Perspectives
Expert opinions on trends and controversies in neuroscience
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Women are systematically under-cited in neuroscience. New tools can change that.
An omitted citation in a high-profile paper led us to examine our own practices and to help others adopt tools that promote citation diversity.

Women are systematically under-cited in neuroscience. New tools can change that.
An omitted citation in a high-profile paper led us to examine our own practices and to help others adopt tools that promote citation diversity.
Neuroscience graduate students deserve comprehensive data-literacy education
Despite growing requirements around how to handle and share data, formal training is lacking.

Neuroscience graduate students deserve comprehensive data-literacy education
Despite growing requirements around how to handle and share data, formal training is lacking.
Leveraging the power of community to strengthen clinical trials for rare genetic syndromes
Families can become not only participants but champions of these research efforts.

Leveraging the power of community to strengthen clinical trials for rare genetic syndromes
Families can become not only participants but champions of these research efforts.
Accounting for a mosaic of sex differences: Q&A with Nicola Grissom
Breaking the binary view of sex traits can enable researchers to represent the broader complexity of behavior and cognition.
Accounting for a mosaic of sex differences: Q&A with Nicola Grissom
Breaking the binary view of sex traits can enable researchers to represent the broader complexity of behavior and cognition.
To develop better nervous-system visualizations, we need to think BIG
With a full mouse connectome on the horizon, neuroscience needs to overcome its legacy of minimalism and embrace the contemporary challenge of representing whole-nervous-system connectivity.
To develop better nervous-system visualizations, we need to think BIG
With a full mouse connectome on the horizon, neuroscience needs to overcome its legacy of minimalism and embrace the contemporary challenge of representing whole-nervous-system connectivity.
Computational and systems neuroscience needs development
Embracing recent advances in developmental biology can drive a new wave of innovation.
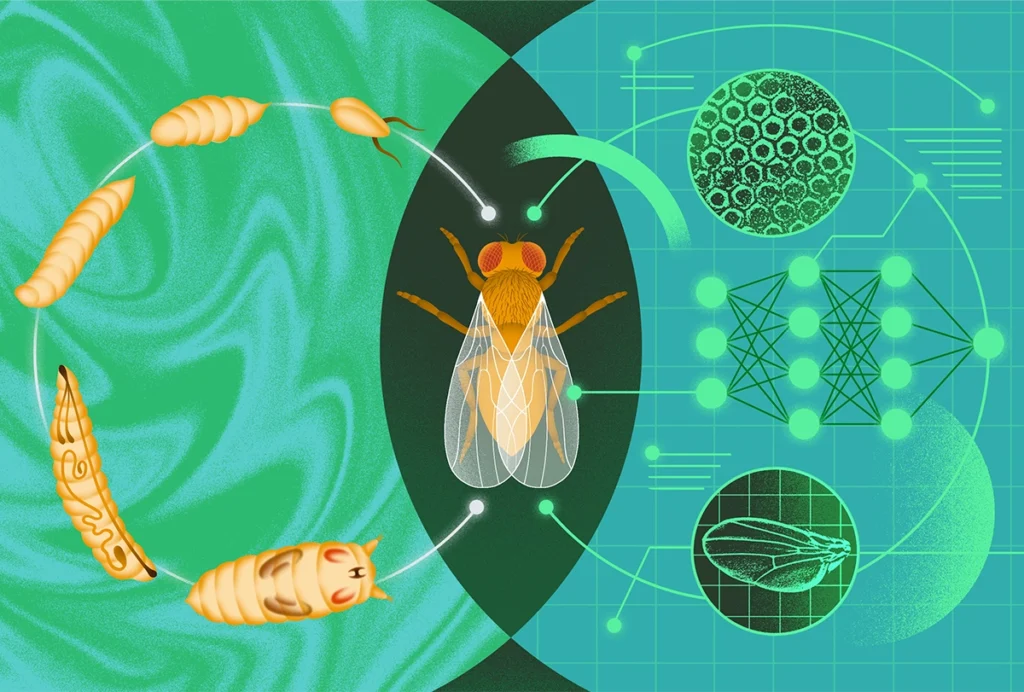

