Learning
Recent articles
Infant visual system categorizes common objects by 2 months of age
Brain activity patterns in the ventral visual cortex appear to distinguish images across 12 categories, including birds and trees, longitudinal functional MRI scans suggest.
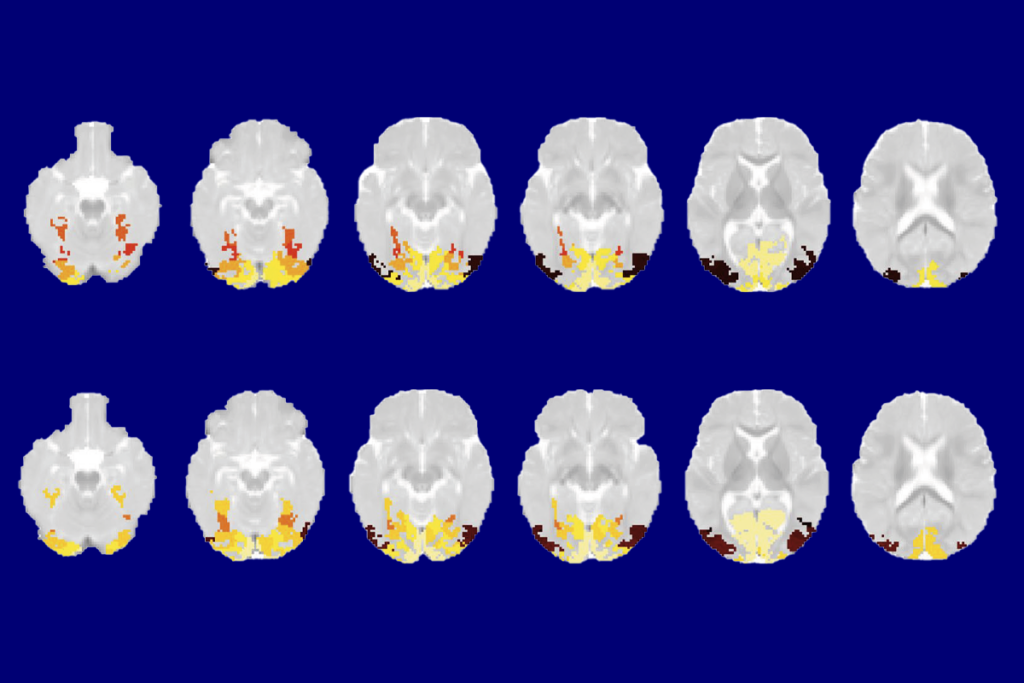
Infant visual system categorizes common objects by 2 months of age
Brain activity patterns in the ventral visual cortex appear to distinguish images across 12 categories, including birds and trees, longitudinal functional MRI scans suggest.
To persist, memories surf molecular waves from thalamus to cortex
During the later stages of learning, the mouse brain progressively activates transcriptional regulators that drive memory consolidation.

To persist, memories surf molecular waves from thalamus to cortex
During the later stages of learning, the mouse brain progressively activates transcriptional regulators that drive memory consolidation.
Sex hormone boosts female rats’ sensitivity to unexpected rewards
During the high-estradiol stages of their estrus cycle, female rats learn faster than they do during other stages—and than male rats overall—thanks to a boost in their dopaminergic response to reward, a new study suggests.

Sex hormone boosts female rats’ sensitivity to unexpected rewards
During the high-estradiol stages of their estrus cycle, female rats learn faster than they do during other stages—and than male rats overall—thanks to a boost in their dopaminergic response to reward, a new study suggests.
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
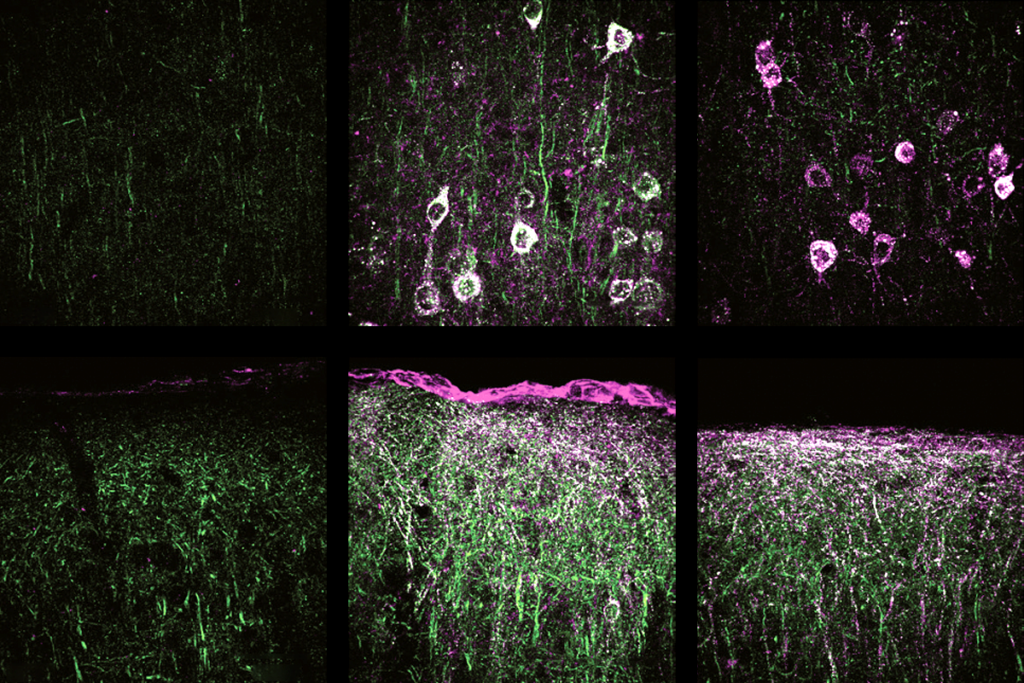
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Top neuroscience prize winners in 2025
The awards recognize lifetime achievements and new discoveries.

