Drosophila
Recent articles
This paper changed my life: John Tuthill reflects on the subjectivity of selfhood
Wittlinger, Wehner and Wolf’s 2006 “stilts and stumps” Science paper revealed how ants pull off extraordinary feats of navigation using a biological odometer, and it inspired Tuthill to consider how other insects sense their own bodies.
This paper changed my life: John Tuthill reflects on the subjectivity of selfhood
Wittlinger, Wehner and Wolf’s 2006 “stilts and stumps” Science paper revealed how ants pull off extraordinary feats of navigation using a biological odometer, and it inspired Tuthill to consider how other insects sense their own bodies.
The best of ‘this paper changed my life’ in 2025
From a study that upended astrocyte research to one that reignited the field of spiking neural networks, experts weighed in on the papers that significantly shaped how they think about and approach neuroscience.
The best of ‘this paper changed my life’ in 2025
From a study that upended astrocyte research to one that reignited the field of spiking neural networks, experts weighed in on the papers that significantly shaped how they think about and approach neuroscience.
Waves of calcium activity dictate eye structure in flies
Synchronized signals in non-neuronal retinal cells draw the tiny compartments of a fruit fly’s compound eye into alignment during pupal development.
Waves of calcium activity dictate eye structure in flies
Synchronized signals in non-neuronal retinal cells draw the tiny compartments of a fruit fly’s compound eye into alignment during pupal development.
Fly database secures funding for another year, but future remains in flux
The FlyBase team’s fundraising efforts have proven successful in the short term, but restoration of its federal grant remains uncertain.

Fly database secures funding for another year, but future remains in flux
The FlyBase team’s fundraising efforts have proven successful in the short term, but restoration of its federal grant remains uncertain.
One year of FlyWire: How the resource is redefining Drosophila research
We asked nine neuroscientists how they are using FlyWire data in their labs, how the connectome has transformed the field and what new tools they would like to see in the future.
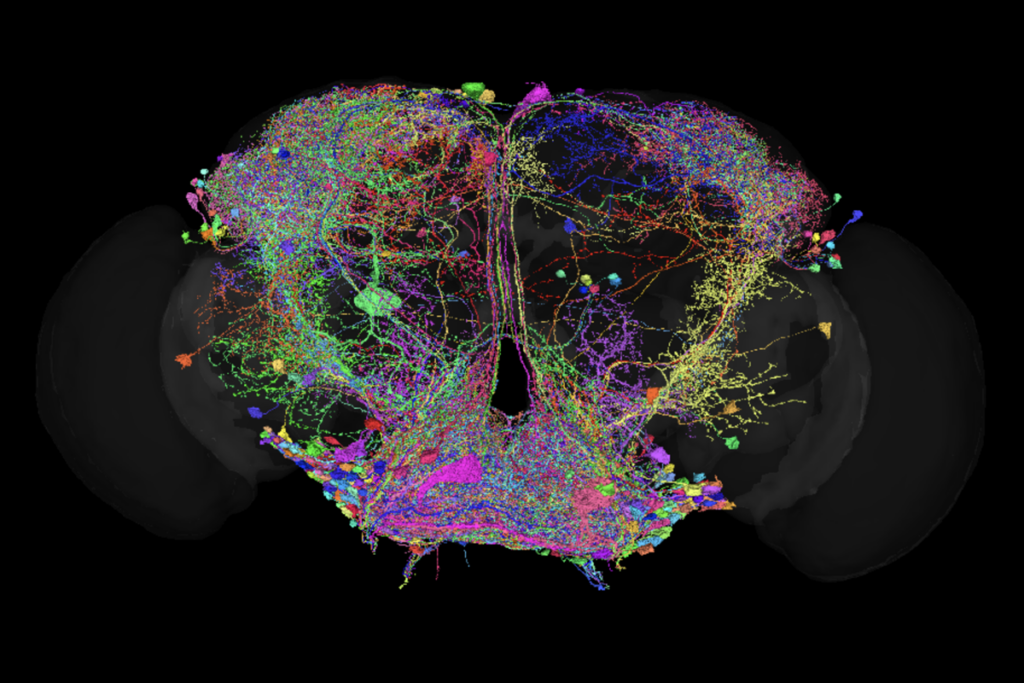
One year of FlyWire: How the resource is redefining Drosophila research
We asked nine neuroscientists how they are using FlyWire data in their labs, how the connectome has transformed the field and what new tools they would like to see in the future.
