Katharine Gammon is an award-winning independent science journalist based in Santa Monica, California. Her work has appeared in The New York Times, The Atlantic, WIRED, The Guardian, Undark, Popular Science, MIT Technology Review, Nature, Hakai and beyond.
Katharine Gammon
From this contributor
Spotted around the web: Mapping histones; COVID-19 births; acetaminophen lawsuits
Here is a roundup of news and research for the week of 31 October.
Spotted around the web: Mapping histones; COVID-19 births; acetaminophen lawsuits
A mix of common and rare variants shapes autism inheritance patterns
The study also reveals a link between language development and common variants.

A mix of common and rare variants shapes autism inheritance patterns
Zebrafish point to new gene involved in brain overgrowth, autism
The gene, YTHDF2, has not previously been linked to autism.
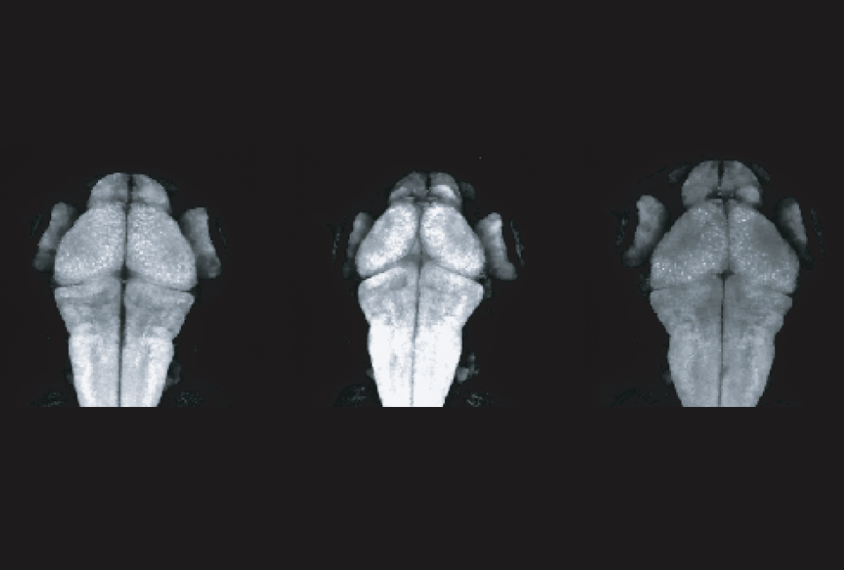
Zebrafish point to new gene involved in brain overgrowth, autism
Lags in genetic testing, variant reporting hinder autism research
Few autistic people undergo the recommended genetic testing for their condition, and test results often do not make their way into public databases, where researchers and clinicians can learn from them.

Lags in genetic testing, variant reporting hinder autism research
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
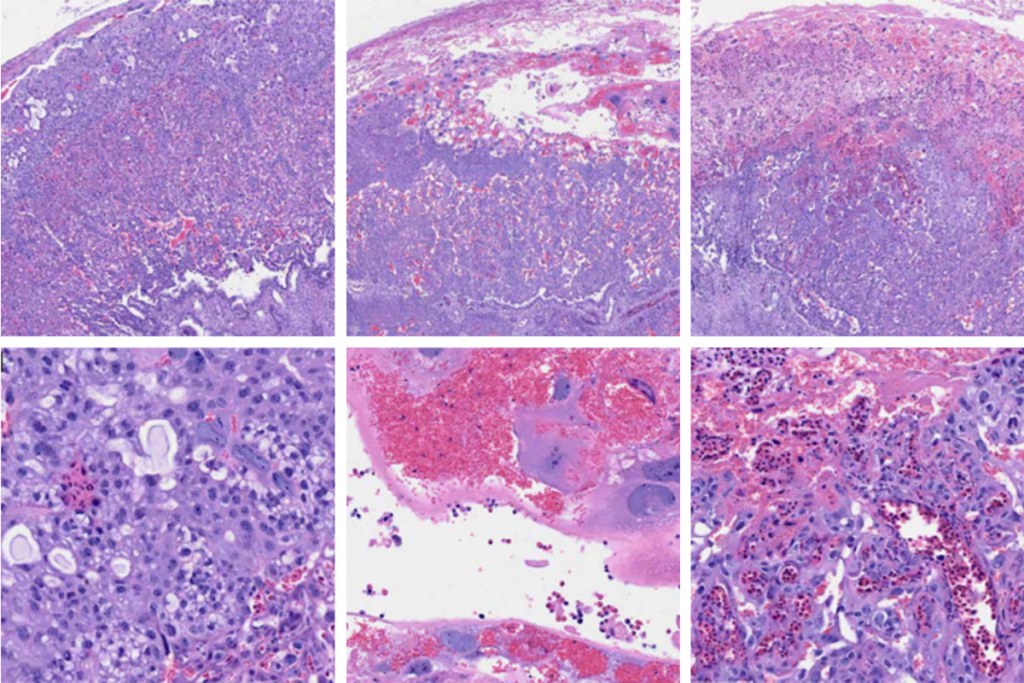
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.