Gene therapy
Recent articles
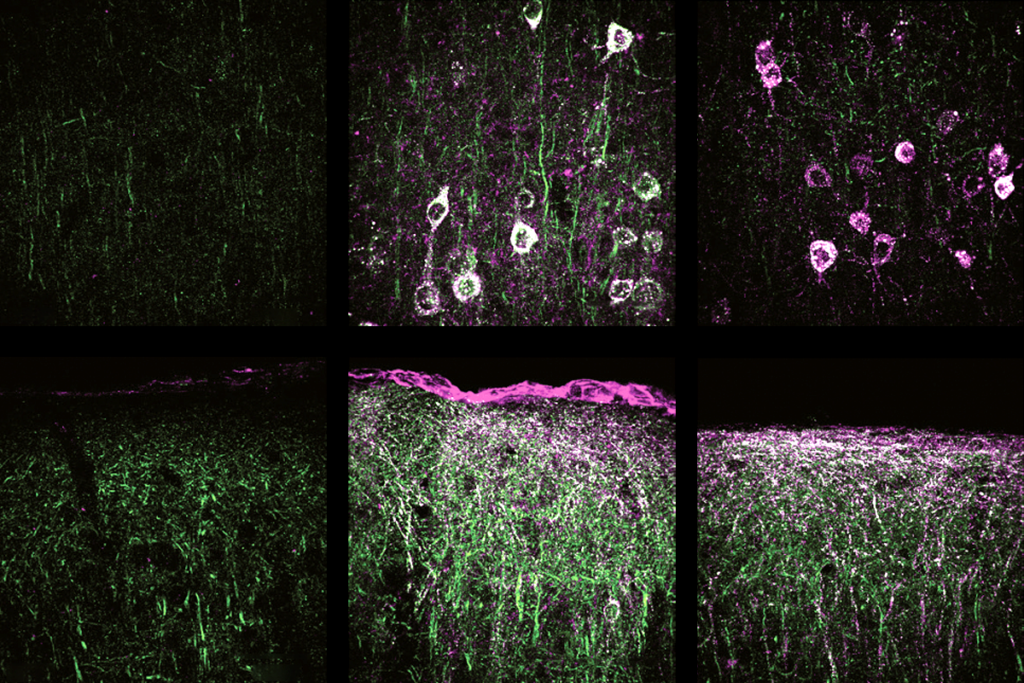
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
Boosting SCN2A expression reduces seizures in mice
A modified form of CRISPR amps up expression of the gene—a strategy that could apply to other gene variations linked to autism.
Expediting clinical trials for profound autism: Q&A with Matthew State
Aligning Research to Impact Autism, a new initiative funded by the Sergey Brin Family Foundation, wants to bring basic science discoveries to the clinic faster.

Expediting clinical trials for profound autism: Q&A with Matthew State
Aligning Research to Impact Autism, a new initiative funded by the Sergey Brin Family Foundation, wants to bring basic science discoveries to the clinic faster.
Split gene therapy delivers promise in mice modeling Dravet syndrome
The new approach overcomes viral packaging limitations by delivering SCN1A piecemeal and stitching it together in target cells.
Split gene therapy delivers promise in mice modeling Dravet syndrome
The new approach overcomes viral packaging limitations by delivering SCN1A piecemeal and stitching it together in target cells.
Molecular changes after MECP2 loss may drive Rett syndrome traits
Knocking out the gene in adult mice triggered up- and down-regulated expression of myriad genes weeks before there were changes in neuronal function.
Molecular changes after MECP2 loss may drive Rett syndrome traits
Knocking out the gene in adult mice triggered up- and down-regulated expression of myriad genes weeks before there were changes in neuronal function.
