Theory of mind
Recent articles
The case for redefining ‘theory of mind’: Q&A with François Quesque
In a new commentary, Quesque and 44 experts in neuroscience and psychology propose a standardized lexicon for research on the attribution of mental states.
The case for redefining ‘theory of mind’: Q&A with François Quesque
In a new commentary, Quesque and 44 experts in neuroscience and psychology propose a standardized lexicon for research on the attribution of mental states.
It’s past time to stop using the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test
The widely used measure of “theory of mind” needs to be re-examined, along with the long-standing claim that autism is linked to a lack of this ability.
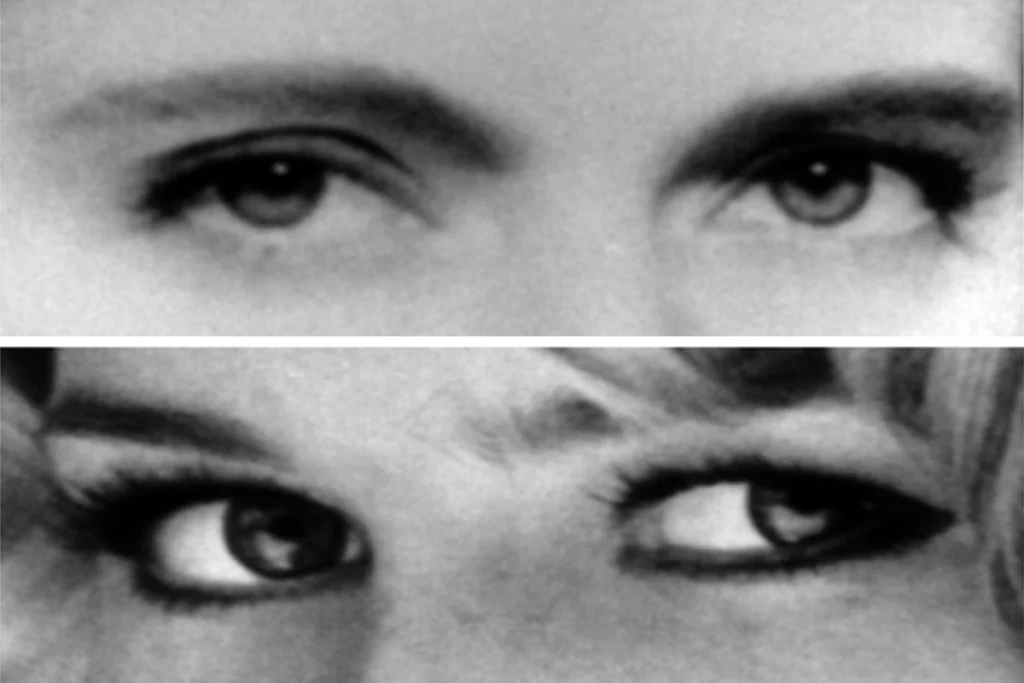
It’s past time to stop using the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test
The widely used measure of “theory of mind” needs to be re-examined, along with the long-standing claim that autism is linked to a lack of this ability.
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
People’s perceptions of ‘social’ animations don’t always square with researchers’ labels
The finding calls into question differences between autistic and non-autistic people on a decades-old theory-of-mind test involving interacting geometric shapes.
People’s perceptions of ‘social’ animations don’t always square with researchers’ labels
The finding calls into question differences between autistic and non-autistic people on a decades-old theory-of-mind test involving interacting geometric shapes.
Noah Sasson: Connecting with the autistic community
Intentional interactions with autistic people led Sasson to refocus his research.

Noah Sasson: Connecting with the autistic community
Intentional interactions with autistic people led Sasson to refocus his research.
Null and Noteworthy: Mind reading, specialist shortage, sleep problems source
This month, a commonly used emotion-recognition test doesn’t perform as expected — nor does a survey of past efforts to train autism specialists or a hunt for the sources of the sleep problems that often accompany the condition.
Null and Noteworthy: Mind reading, specialist shortage, sleep problems source
This month, a commonly used emotion-recognition test doesn’t perform as expected — nor does a survey of past efforts to train autism specialists or a hunt for the sources of the sleep problems that often accompany the condition.
X chromosome exerts extra influence on brain development
The X chromosome holds stronger-than-expected genetic sway over the structure of several brain regions. The genes that may underlie this oversized influence have ties to autism.
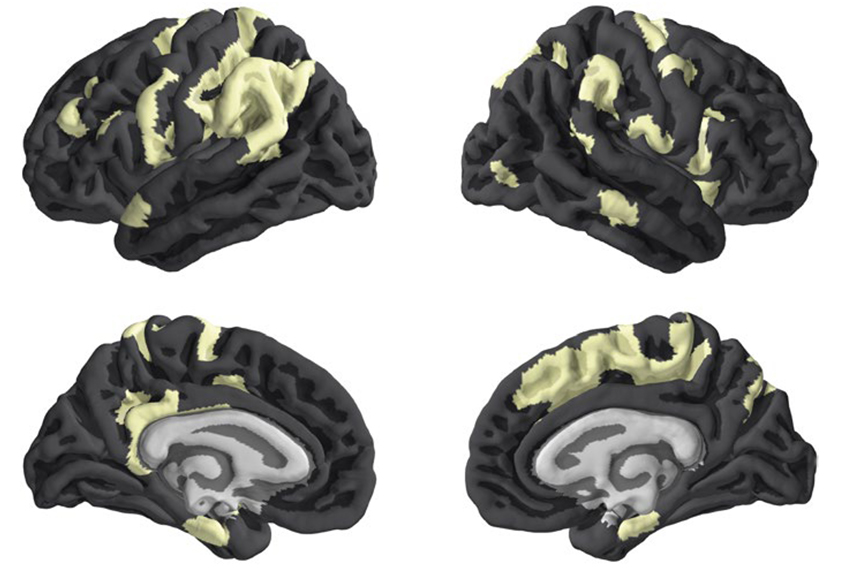
X chromosome exerts extra influence on brain development
The X chromosome holds stronger-than-expected genetic sway over the structure of several brain regions. The genes that may underlie this oversized influence have ties to autism.
Getting eight arms around autism
Octopuses can solve some of the same problems as people but do so in unusual ways.

Getting eight arms around autism
Octopuses can solve some of the same problems as people but do so in unusual ways.
Double empathy, explained
The double empathy theory challenges the idea that social difficulties are specific to autism and suggests that problems arise from a mismatch in perspective between autistic and non-autistic people.
Double empathy, explained
The double empathy theory challenges the idea that social difficulties are specific to autism and suggests that problems arise from a mismatch in perspective between autistic and non-autistic people.
Single neurons may power key ‘theory of mind’ skills
A subset of brain cells signal when someone tries to infer another person’s thoughts, according to a new study.

Single neurons may power key ‘theory of mind’ skills
A subset of brain cells signal when someone tries to infer another person’s thoughts, according to a new study.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.