In pursuit of gene therapies for autism-linked conditions
Recent articles
Latest ‘prime-editing’ tools tackle delivery, safety issues
The gene-editing advances make it easier to target specific tissues in mice and detect off-target effects.
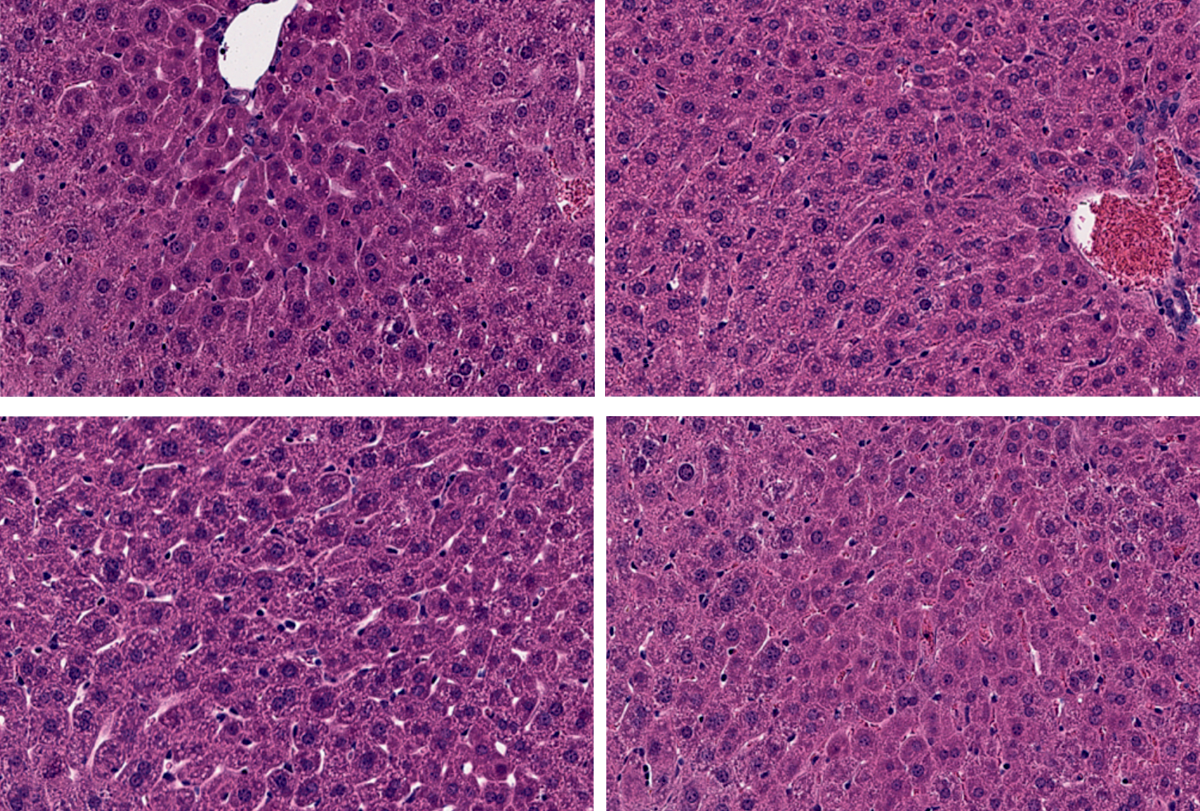
Latest ‘prime-editing’ tools tackle delivery, safety issues
The gene-editing advances make it easier to target specific tissues in mice and detect off-target effects.
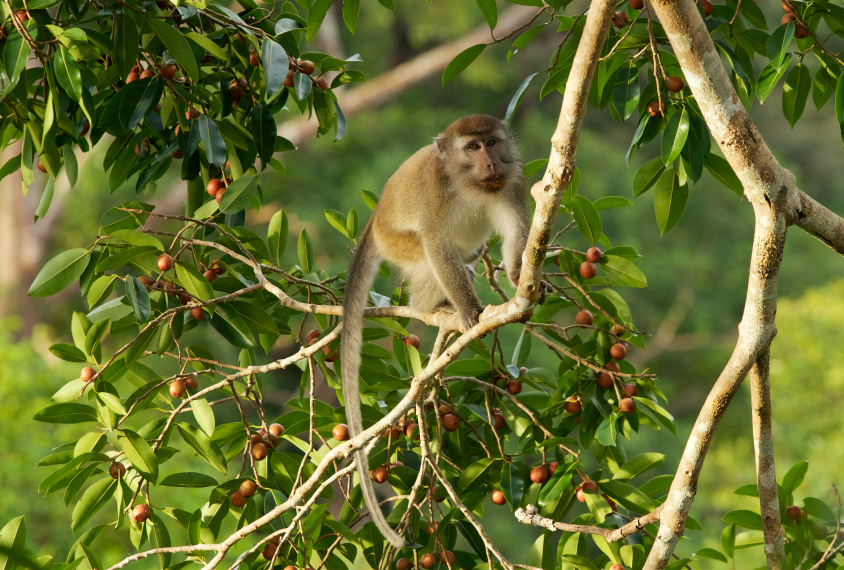
RNA therapy restores gene function in monkeys modeling Angelman syndrome
The result raises hopes for an ongoing clinical trial in people — and offers fresh insight into the biology of imprinting and the UBE3A antisense transcript.