Top neuroscience prize winners in 2025
The awards recognize lifetime achievements and new discoveries.
‘What Is Intelligence?’: An excerpt
In his new book, published today, Blaise Agüera y Arcas examines the fundamental aspects of intelligence in biological and artificial systems. In this excerpt from Chapter 4, he examines temporal difference, a reinforcement learning algorithm.

‘What Is Intelligence?’: An excerpt
In his new book, published today, Blaise Agüera y Arcas examines the fundamental aspects of intelligence in biological and artificial systems. In this excerpt from Chapter 4, he examines temporal difference, a reinforcement learning algorithm.
How to build a truly global computational neuroscience community
Computational sciences offer an opportunity to increase global access to, and participation in, neuroscience. Neuromatch’s inclusive, scalable model for community building shows how to realize this promise.
How to build a truly global computational neuroscience community
Computational sciences offer an opportunity to increase global access to, and participation in, neuroscience. Neuromatch’s inclusive, scalable model for community building shows how to realize this promise.
Spatial learning circuitry fluctuates in step with estrous cycle in mice
Cyclic shifts in estradiol levels coincide with changes in dendritic spine density and the activity of place cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a new study shows.
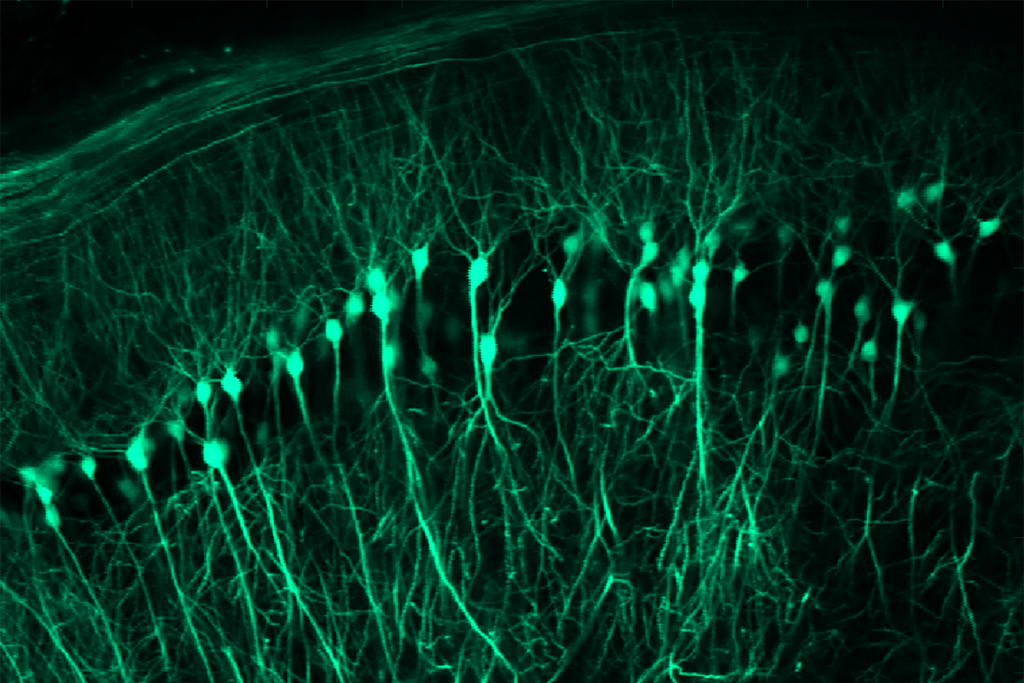
Spatial learning circuitry fluctuates in step with estrous cycle in mice
Cyclic shifts in estradiol levels coincide with changes in dendritic spine density and the activity of place cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a new study shows.
Many students want to learn to use artificial intelligence responsibly. But their professors are struggling to meet that need.
Effectively teaching students how to employ AI in their writing assignments requires clear guidelines—and detailed, case-specific examples.

Many students want to learn to use artificial intelligence responsibly. But their professors are struggling to meet that need.
Effectively teaching students how to employ AI in their writing assignments requires clear guidelines—and detailed, case-specific examples.
Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.

Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
In-vivo base editing in a mouse model of autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 23 February.
In-vivo base editing in a mouse model of autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 23 February.
How insights from network theory can boost interdisciplinary efforts
Communication on one interdisciplinary research team improved after the researchers turned an analysis technique used to study the brain on themselves and identified the roles people played in lab meetings.
How insights from network theory can boost interdisciplinary efforts
Communication on one interdisciplinary research team improved after the researchers turned an analysis technique used to study the brain on themselves and identified the roles people played in lab meetings.