Whole-genome sequencing
Recent articles
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
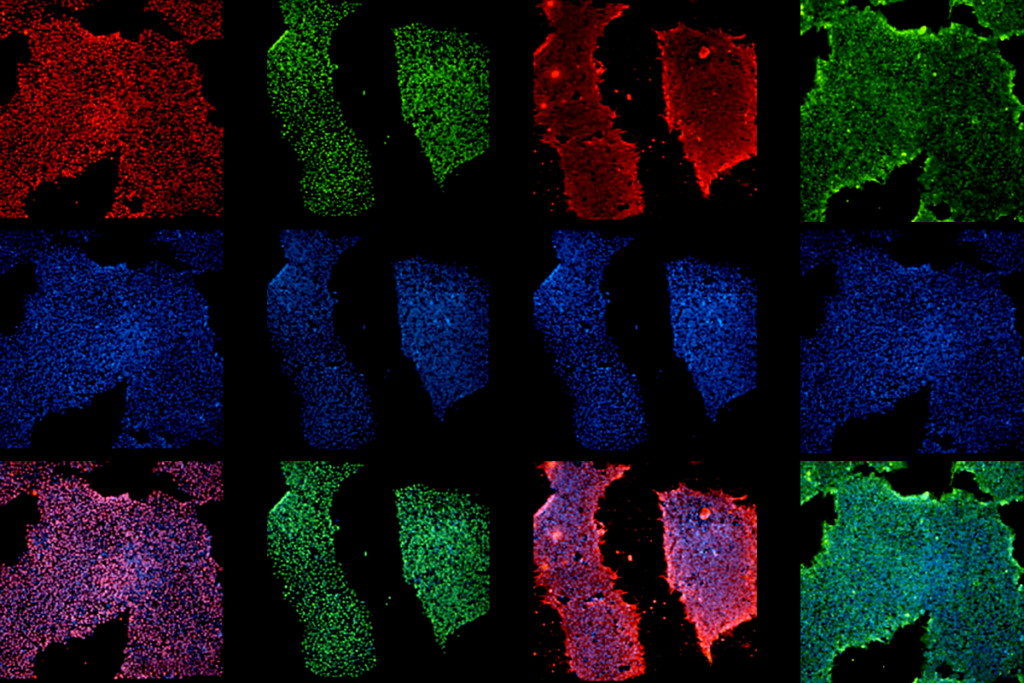
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
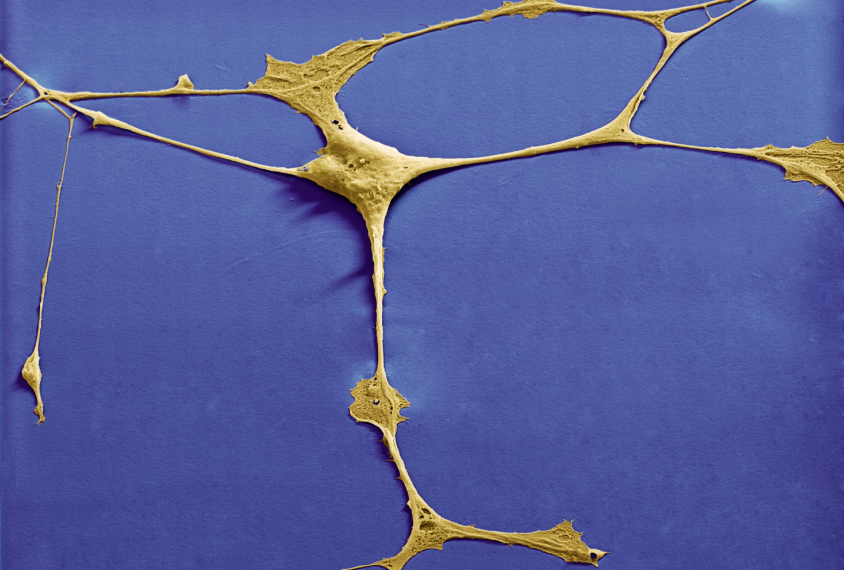
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Why hasn’t genetics taught us more about schizophrenia?
Large-scale genomics studies have failed to identify specific pathways that go awry in schizophrenia. Alternative approaches focusing on cellular, molecular and systems-level changes may be needed.

Why hasn’t genetics taught us more about schizophrenia?
Large-scale genomics studies have failed to identify specific pathways that go awry in schizophrenia. Alternative approaches focusing on cellular, molecular and systems-level changes may be needed.
X marks the spot in search for autism variants
Genetic variants on the X chromosome, including those in the gene DDX53, contribute to autism’s gender imbalance, two new studies suggest.
X marks the spot in search for autism variants
Genetic variants on the X chromosome, including those in the gene DDX53, contribute to autism’s gender imbalance, two new studies suggest.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Faulty mTOR signaling, implicated in syndromic forms of autism, also hinders cells grown from people with idiopathic autism or autism-linked deletions on chromosome 16.
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Faulty mTOR signaling, implicated in syndromic forms of autism, also hinders cells grown from people with idiopathic autism or autism-linked deletions on chromosome 16.
Genome structure could be key factor in some forms of autism
Variants in DNA stretches that do not code for proteins may alter the genome’s 3D architecture, influencing the expression of distant genes linked to autism.

Genome structure could be key factor in some forms of autism
Variants in DNA stretches that do not code for proteins may alter the genome’s 3D architecture, influencing the expression of distant genes linked to autism.
How long-read sequencing will transform neuroscience
New technology that delivers much more than a simple DNA sequence could have a major impact on brain research, enabling researchers to study transcript diversity, imprinting and more.

How long-read sequencing will transform neuroscience
New technology that delivers much more than a simple DNA sequence could have a major impact on brain research, enabling researchers to study transcript diversity, imprinting and more.
Common genetic variants shape the structure of the cortex
A genome-wide association study lays a foundation for deeper investigation of these variants in neurodevelopmental conditions.
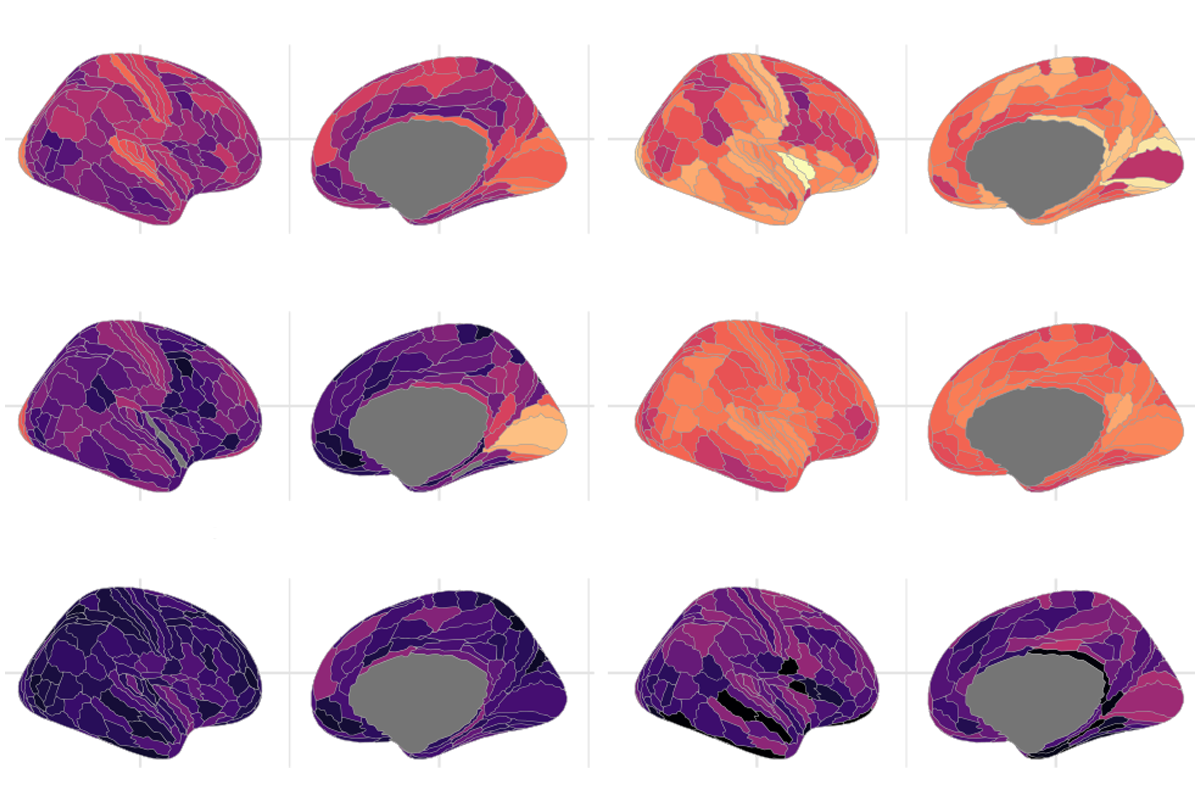
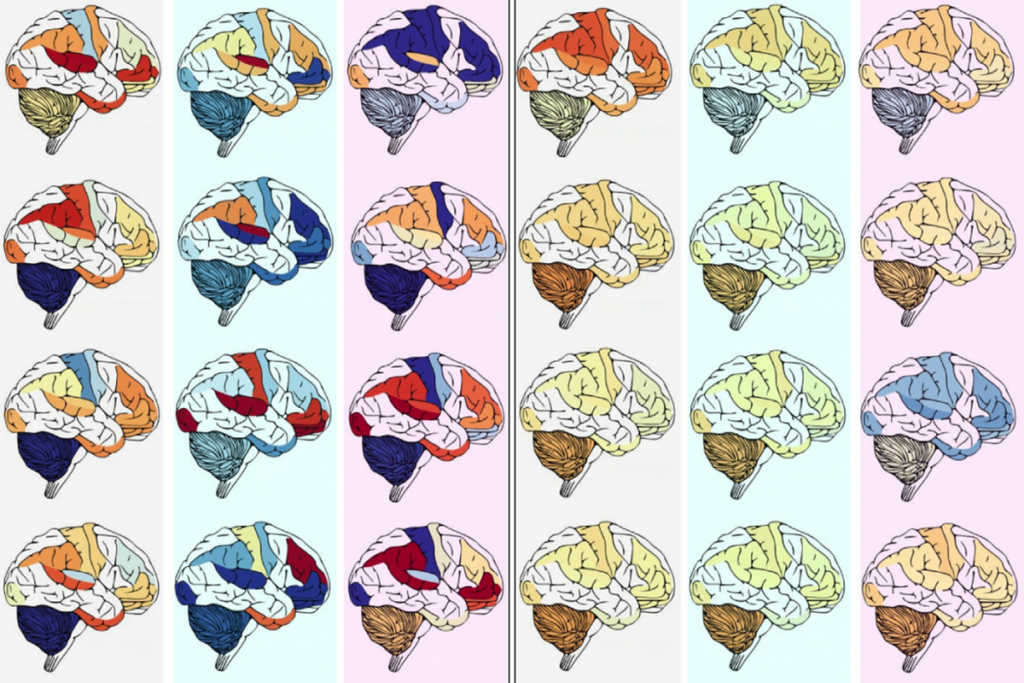
Common genetic variants shape the structure of the cortex
A genome-wide association study lays a foundation for deeper investigation of these variants in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
An imbalance in the number of excitatory neurons in early brain development may account for the difference.
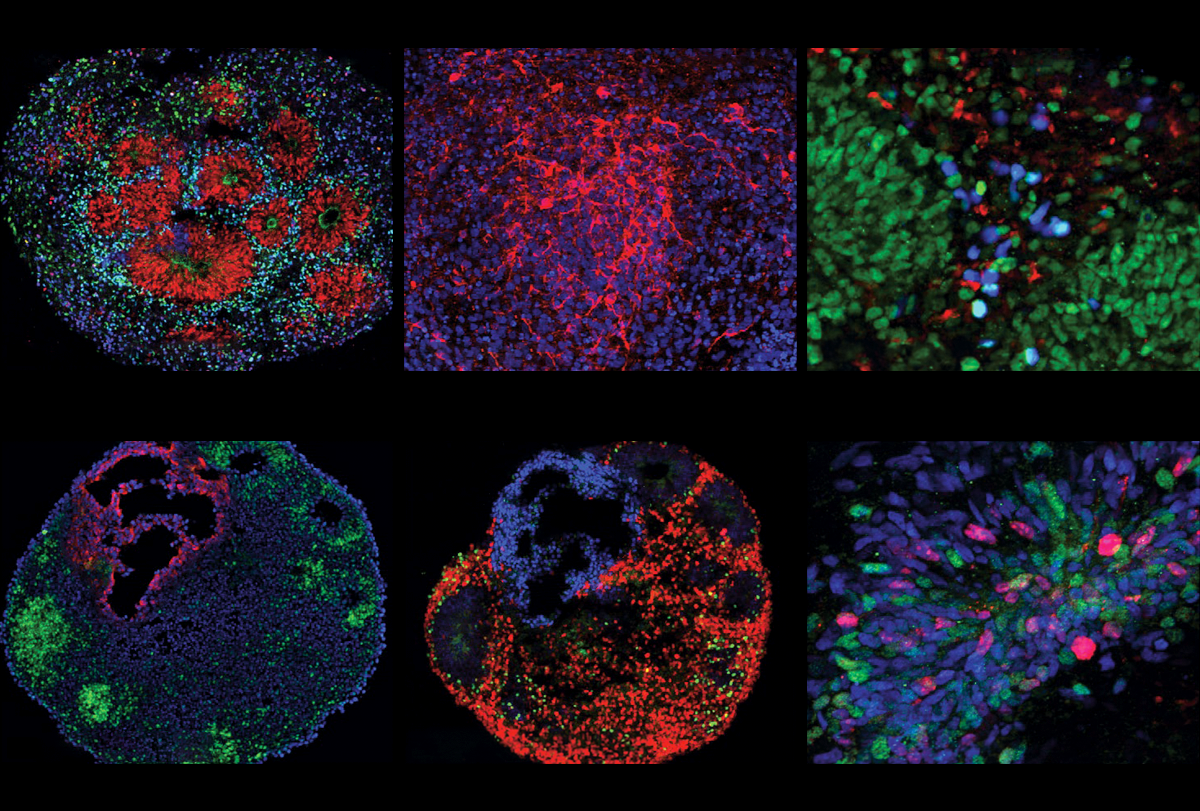
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
An imbalance in the number of excitatory neurons in early brain development may account for the difference.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune-conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
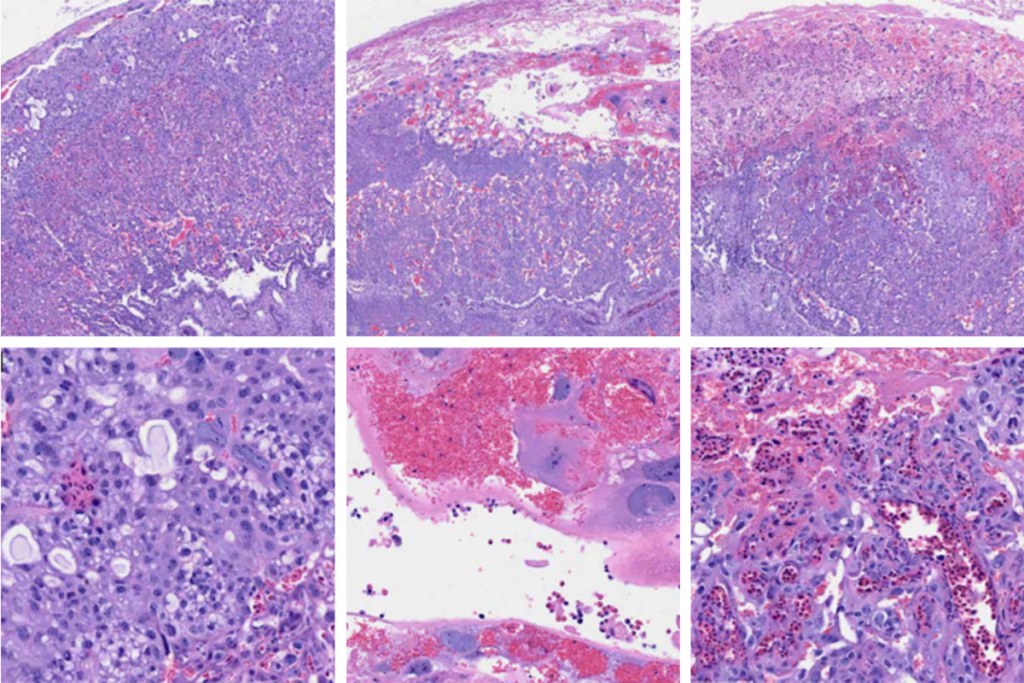
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune-conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.

Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.