Local circuit loops within body control fly behavior, new ‘embodied’ connectome reveals
The mapping, which traces how the central nervous system interacts with the rest of the body, challenges the idea that behavior control is centralized.
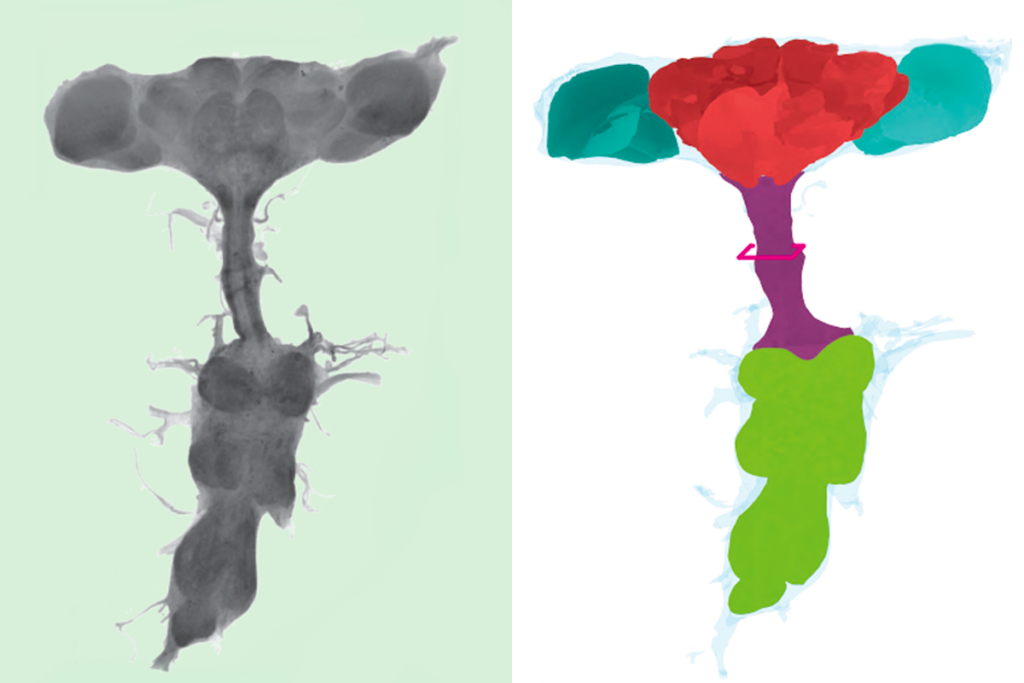
Local circuit loops within body control fly behavior, new ‘embodied’ connectome reveals
The mapping, which traces how the central nervous system interacts with the rest of the body, challenges the idea that behavior control is centralized.
Mitochondria set ‘ancient’ metabolic thermostat for sleep in flies, separate from circadian rhythms
During waking hours, a specialized set of sleep neurons in the fly brain accumulates reactive oxygen species, which eventually trigger sleep to clean up and repair the damage they do.
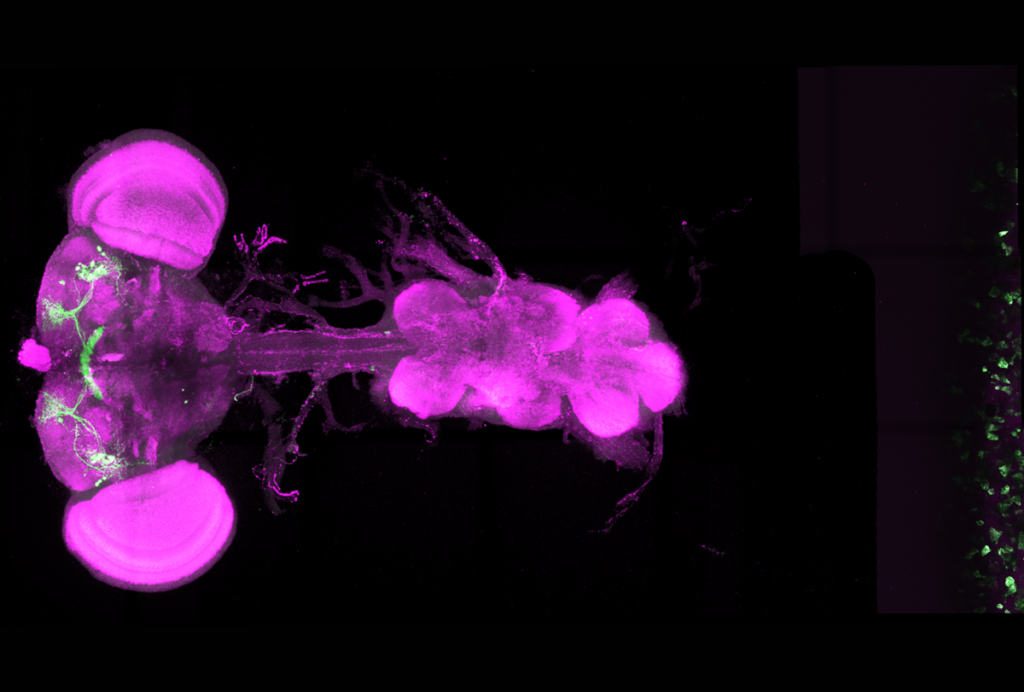
Mitochondria set ‘ancient’ metabolic thermostat for sleep in flies, separate from circadian rhythms
During waking hours, a specialized set of sleep neurons in the fly brain accumulates reactive oxygen species, which eventually trigger sleep to clean up and repair the damage they do.