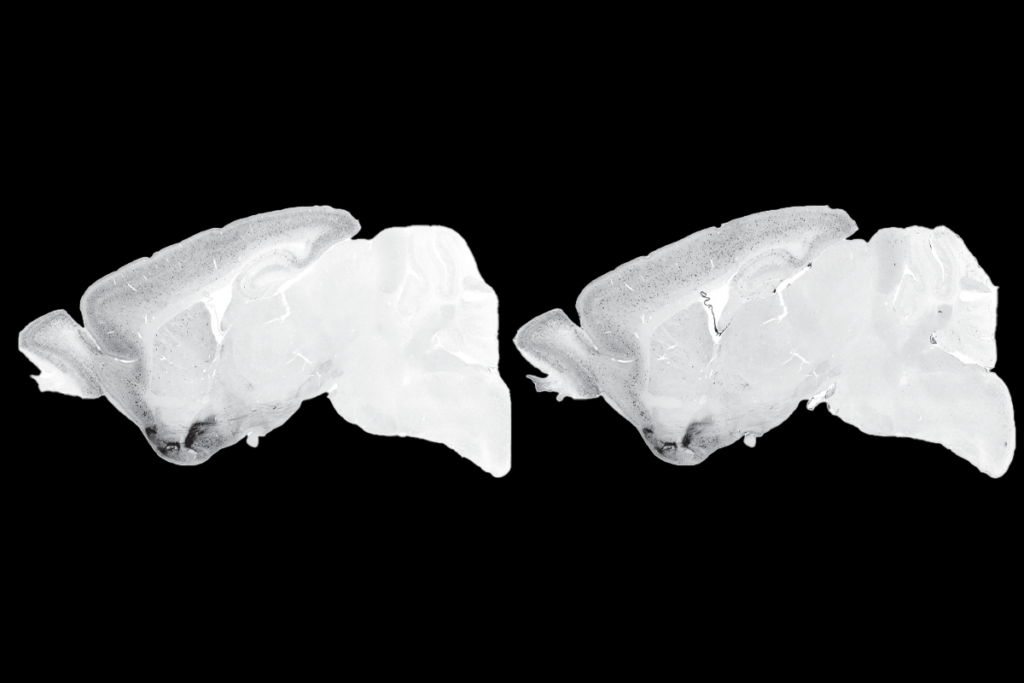
What’s next for brain-directed gene therapy after death in Neurogene trial
The incident highlights that viral vectors can trigger deadly immune responses even when delivered directly to the nervous system.
What’s next for brain-directed gene therapy after death in Neurogene trial
The incident highlights that viral vectors can trigger deadly immune responses even when delivered directly to the nervous system.
Expanding set of viral tools targets almost any brain cell type
Harmless viruses that encase short noncoding DNA elements called enhancers enable cell-type-specific gene delivery across the central nervous system in rodents and primates.
Expanding set of viral tools targets almost any brain cell type
Harmless viruses that encase short noncoding DNA elements called enhancers enable cell-type-specific gene delivery across the central nervous system in rodents and primates.
Leveraging the power of community to strengthen clinical trials for rare genetic syndromes
Families can become not only participants but champions of these research efforts.

