Postsynaptic density
Recent articles
Pruning protein; cultural connection; cannabis consent and more
A pruning protein reshapes neurons, culture should be a consideration in trials of autism treatments, and another U.S. state adds autism to the list of indications for medical cannabis.
Pruning protein; cultural connection; cannabis consent and more
A pruning protein reshapes neurons, culture should be a consideration in trials of autism treatments, and another U.S. state adds autism to the list of indications for medical cannabis.
Protein factories at neuronal junctions take center stage in autism
Some genes linked to autism regulate the production of proteins at neuronal junctions, suggesting that disrupted protein synthesis contributes to the condition.
Protein factories at neuronal junctions take center stage in autism
Some genes linked to autism regulate the production of proteins at neuronal junctions, suggesting that disrupted protein synthesis contributes to the condition.
Proteins that spark learning may play key part in autism
A new study ties autism risk to a core team of proteins that facilitate neuronal signaling as an animal learns.
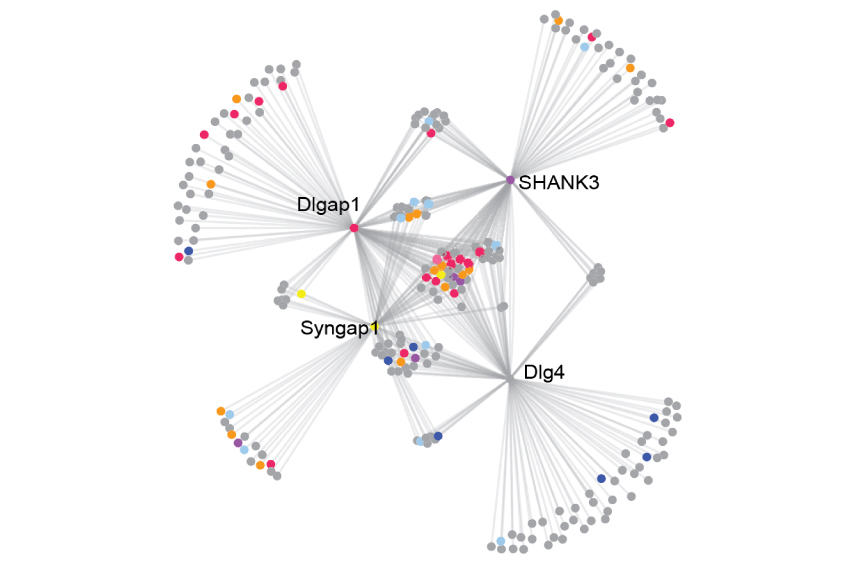
Proteins that spark learning may play key part in autism
A new study ties autism risk to a core team of proteins that facilitate neuronal signaling as an animal learns.
Cell skeleton breakdown may spur autism symptoms in mice
An autism-linked mutation in the SHANK3 gene alters the protein skeleton of mouse neurons. Repairing the scaffold eases the animals’ social deficits.

Cell skeleton breakdown may spur autism symptoms in mice
An autism-linked mutation in the SHANK3 gene alters the protein skeleton of mouse neurons. Repairing the scaffold eases the animals’ social deficits.
Method isolates protein complexes from neuronal junctions
Researchers have for the first time isolated and characterized protein complexes found at the points of connection between neurons. Mutations in some of these proteins are linked to autism.

Method isolates protein complexes from neuronal junctions
Researchers have for the first time isolated and characterized protein complexes found at the points of connection between neurons. Mutations in some of these proteins are linked to autism.
Large study underscores role of gene copy number in autism
People with autism tend to carry mutations that duplicate or delete several genes at once, according to a large study published 1 May in the American Journal of Human Genetics.

Large study underscores role of gene copy number in autism
People with autism tend to carry mutations that duplicate or delete several genes at once, according to a large study published 1 May in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
Brain atlas maps gene expression in three dimensions
Researchers have charted patterns of gene expression in a three-dimensional representation of the human brain. The results, published 20 September in Nature, show that different brain regions have distinct molecular and functional roles.

Brain atlas maps gene expression in three dimensions
Researchers have charted patterns of gene expression in a three-dimensional representation of the human brain. The results, published 20 September in Nature, show that different brain regions have distinct molecular and functional roles.
Defects in autism risk genes may lead to slower signals
Mutations in two genes linked to autism, neurexin and neuroligin, slow down neuronal signaling, according to research published 2 August in Science. Analyzing the mutations in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the study found that mutations in these genes affect signaling in the opposite direction than is typical.

Defects in autism risk genes may lead to slower signals
Mutations in two genes linked to autism, neurexin and neuroligin, slow down neuronal signaling, according to research published 2 August in Science. Analyzing the mutations in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the study found that mutations in these genes affect signaling in the opposite direction than is typical.
Molecular mechanisms: Autism gene tied to neuronal junctions
Neurobeachin, or NBEA, an autism–associated gene, may regulate the transport of signaling molecules to neuronal branches, according to a study published 22 November in Nature Communications.

Molecular mechanisms: Autism gene tied to neuronal junctions
Neurobeachin, or NBEA, an autism–associated gene, may regulate the transport of signaling molecules to neuronal branches, according to a study published 22 November in Nature Communications.
Molecular mechanisms: SHANK2 mutants alter synapses
Three mutations in SHANK2, an autism-associated gene, each lead to abnormal synapses, the junctions between neurons, according to a study in Human Molecular Genetics.

Molecular mechanisms: SHANK2 mutants alter synapses
Three mutations in SHANK2, an autism-associated gene, each lead to abnormal synapses, the junctions between neurons, according to a study in Human Molecular Genetics.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.