Modeling
Recent articles
How to collaborate with AI
To make the best use of LLMs in research, turn your scientific question into a set of concrete, checkable proposals, wire up an automatic scoring loop, and let the AI iterate.

How to collaborate with AI
To make the best use of LLMs in research, turn your scientific question into a set of concrete, checkable proposals, wire up an automatic scoring loop, and let the AI iterate.
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
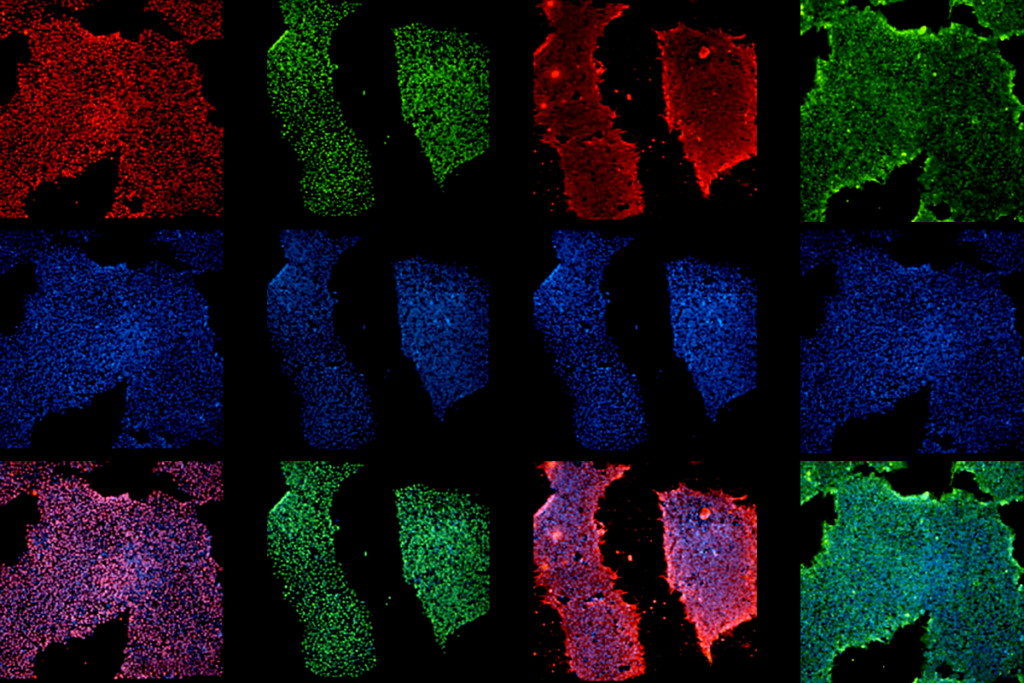
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
The 1,000 neuron challenge
A competition to design small, efficient neural models might provide new insight into real brains—and perhaps unite disparate modeling efforts.

The 1,000 neuron challenge
A competition to design small, efficient neural models might provide new insight into real brains—and perhaps unite disparate modeling efforts.
The Transmitter’s favorite essays of 2025
Throughout a tumultuous year in science, researchers opined on policy changes and funding uncertainty, as well as scientific trends and the impact of artificial-intelligence tools on the field.

