Evolution
Recent articles
Inner retina of birds powers sight sans oxygen
The energy-intensive neural tissue relies instead on anaerobic glucose metabolism provided by the pecten oculi, a structure unique to the avian eye.
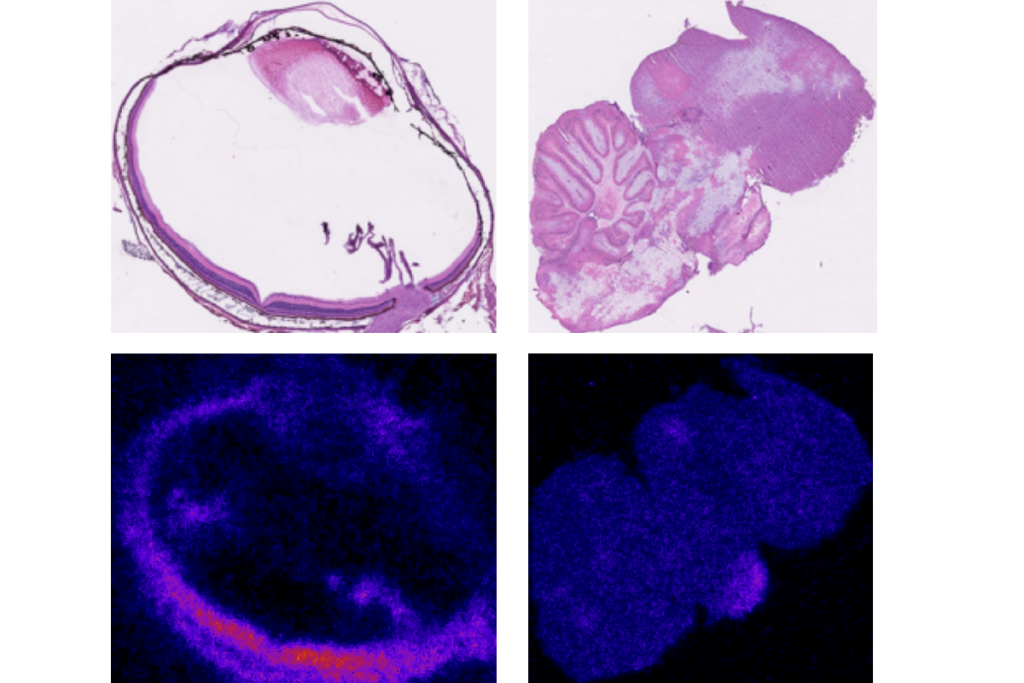
Inner retina of birds powers sight sans oxygen
The energy-intensive neural tissue relies instead on anaerobic glucose metabolism provided by the pecten oculi, a structure unique to the avian eye.
‘Tour de force’ study flags fount of interneurons in human brain
The newly discovered cell type might point to the origins of the inhibitory imbalance linked to autism and other conditions.
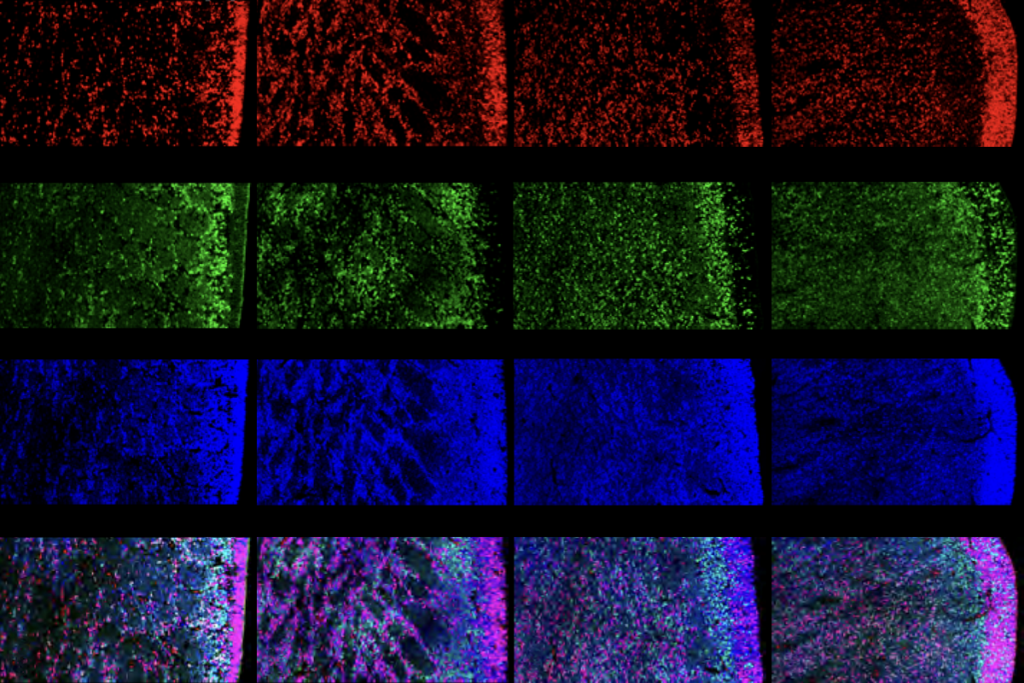
‘Tour de force’ study flags fount of interneurons in human brain
The newly discovered cell type might point to the origins of the inhibitory imbalance linked to autism and other conditions.
