Theories of autism
Recent articles
The signaling imbalance theory of autism, explained
The signaling imbalance theory holds that the brains of autistic people are hyper-excitable because of either excess neuronal activity or weak brakes on that activity.

The signaling imbalance theory of autism, explained
The signaling imbalance theory holds that the brains of autistic people are hyper-excitable because of either excess neuronal activity or weak brakes on that activity.
The female protective effect, explained
One of the leading theories of autism posits that girls and women are biologically protected from the condition.
The female protective effect, explained
One of the leading theories of autism posits that girls and women are biologically protected from the condition.
The extreme male brain, explained
The ‘extreme male brain’ theory suggests that autism is an exaggeration of systematic sex differences in ways of thinking.
The extreme male brain, explained
The ‘extreme male brain’ theory suggests that autism is an exaggeration of systematic sex differences in ways of thinking.
Serotonin’s link to autism, explained
Serotonin, the brain chemical best known for its link to depression, may also be involved in autism.

Serotonin’s link to autism, explained
Serotonin, the brain chemical best known for its link to depression, may also be involved in autism.
The multiple hits theory of autism, explained
Researchers are studying how a combination of genetic ‘hits’ may contribute to autism’s diversity.

The multiple hits theory of autism, explained
Researchers are studying how a combination of genetic ‘hits’ may contribute to autism’s diversity.
The predictive coding theory of autism, explained
In autism, a person's brain may not form accurate predictions of imminent experiences, or even if it does, sensory input may override those predictions.

The predictive coding theory of autism, explained
In autism, a person's brain may not form accurate predictions of imminent experiences, or even if it does, sensory input may override those predictions.
The connectivity theory of autism, explained
A growing body of evidence suggests that autism involves atypical communication between brain regions, but how and where in the brain this plays out is unclear.
The connectivity theory of autism, explained
A growing body of evidence suggests that autism involves atypical communication between brain regions, but how and where in the brain this plays out is unclear.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
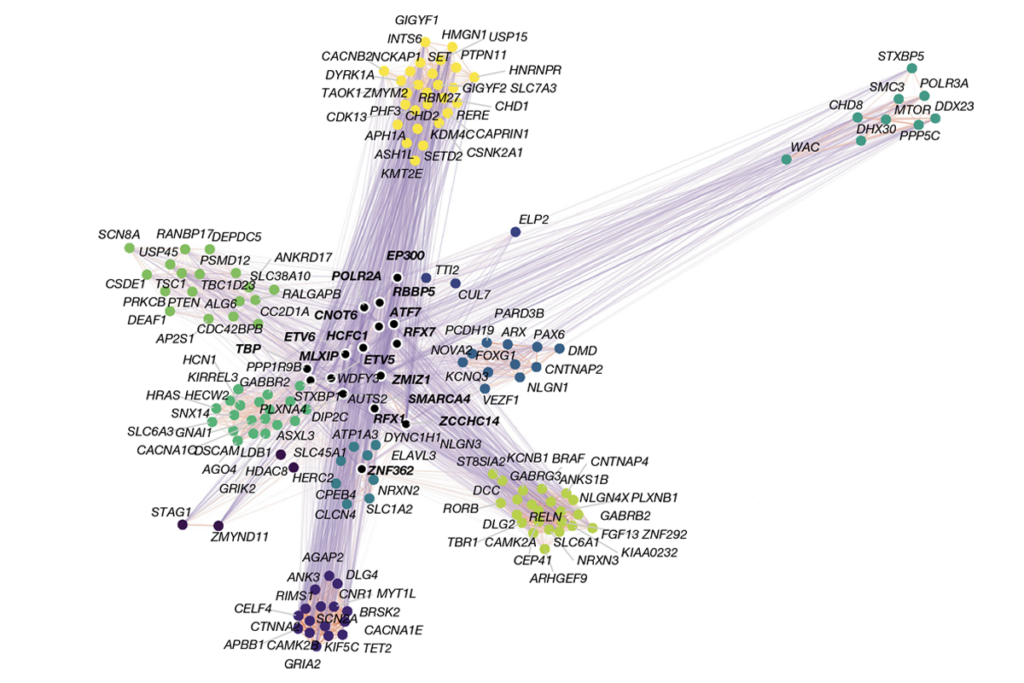
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
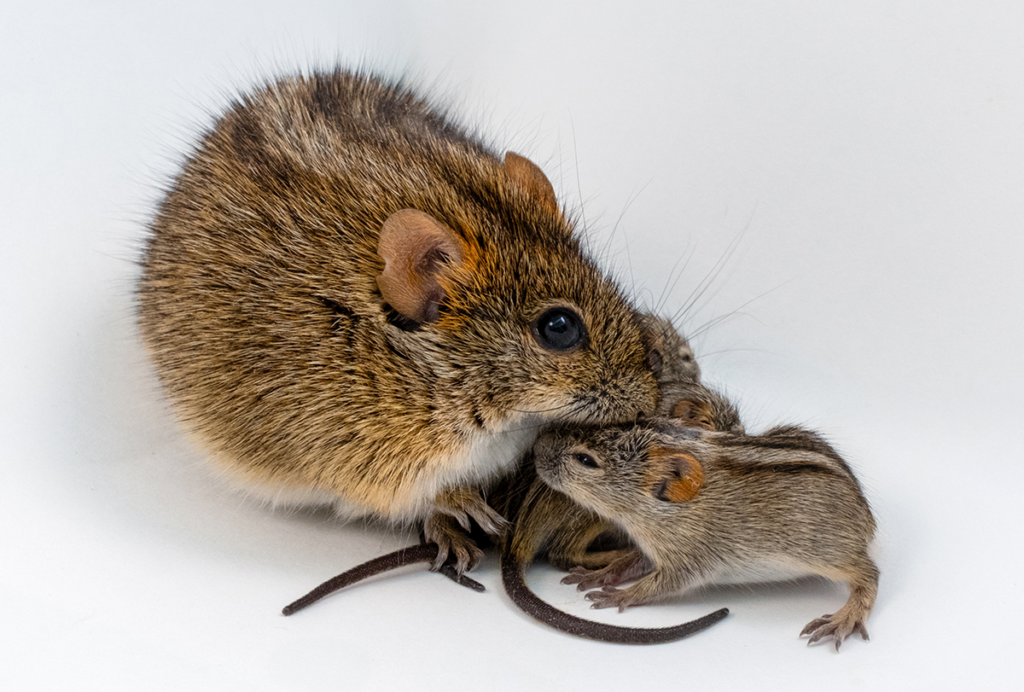

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.