RNA therapy restores gene function in monkeys modeling Angelman syndrome
The result raises hopes for an ongoing clinical trial in people — and offers fresh insight into the biology of imprinting and the UBE3A antisense transcript.
Lessons from n-of-1 trials: A conversation with Joseph Gleeson
Some conditions are too rare for conventional drug trials, leading some scientists to test bespoke treatments in single participants. Gleeson discusses the merits — and limitations — of these tiny trials.

Lessons from n-of-1 trials: A conversation with Joseph Gleeson
Some conditions are too rare for conventional drug trials, leading some scientists to test bespoke treatments in single participants. Gleeson discusses the merits — and limitations — of these tiny trials.
What next for Angelman?
A meeting in Texas reckons with the future of treatment, following two setbacks in 2020.

What next for Angelman?
A meeting in Texas reckons with the future of treatment, following two setbacks in 2020.
Angelman therapy appears safer in restarted trial
Interim results from the previously paused trial suggest that doses of the experimental gene therapy drug GTX-102 are well tolerated in children with the autism-linked condition.

Angelman therapy appears safer in restarted trial
Interim results from the previously paused trial suggest that doses of the experimental gene therapy drug GTX-102 are well tolerated in children with the autism-linked condition.
Neuron-specific virus overcomes barriers to brain-related gene therapy
A new viral variant can deliver genes exclusively to the brain, overcoming a key hurdle in treating neurological conditions using gene therapy.
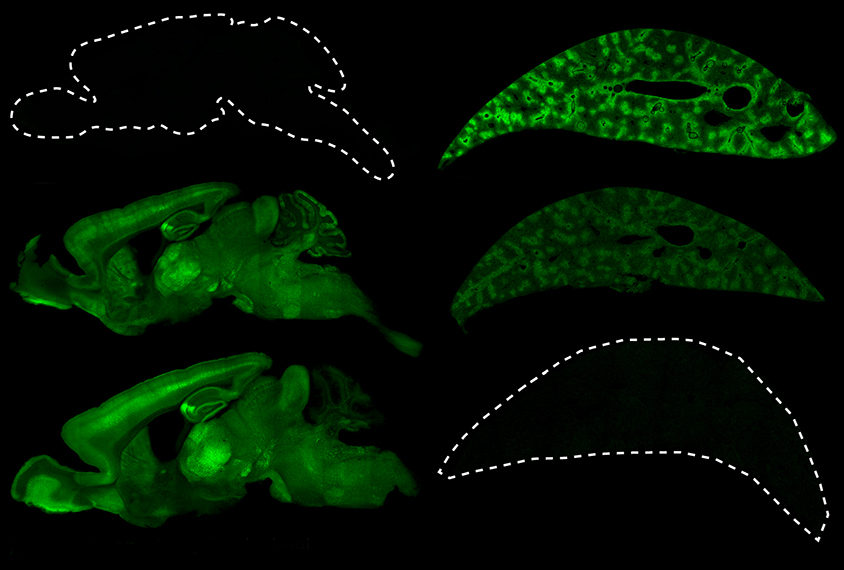
Neuron-specific virus overcomes barriers to brain-related gene therapy
A new viral variant can deliver genes exclusively to the brain, overcoming a key hurdle in treating neurological conditions using gene therapy.
Alternative gene-therapy approaches take aim at Rett syndrome
Methods that selectively increase levels of the Rett protein make for safer and more effective treatment strategies, some researchers say.

Alternative gene-therapy approaches take aim at Rett syndrome
Methods that selectively increase levels of the Rett protein make for safer and more effective treatment strategies, some researchers say.
New gene therapy methods deliver promise
Two unpublished studies detail improved techniques for delivering gene therapies to the brain.
New gene therapy methods deliver promise
Two unpublished studies detail improved techniques for delivering gene therapies to the brain.
A quest for Quincy: Gene therapies come of age for some forms of autism
A gene therapy for Angelman syndrome stands at the forefront of efforts to treat autism-linked conditions that stem from single genes.

A quest for Quincy: Gene therapies come of age for some forms of autism
A gene therapy for Angelman syndrome stands at the forefront of efforts to treat autism-linked conditions that stem from single genes.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.

Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.