Exclusive: Harvard University lays off fly database team
The layoffs jeopardize this resource, which has served more than 4,000 labs for about three decades.

Exclusive: Harvard University lays off fly database team
The layoffs jeopardize this resource, which has served more than 4,000 labs for about three decades.
Cross-species connectome comparison shows uneven olfactory circuit evolution in flies
The findings start to reveal evolutionary changes that may have helped two species develop different olfactory preferences and adapt to their particular environments.
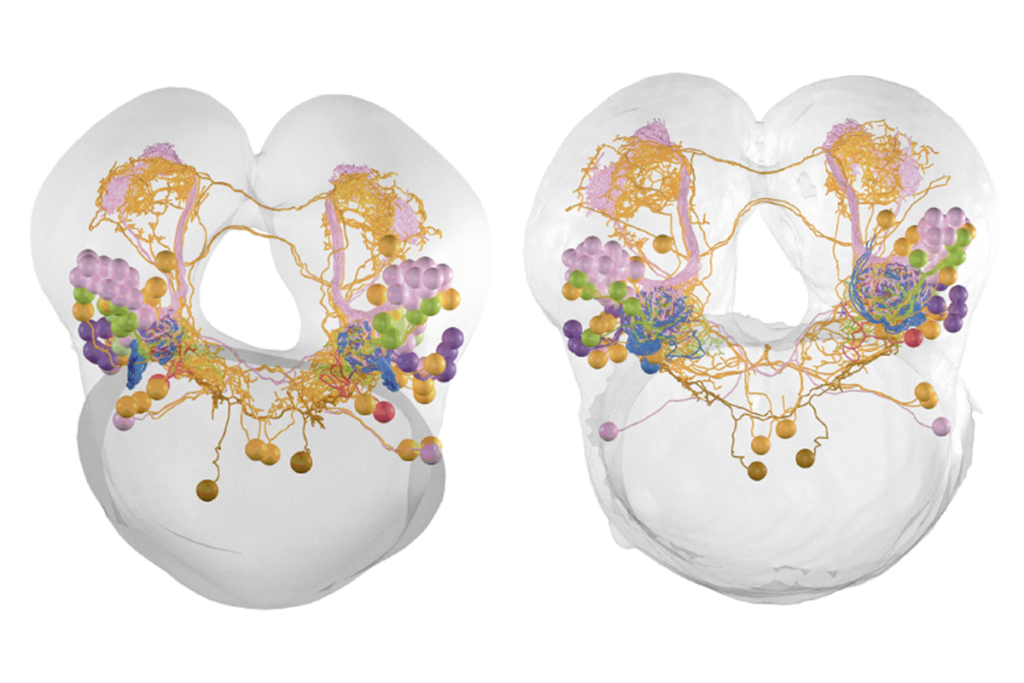
Cross-species connectome comparison shows uneven olfactory circuit evolution in flies
The findings start to reveal evolutionary changes that may have helped two species develop different olfactory preferences and adapt to their particular environments.
Systems and circuit neuroscience need an evolutionary perspective
To identify fundamental neuroscientific principles that generalize across species, neuroscientists must frame their research through an evolutionary lens.

