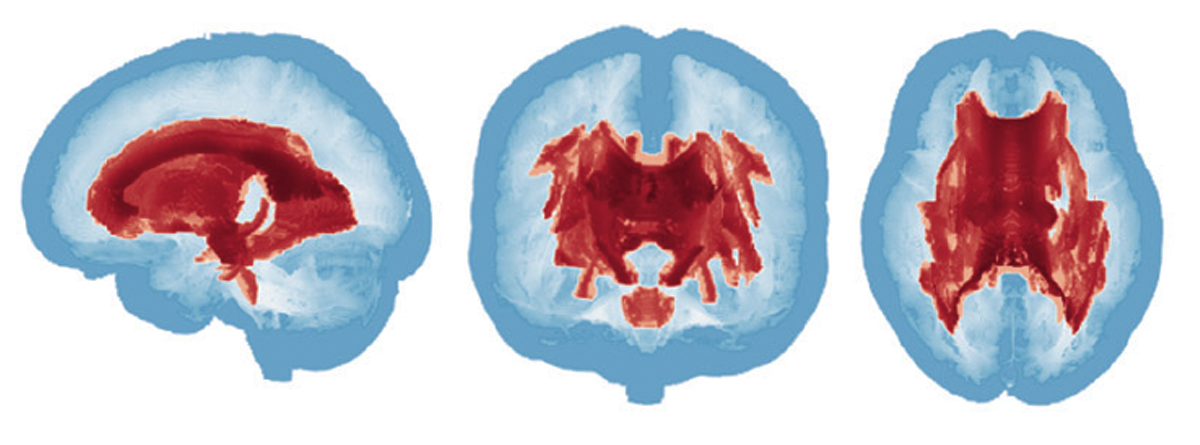
Route mapping: Infants who are later diagnosed with autism have less white matter in autism-related functional pathways than their non-autistic peers; red indicates group differences.
- Oxytocin appears to lose efficacy with repeated treatment in conditions such as autism, according to a review of studies. Peptides
- Most U.S.-based medical schools do not prepare their students to provide health care for autistic or disabled people. STAT
- Neurodevelopmental conditions with a male bias, such as autism, Tourette syndrome and ADHD, are associated with genes on the X chromosome. Nature Communications
- High blood levels of vitamin D during pregnancy are associated with a decreased likelihood of having a child with autism or ADHD, but vitamin D supplementation has no effect on the association, according to a clinical trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- People who carry mitochondrial DNA in the haplogroup K have a lower prevalence of autism in cohorts of European and Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry