CNTNAP2
Recent articles
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
On the periphery: Thinking ‘outside the brain’ offers new ideas about autism
Neuronal alterations outside the brain may help to explain a host of the condition’s characteristic traits, including sensory changes, gut problems and motor differences.
On the periphery: Thinking ‘outside the brain’ offers new ideas about autism
Neuronal alterations outside the brain may help to explain a host of the condition’s characteristic traits, including sensory changes, gut problems and motor differences.
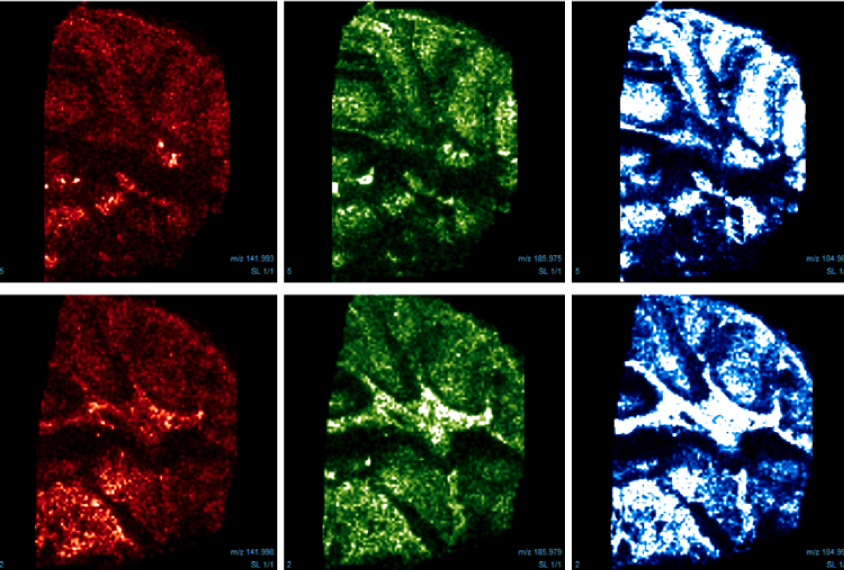
Multi-omics study captures CNTNAP2’s far-ranging effects
The in-depth approach shows mutations in the autism-linked gene disrupt neuronal growth and communication, as well as mitochondrial gene expression.
Multi-omics study captures CNTNAP2’s far-ranging effects
The in-depth approach shows mutations in the autism-linked gene disrupt neuronal growth and communication, as well as mitochondrial gene expression.
Mouse models help sniff out olfactory differences in autism
A range of presentations at Neuroscience 2022 tie atypical social behavior to trouble discriminating between odors in the animals.

Mouse models help sniff out olfactory differences in autism
A range of presentations at Neuroscience 2022 tie atypical social behavior to trouble discriminating between odors in the animals.
Oxytocin alters brain activity to boost sociability in mice missing autism gene
Infusions of the hormone oxytocin may make mice that model autism more social by normalizing their brain activity patterns.
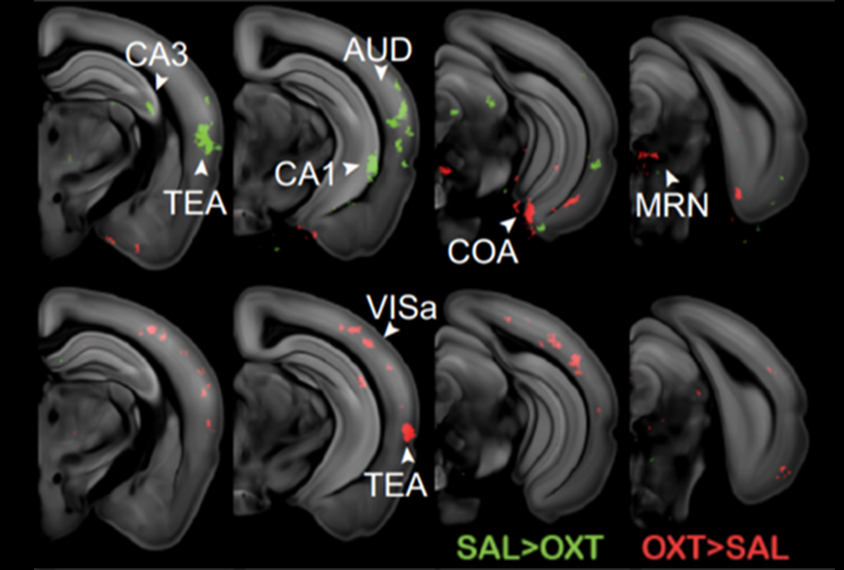
Oxytocin alters brain activity to boost sociability in mice missing autism gene
Infusions of the hormone oxytocin may make mice that model autism more social by normalizing their brain activity patterns.
Fish, frogs, flies and other fauna in scientific firsts
Over the past century, scientists have used a variety of animal models to advance their understanding of the developing brain and autism.

Fish, frogs, flies and other fauna in scientific firsts
Over the past century, scientists have used a variety of animal models to advance their understanding of the developing brain and autism.
What studying worms, flies and fish says about autism
Researchers are increasingly turning to simple animals to learn about autism biology and find leads for new drugs.

What studying worms, flies and fish says about autism
Researchers are increasingly turning to simple animals to learn about autism biology and find leads for new drugs.
GABA agonist rescues auditory hypersensitivity in rats missing autism-linked gene CNTNAP2
The investigational drug arbaclofen may right an imbalance between inhibitory and excitatory signaling in the animals’ brains.
GABA agonist rescues auditory hypersensitivity in rats missing autism-linked gene CNTNAP2
The investigational drug arbaclofen may right an imbalance between inhibitory and excitatory signaling in the animals’ brains.
Cerebellum alterations crop up in mice missing autism gene
Deleting the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2 from mice leads to distinct cellular and electrical changes in the cerebellum, according to two unpublished studies presented virtually today at the 2021 Society for Neuroscience Global Connectome.

Cerebellum alterations crop up in mice missing autism gene
Deleting the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2 from mice leads to distinct cellular and electrical changes in the cerebellum, according to two unpublished studies presented virtually today at the 2021 Society for Neuroscience Global Connectome.
‘MoSeq’ identifies drug-specific behaviors in autism mouse model
A tool that relies on video cameras and machine learning can identify mice that have mutations in a top autism gene by their behaviors. It also detects how a widely used autism drug affects their movements.
‘MoSeq’ identifies drug-specific behaviors in autism mouse model
A tool that relies on video cameras and machine learning can identify mice that have mutations in a top autism gene by their behaviors. It also detects how a widely used autism drug affects their movements.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
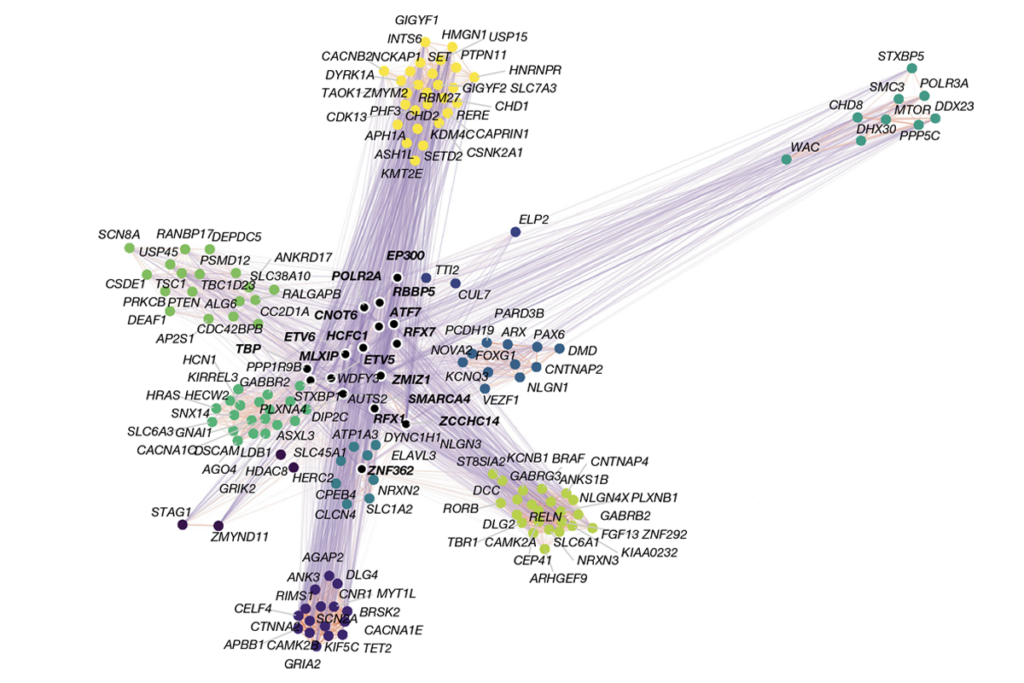
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
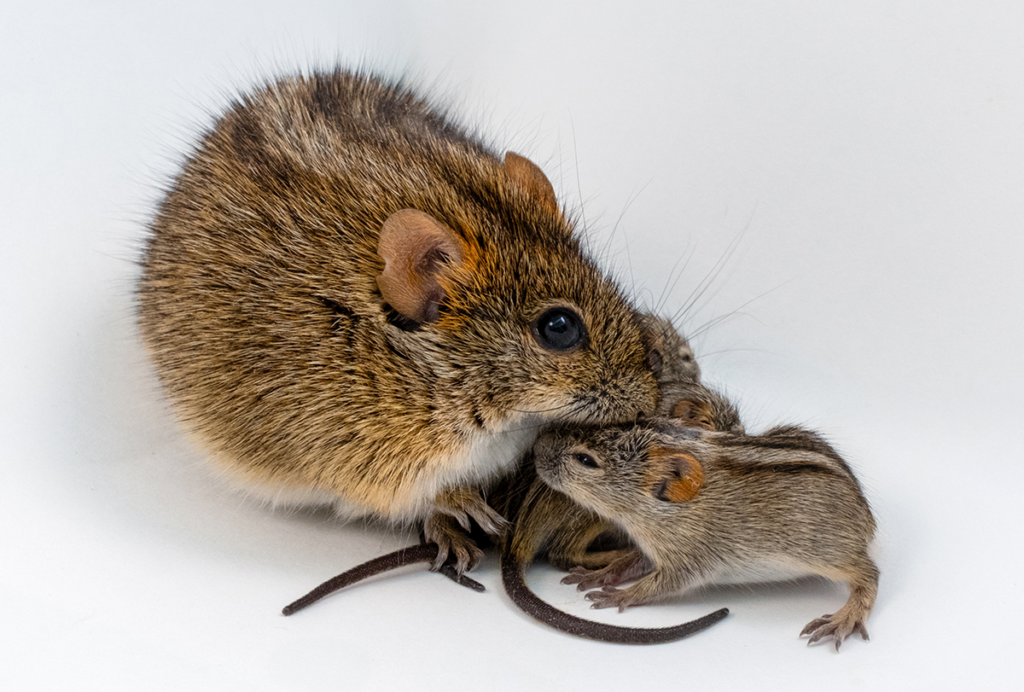

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.