Postmortem brains
Recent articles
Exclusive: Recruitment issues jeopardize ambitious plan for human brain atlas
A lack of six new brain donors may stop the project from meeting its goal to pair molecular and cellular data with the functional organization of the cortex.
Exclusive: Recruitment issues jeopardize ambitious plan for human brain atlas
A lack of six new brain donors may stop the project from meeting its goal to pair molecular and cellular data with the functional organization of the cortex.
To make a meaningful contribution to neuroscience, fMRI must break out of its silo
We need to develop research programs that link phenomena across levels, from genes and molecules to cells, circuits, networks and behavior.

To make a meaningful contribution to neuroscience, fMRI must break out of its silo
We need to develop research programs that link phenomena across levels, from genes and molecules to cells, circuits, networks and behavior.
Single-cell genomics technologies and cell atlases have ushered in a new era of human neurobiology
Single-cell approaches are already shedding light on the human brain, identifying cell types that are most vulnerable in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, for example.
Single-cell genomics technologies and cell atlases have ushered in a new era of human neurobiology
Single-cell approaches are already shedding light on the human brain, identifying cell types that are most vulnerable in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, for example.
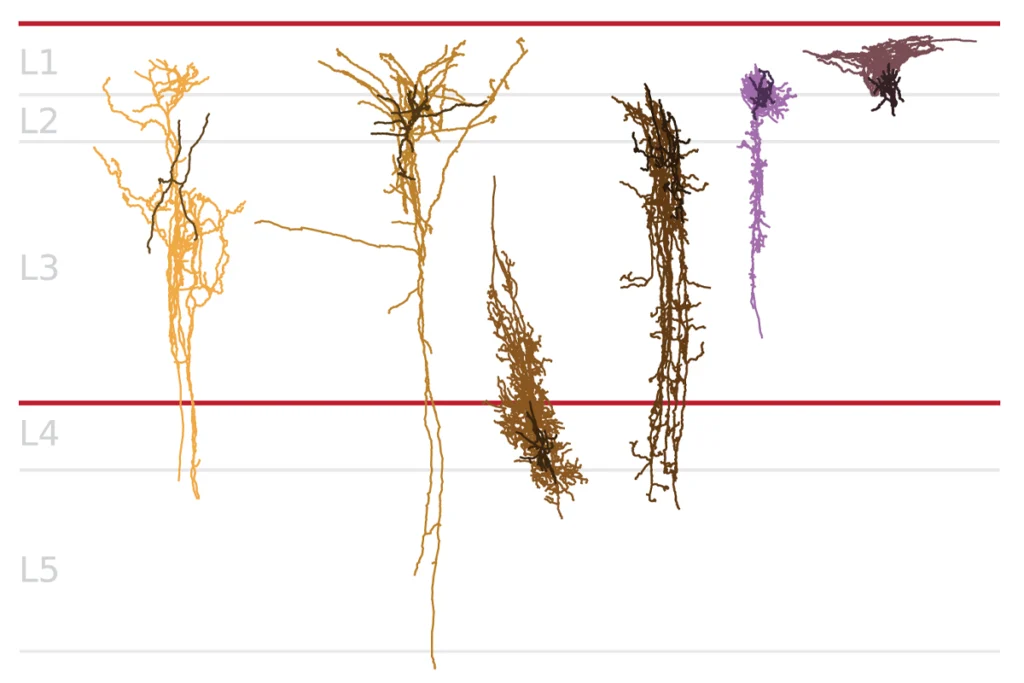
Cell ‘fingerprints’ identify distinct cortical networks
These networks align with different assemblages of cells, a finding that could reveal how cellular diversity influences brain function, according to a new study.