Leveraging the power of community to strengthen clinical trials for rare genetic syndromes
Families can become not only participants but champions of these research efforts.
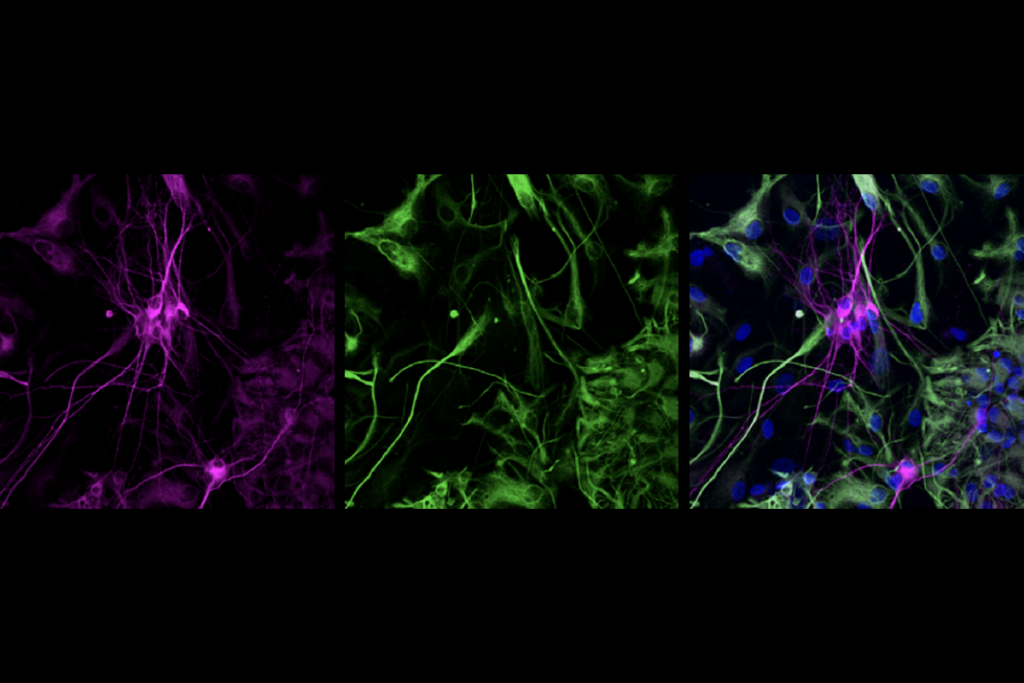
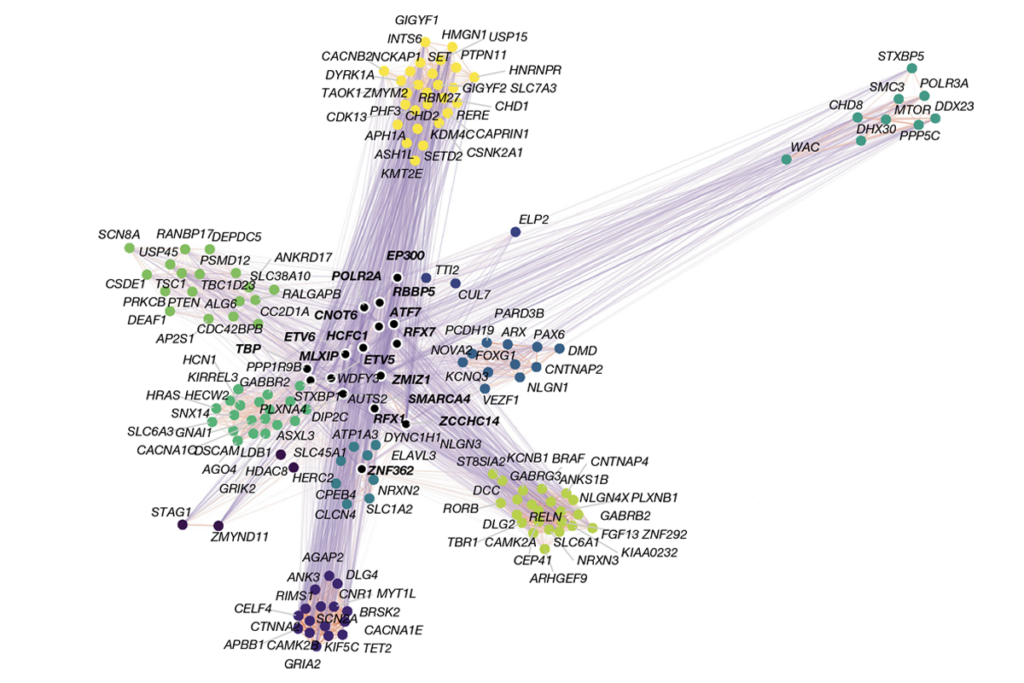
CRISPR gives autism-linked genes a boost, rescues functioning
A modified form of the gene-editing tool increases the expression of CHD8 and SCN2A, showing potential for autism therapies.
CRISPR gives autism-linked genes a boost, rescues functioning
A modified form of the gene-editing tool increases the expression of CHD8 and SCN2A, showing potential for autism therapies.
New RNA editor boasts increased versatility, safety
The “PRECISE” technique reprograms cells in a way that, unlike DNA editors, avoids potentially permanent off-target effects.
New RNA editor boasts increased versatility, safety
The “PRECISE” technique reprograms cells in a way that, unlike DNA editors, avoids potentially permanent off-target effects.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
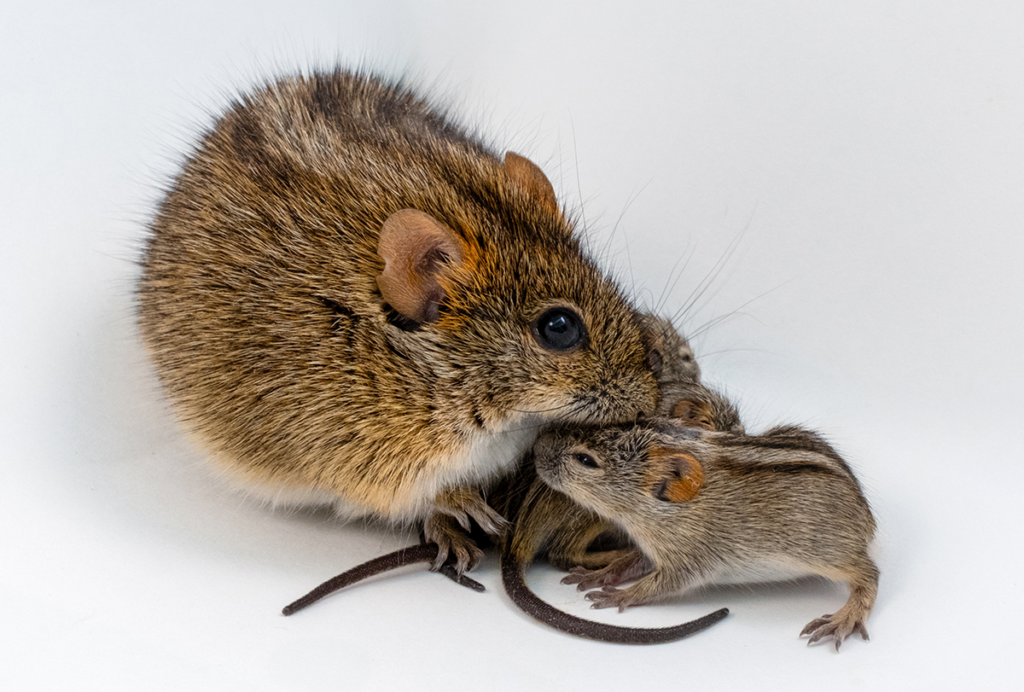
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.