Computational and systems neuroscience needs development
Embracing recent advances in developmental biology can drive a new wave of innovation.
Mind control in zombie flies: Q&A with Carolyn Elya
A parasitic fungus compels its insect host to behave in strange ways by hijacking secretory neurons and circadian pathways.
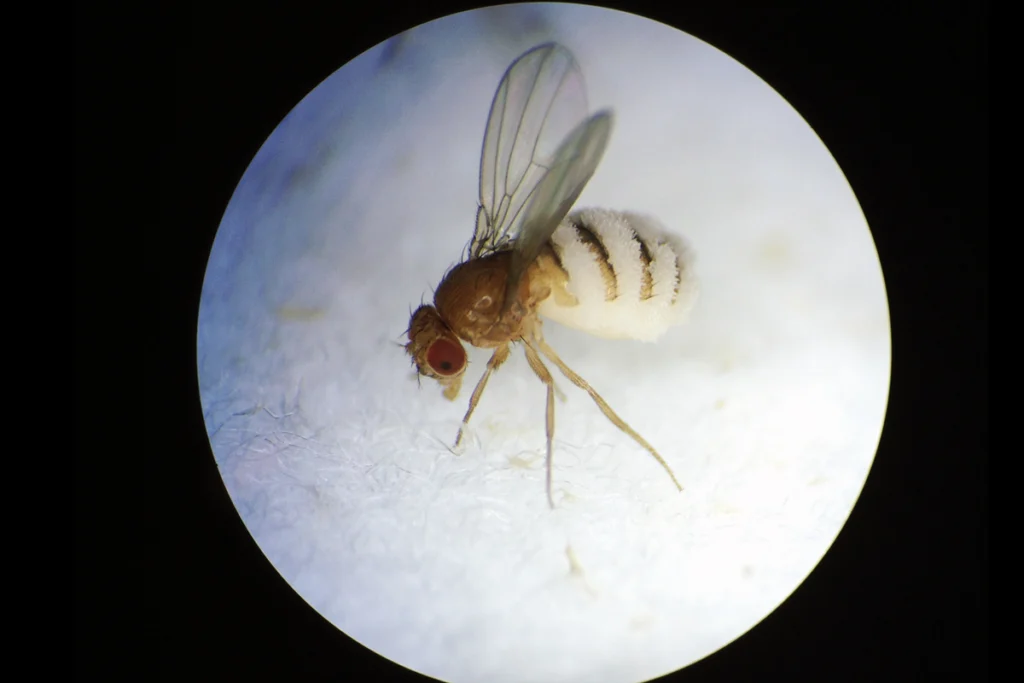

Mind control in zombie flies: Q&A with Carolyn Elya
A parasitic fungus compels its insect host to behave in strange ways by hijacking secretory neurons and circadian pathways.
How to teach this paper: ‘Behavioral time scale synaptic plasticity underlies CA1 place fields,’ by Bittner and Milstein et al. (2017)
Katie Bittner, Aaron Milstein and their colleagues found that cellular learning can happen over longer timescales than Hebb’s rule predicts. How long should we wait to teach students about this phenomenon?