Viral remnant in chimpanzees silences brain gene humans still use
The retroviral insert appears to inadvertently switch off a gene involved in brain development.
Viral remnant in chimpanzees silences brain gene humans still use
The retroviral insert appears to inadvertently switch off a gene involved in brain development.
Snoozing dragons stir up ancient evidence of sleep’s dual nature
Deep-sleep cycling between brain waves of higher and lower amplitude dates far back on the evolutionary tree, according to a new comparative study of mammals and reptiles.
Snoozing dragons stir up ancient evidence of sleep’s dual nature
Deep-sleep cycling between brain waves of higher and lower amplitude dates far back on the evolutionary tree, according to a new comparative study of mammals and reptiles.
Protein tug-of-war controls pace of synaptic development, sets human brains apart
Human-specific duplicates of SRGAP2 prolong cortical development by manipulating SYNGAP, an autism-linked protein that slows synaptic growth.
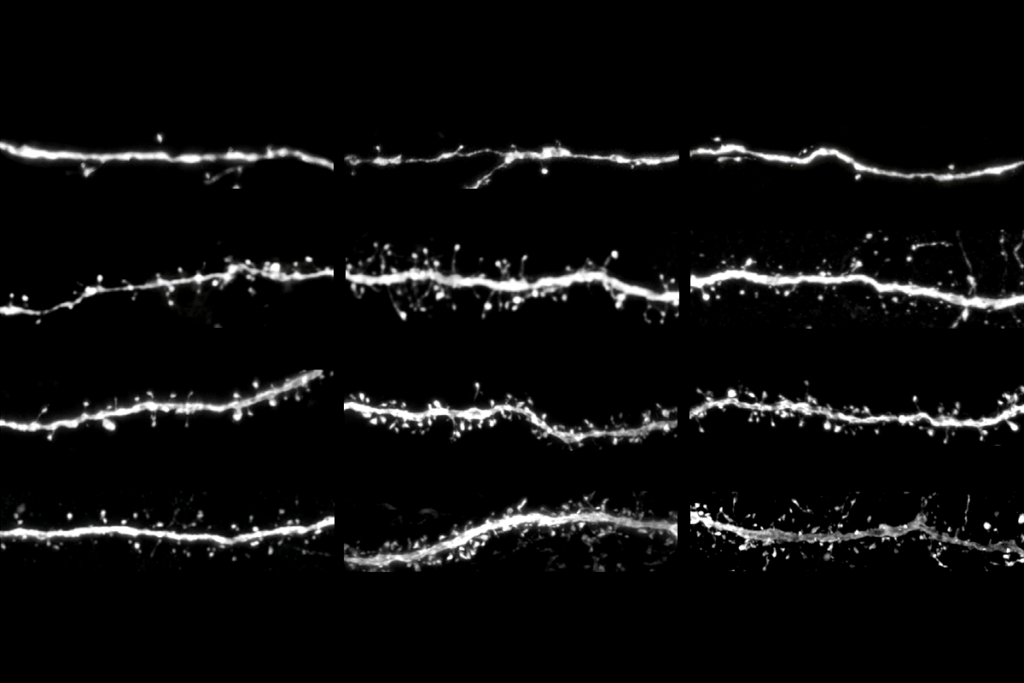
Protein tug-of-war controls pace of synaptic development, sets human brains apart
Human-specific duplicates of SRGAP2 prolong cortical development by manipulating SYNGAP, an autism-linked protein that slows synaptic growth.
Nikolay Kukushkin discusses his book, ‘One Hand Clapping: Unraveling the Mystery of the Human Mind’
He explains how meaning arises in the interactions found throughout nature and evolution, from molecules to minds.