Systems and circuit neuroscience need an evolutionary perspective
To identify fundamental neuroscientific principles that generalize across species, neuroscientists must frame their research through an evolutionary lens.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
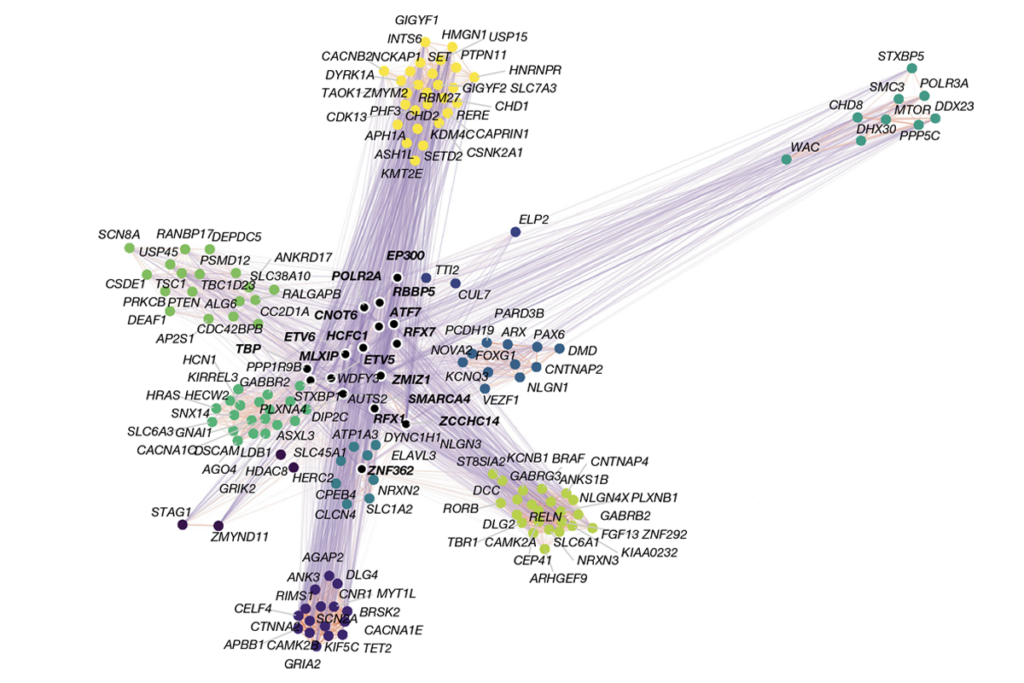
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
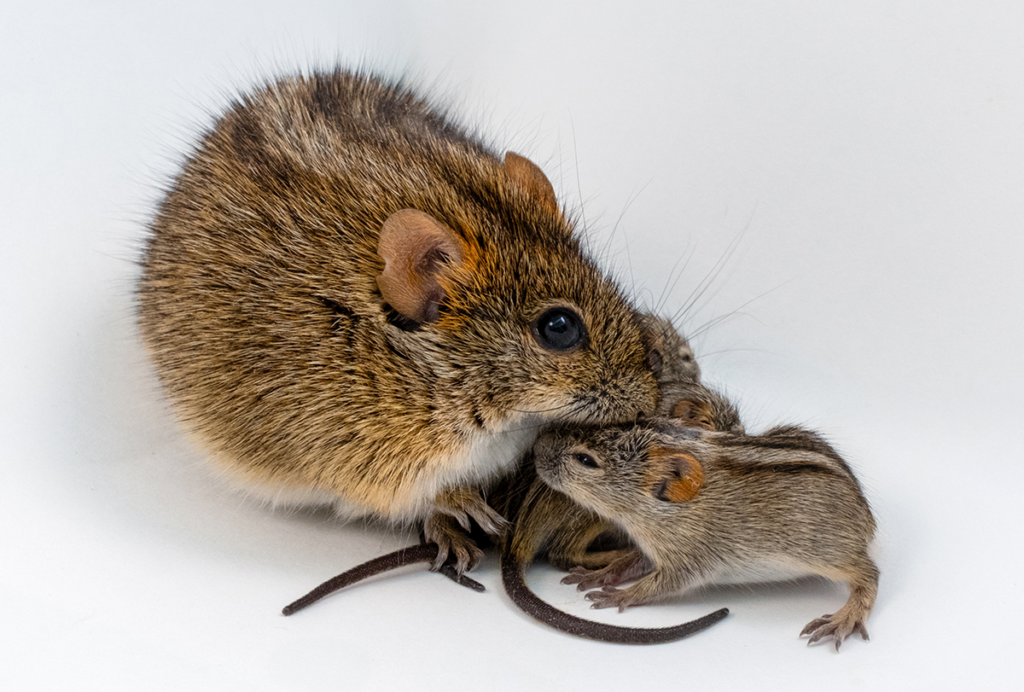

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.