How to teach this paper: ‘Behavioral time scale synaptic plasticity underlies CA1 place fields,’ by Bittner and Milstein et al. (2017)
Katie Bittner, Aaron Milstein and their colleagues found that cellular learning can happen over longer timescales than Hebb’s rule predicts. How long should we wait to teach students about this phenomenon?
Designing an open-source microscope
Funding for the development of open-source tools is on the rise, but support for their maintenance and dissemination, both crucial for their meaningful uptake, remains a major challenge.
Designing an open-source microscope
Funding for the development of open-source tools is on the rise, but support for their maintenance and dissemination, both crucial for their meaningful uptake, remains a major challenge.
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
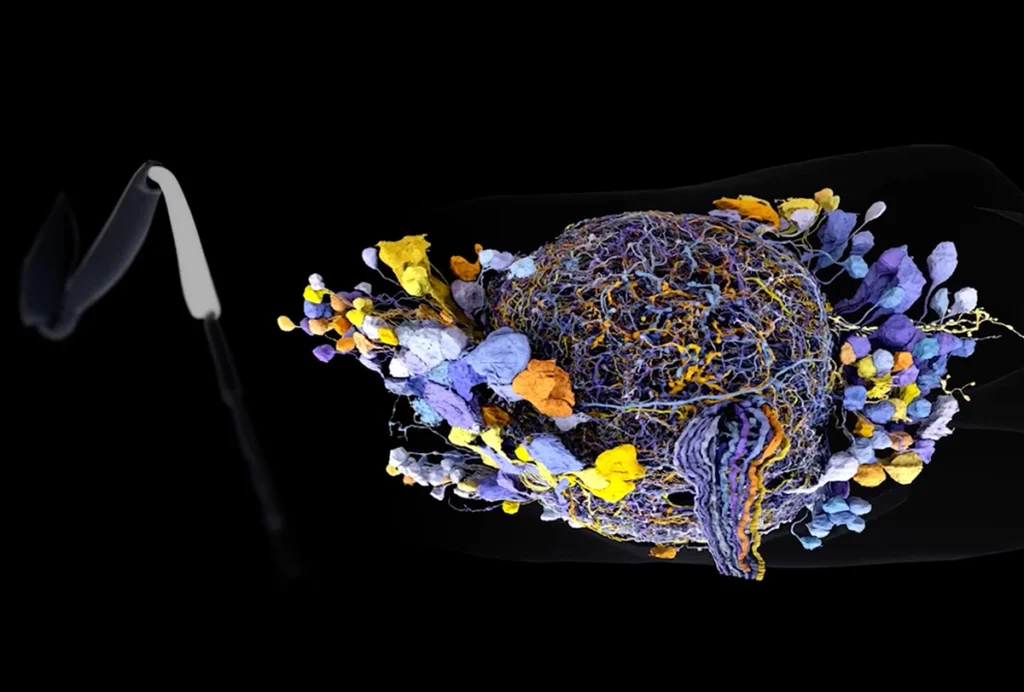
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
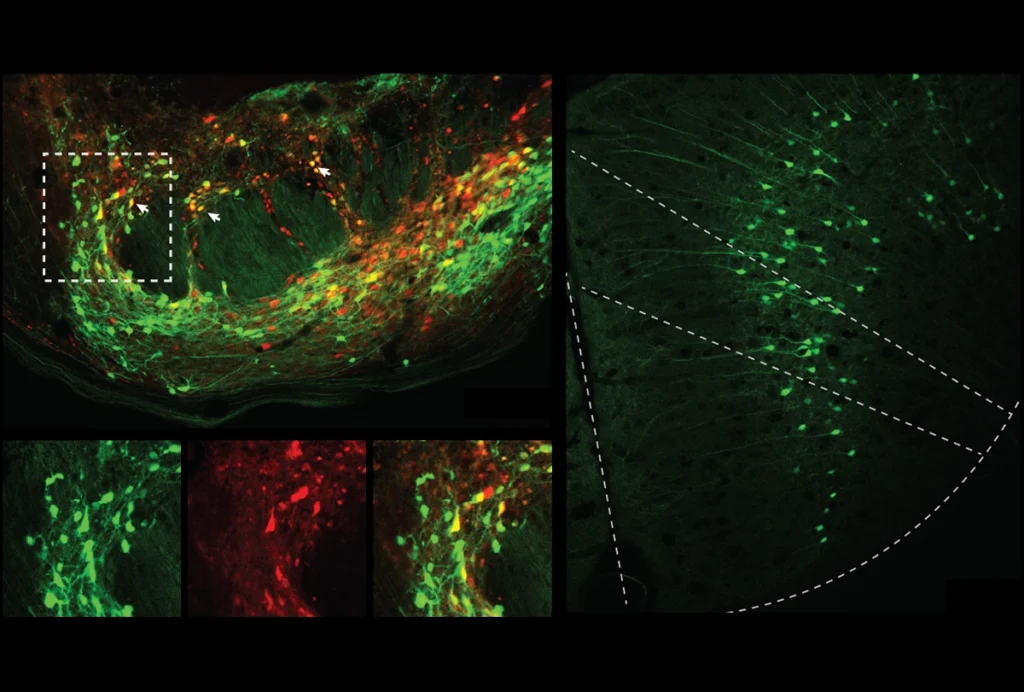
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
New ‘decoder’ tool translates functional neuroimaging terms across labs
The compendium of brain-parcellation atlases makes it possible to compare large-scale network data, which often involves different and overlapping network names.
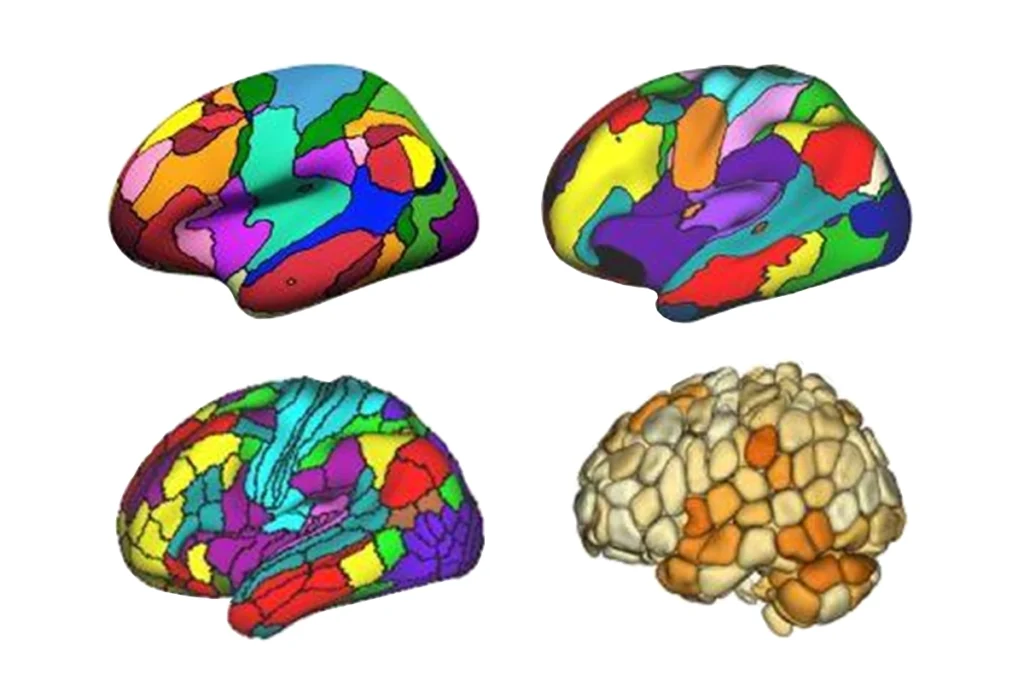
New ‘decoder’ tool translates functional neuroimaging terms across labs
The compendium of brain-parcellation atlases makes it possible to compare large-scale network data, which often involves different and overlapping network names.