Nikolay Kukushkin discusses his book, ‘One Hand Clapping: Unraveling the Mystery of the Human Mind’
He explains how meaning arises in the interactions found throughout nature and evolution, from molecules to minds.
One year of FlyWire: How the resource is redefining Drosophila research
We asked nine neuroscientists how they are using FlyWire data in their labs, how the connectome has transformed the field and what new tools they would like to see in the future.
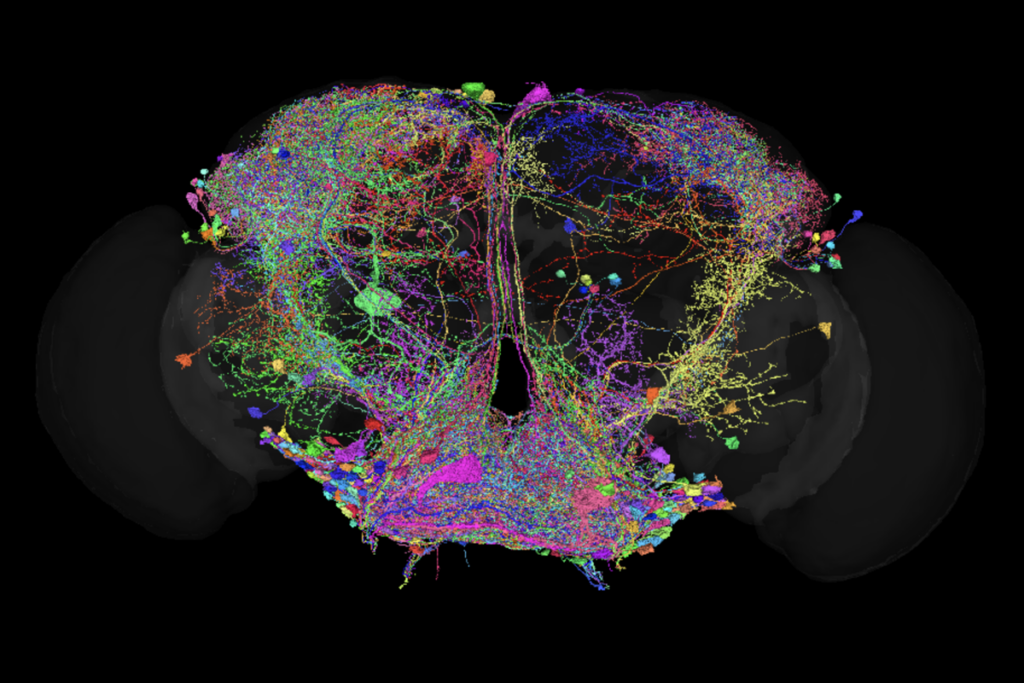
One year of FlyWire: How the resource is redefining Drosophila research
We asked nine neuroscientists how they are using FlyWire data in their labs, how the connectome has transformed the field and what new tools they would like to see in the future.
Cross-species connectome comparison shows uneven olfactory circuit evolution in flies
The findings start to reveal evolutionary changes that may have helped two species develop different olfactory preferences and adapt to their particular environments.
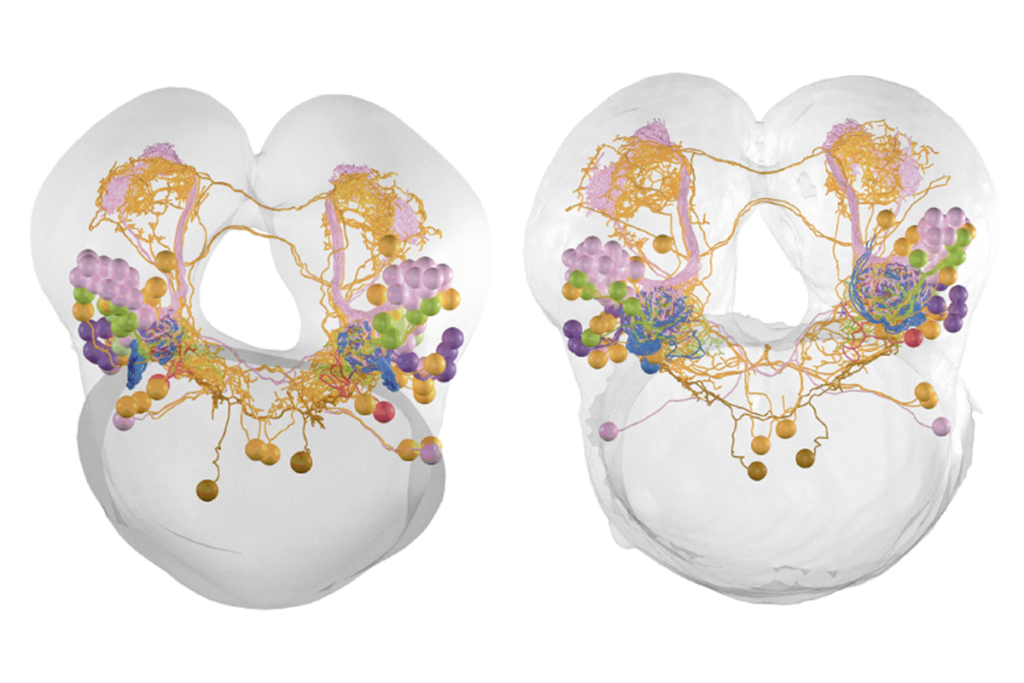
Cross-species connectome comparison shows uneven olfactory circuit evolution in flies
The findings start to reveal evolutionary changes that may have helped two species develop different olfactory preferences and adapt to their particular environments.