The Transmitter’s favorite essays of 2025
Throughout a tumultuous year in science, researchers opined on policy changes and funding uncertainty, as well as scientific trends and the impact of artificial-intelligence tools on the field.
What is the future of organoid and assembloid regulation?
Four experts weigh in on how to establish ethical guardrails for research on the 3D neuron clusters as these models become ever more complex.
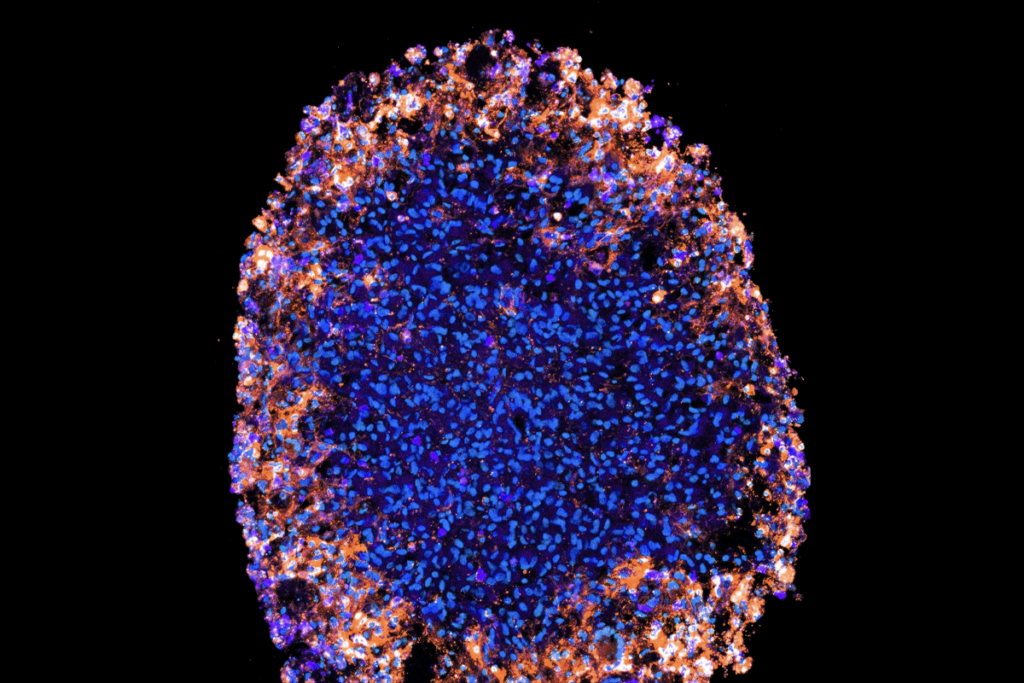
What is the future of organoid and assembloid regulation?
Four experts weigh in on how to establish ethical guardrails for research on the 3D neuron clusters as these models become ever more complex.
Tatiana Engel explains how to connect high-dimensional neural circuitry with low-dimensional cognitive functions
Neuroscientists have long sought to understand the relationship between structure and function in the vast connectivity and activity patterns in the brain. Engel discusses her modeling approach to discovering the hidden patterns that connect the two.
Tatiana Engel explains how to connect high-dimensional neural circuitry with low-dimensional cognitive functions
Neuroscientists have long sought to understand the relationship between structure and function in the vast connectivity and activity patterns in the brain. Engel discusses her modeling approach to discovering the hidden patterns that connect the two.
Whole-brain, bottom-up neuroscience: The time for it is now
Applying new tools to entire brains, starting with C. elegans, offers the opportunity to uncover how molecules work together to generate neural physiology and how neurons work together to generate behavior.
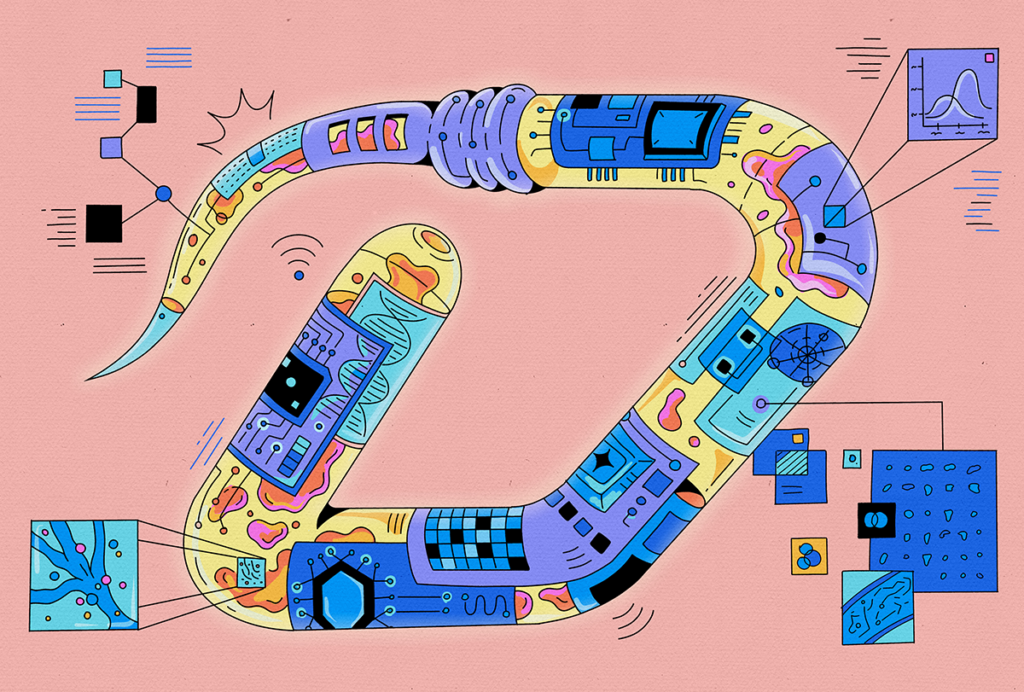
Whole-brain, bottom-up neuroscience: The time for it is now
Applying new tools to entire brains, starting with C. elegans, offers the opportunity to uncover how molecules work together to generate neural physiology and how neurons work together to generate behavior.
The visual system’s lingering mystery: Connecting neural activity and perception
Figuring out how the brain uses information from visual neurons may require new tools. I asked 10 neuroscientists what experimental and conceptual methods they think we’re missing.

