Internal state
Recent articles
Should I stay (and eat) or should I go? How the brain balances hunger with competing drives
Understanding the interplay among rival signals, such as pain, thirst and fear, could provide insights into anxiety and other neuropsychiatric conditions.

Should I stay (and eat) or should I go? How the brain balances hunger with competing drives
Understanding the interplay among rival signals, such as pain, thirst and fear, could provide insights into anxiety and other neuropsychiatric conditions.
Neurons in rat olfactory bulb ‘feel the pulse’
Mechanical receptors can detect intracranial pressure changes caused by blood flow, which enables neurons to synchronize with the heartbeat.
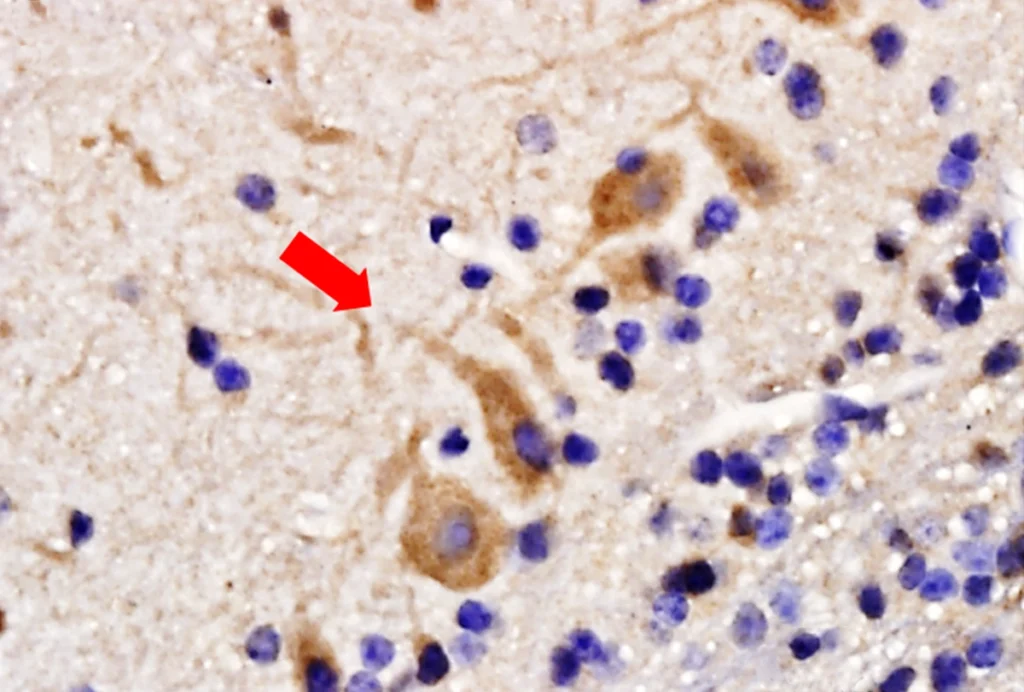
Neurons in rat olfactory bulb ‘feel the pulse’
Mechanical receptors can detect intracranial pressure changes caused by blood flow, which enables neurons to synchronize with the heartbeat.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.
Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.

Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.