Systems and circuit neuroscience need an evolutionary perspective
To identify fundamental neuroscientific principles that generalize across species, neuroscientists must frame their research through an evolutionary lens.

Systems and circuit neuroscience need an evolutionary perspective
To identify fundamental neuroscientific principles that generalize across species, neuroscientists must frame their research through an evolutionary lens.
This paper changed my life: Bradley Dickerson on how a 1940s fly neuroanatomy paper influences his research to this day
This classic paper by zoologist John Pringle describes the haltere—a small structure in flies that plays a crucial role in flight control. It taught me to think about circuits and behavior as greater than the sum of their parts.
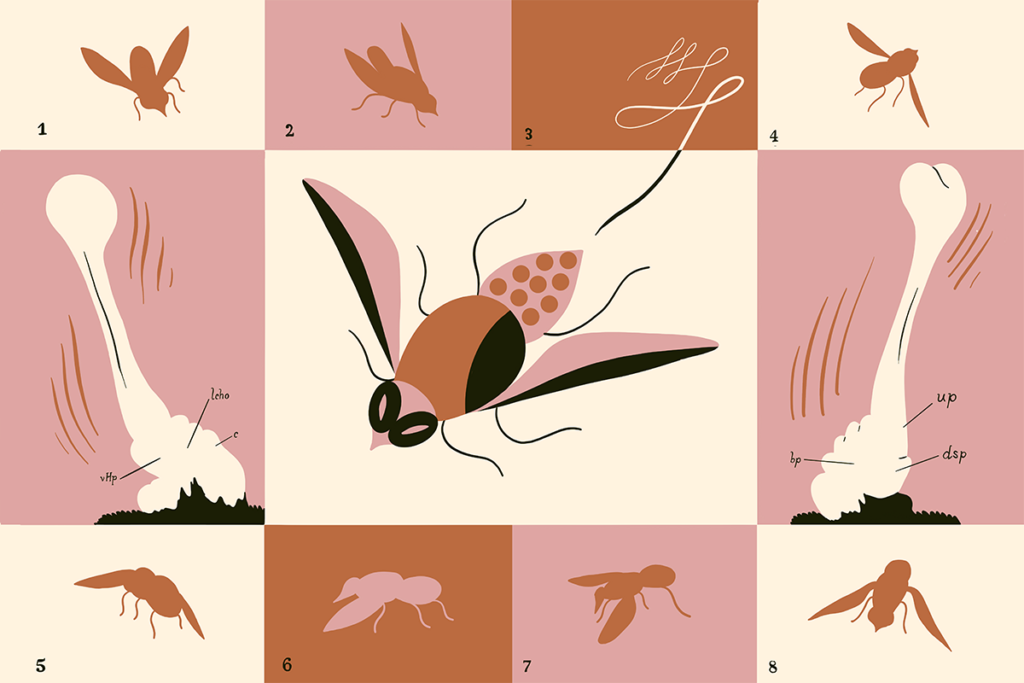

This paper changed my life: Bradley Dickerson on how a 1940s fly neuroanatomy paper influences his research to this day
This classic paper by zoologist John Pringle describes the haltere—a small structure in flies that plays a crucial role in flight control. It taught me to think about circuits and behavior as greater than the sum of their parts.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.