Touch
Recent articles
Neuro’s ark: Understanding fast foraging with star-nosed moles
“MacArthur genius” Kenneth Catania outlined the physiology behind the moles’ stellar foraging skills two decades ago. Next, he wants to better characterize their food-seeking behavior.

Neuro’s ark: Understanding fast foraging with star-nosed moles
“MacArthur genius” Kenneth Catania outlined the physiology behind the moles’ stellar foraging skills two decades ago. Next, he wants to better characterize their food-seeking behavior.
PIEZO channels are opening the study of mechanosensation in unexpected places
The force-activated ion channels underlie the senses of touch and proprioception. Now scientists are using them as a tool to explore molecular mechanisms at work in internal organs, including the heart, bladder, uterus and kidney.

PIEZO channels are opening the study of mechanosensation in unexpected places
The force-activated ion channels underlie the senses of touch and proprioception. Now scientists are using them as a tool to explore molecular mechanisms at work in internal organs, including the heart, bladder, uterus and kidney.
Noisy brain may underlie some of autism’s sensory features
Random fluctuations in neuronal activity are more variable in a fragile X mouse model than in wildtype mice.
Noisy brain may underlie some of autism’s sensory features
Random fluctuations in neuronal activity are more variable in a fragile X mouse model than in wildtype mice.
Mouse studies cast astrocytes as stars of sensory perception
Data from two separate research teams suggest the cells are key to sensory hypersensitivity in fragile X syndrome.
Mouse studies cast astrocytes as stars of sensory perception
Data from two separate research teams suggest the cells are key to sensory hypersensitivity in fragile X syndrome.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
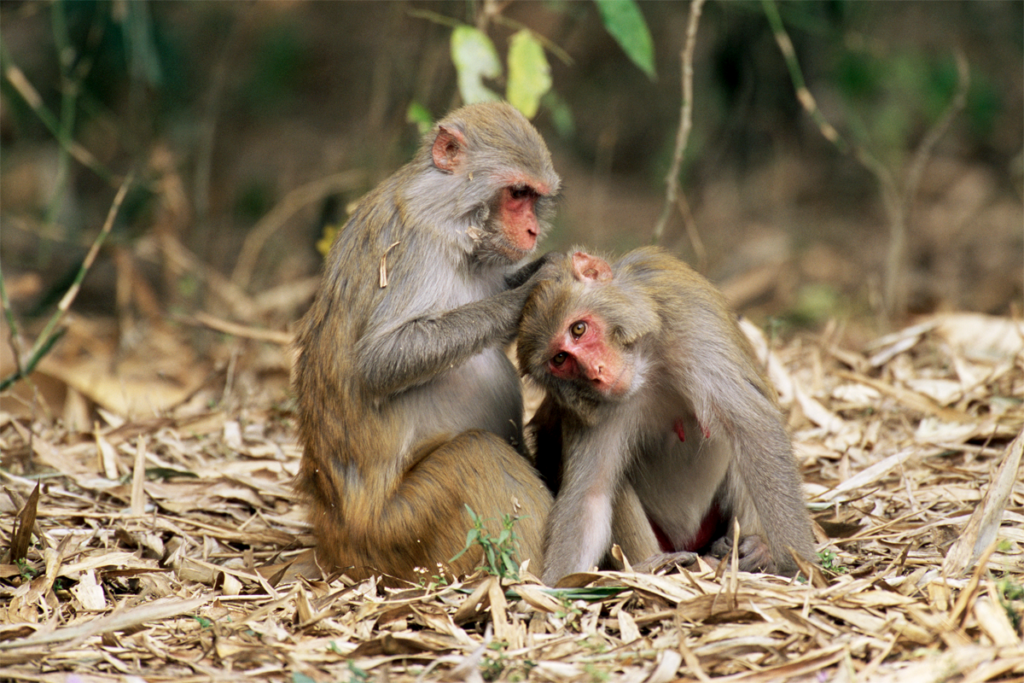

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.