Theories of autism
Recent articles
The signaling imbalance theory of autism, explained
The signaling imbalance theory holds that the brains of autistic people are hyper-excitable because of either excess neuronal activity or weak brakes on that activity.

The signaling imbalance theory of autism, explained
The signaling imbalance theory holds that the brains of autistic people are hyper-excitable because of either excess neuronal activity or weak brakes on that activity.
The female protective effect, explained
One of the leading theories of autism posits that girls and women are biologically protected from the condition.
The female protective effect, explained
One of the leading theories of autism posits that girls and women are biologically protected from the condition.
The extreme male brain, explained
The ‘extreme male brain’ theory suggests that autism is an exaggeration of systematic sex differences in ways of thinking.
The extreme male brain, explained
The ‘extreme male brain’ theory suggests that autism is an exaggeration of systematic sex differences in ways of thinking.
Serotonin’s link to autism, explained
Serotonin, the brain chemical best known for its link to depression, may also be involved in autism.

Serotonin’s link to autism, explained
Serotonin, the brain chemical best known for its link to depression, may also be involved in autism.
The multiple hits theory of autism, explained
Researchers are studying how a combination of genetic ‘hits’ may contribute to autism’s diversity.

The multiple hits theory of autism, explained
Researchers are studying how a combination of genetic ‘hits’ may contribute to autism’s diversity.
The predictive coding theory of autism, explained
In autism, a person's brain may not form accurate predictions of imminent experiences, or even if it does, sensory input may override those predictions.

The predictive coding theory of autism, explained
In autism, a person's brain may not form accurate predictions of imminent experiences, or even if it does, sensory input may override those predictions.
The connectivity theory of autism, explained
A growing body of evidence suggests that autism involves atypical communication between brain regions, but how and where in the brain this plays out is unclear.
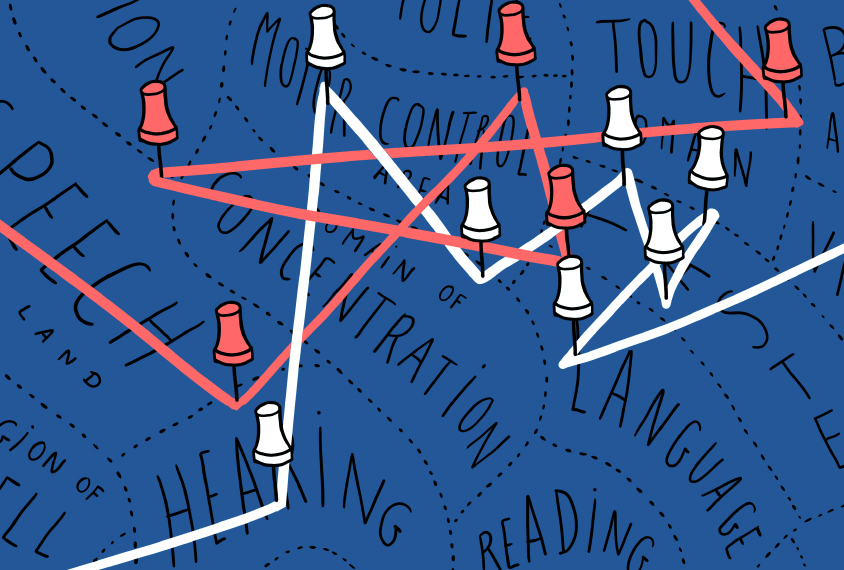
The connectivity theory of autism, explained
A growing body of evidence suggests that autism involves atypical communication between brain regions, but how and where in the brain this plays out is unclear.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.