The visual system’s lingering mystery: Connecting neural activity and perception
Figuring out how the brain uses information from visual neurons may require new tools. I asked 10 neuroscientists what experimental and conceptual methods they think we’re missing.
Meet the Autism Data Science Initiative grantees
The awarded projects plan to study gene-and-environment interactions in people, stem cells and organoids, as well as predictors of positive life outcomes in autistic youth and adults.

Meet the Autism Data Science Initiative grantees
The awarded projects plan to study gene-and-environment interactions in people, stem cells and organoids, as well as predictors of positive life outcomes in autistic youth and adults.
Worms help untangle brain structure/function mystery
The synaptic connectome of most animals bears little resemblance to functional brain maps, but it can still predict neuronal activity, according to two preprints that tackle the puzzle in C. elegans.

Worms help untangle brain structure/function mystery
The synaptic connectome of most animals bears little resemblance to functional brain maps, but it can still predict neuronal activity, according to two preprints that tackle the puzzle in C. elegans.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
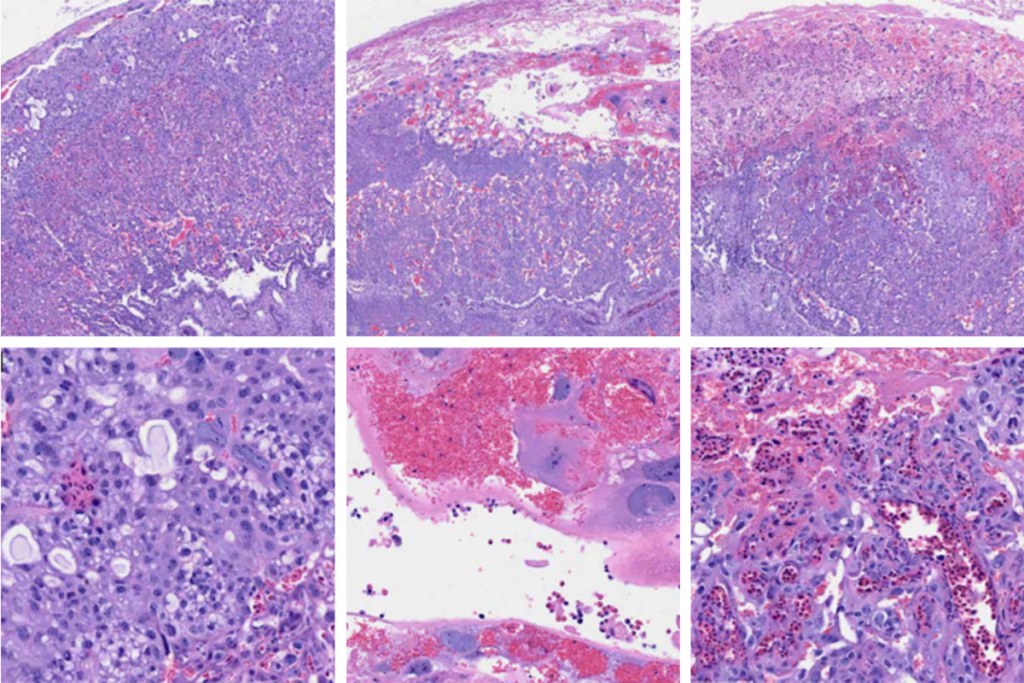
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.