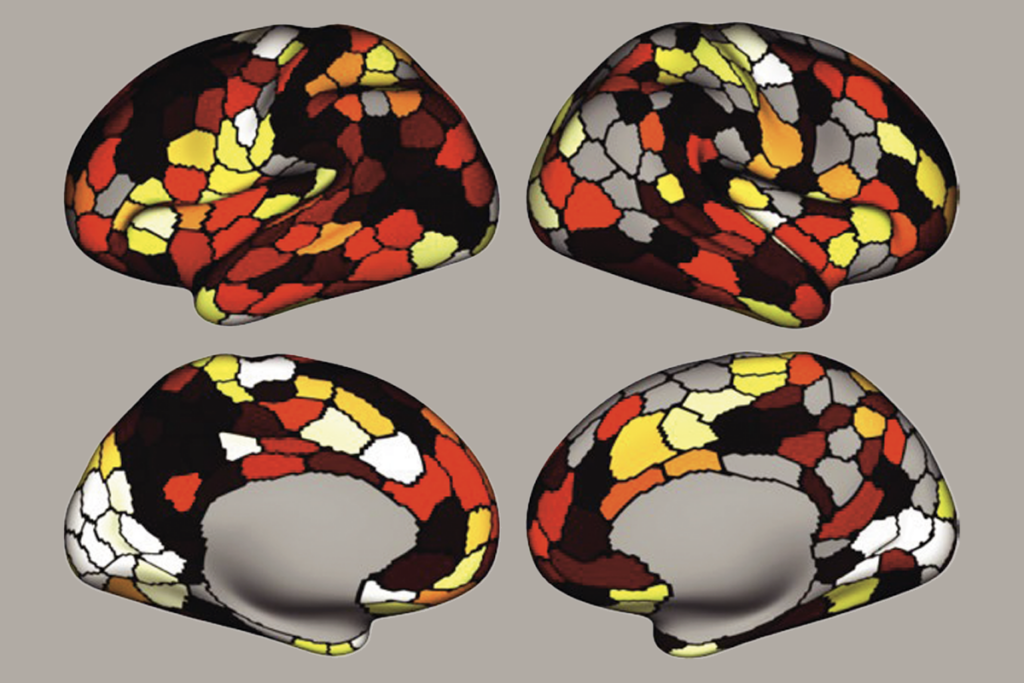
Cell ‘fingerprints’ identify distinct cortical networks
These networks align with different assemblages of cells, a finding that could reveal how cellular diversity influences brain function, according to a new study.
‘Spoonful of plastics in your brain’ paper has duplicated images
The duplications likely do not alter the conclusions, but the paper contains other methodological issues, two independent microplastics researchers say.
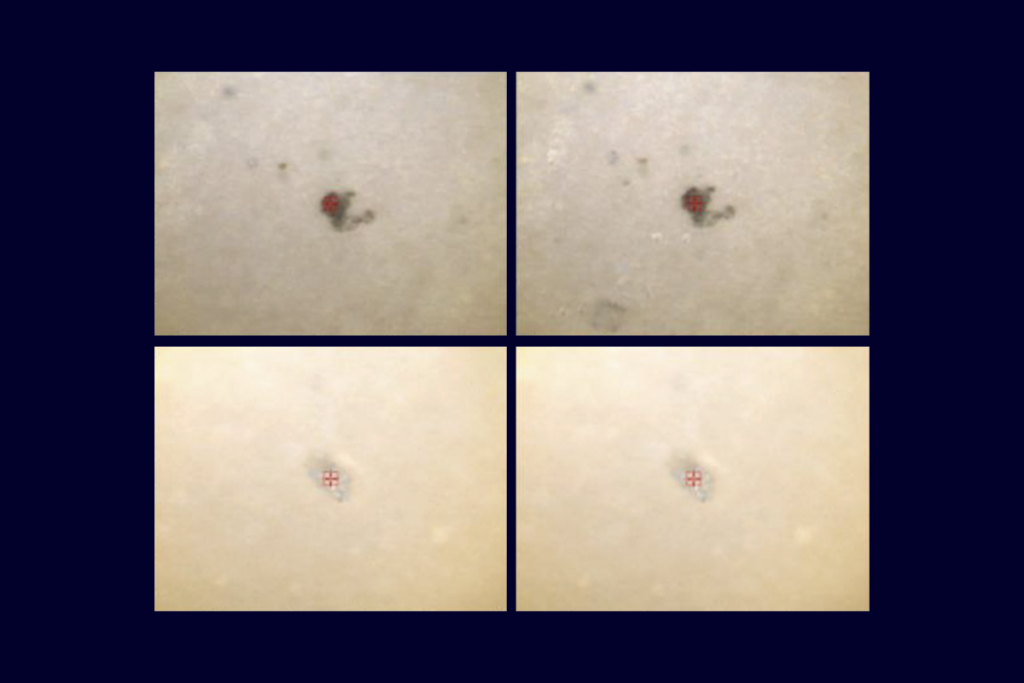
‘Spoonful of plastics in your brain’ paper has duplicated images
The duplications likely do not alter the conclusions, but the paper contains other methodological issues, two independent microplastics researchers say.
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
Giant analysis reveals how autism-linked genes affect brain cell types
Genes that predispose people to autism account for a large portion of the neuronal and glial cell changes seen in those with the condition.
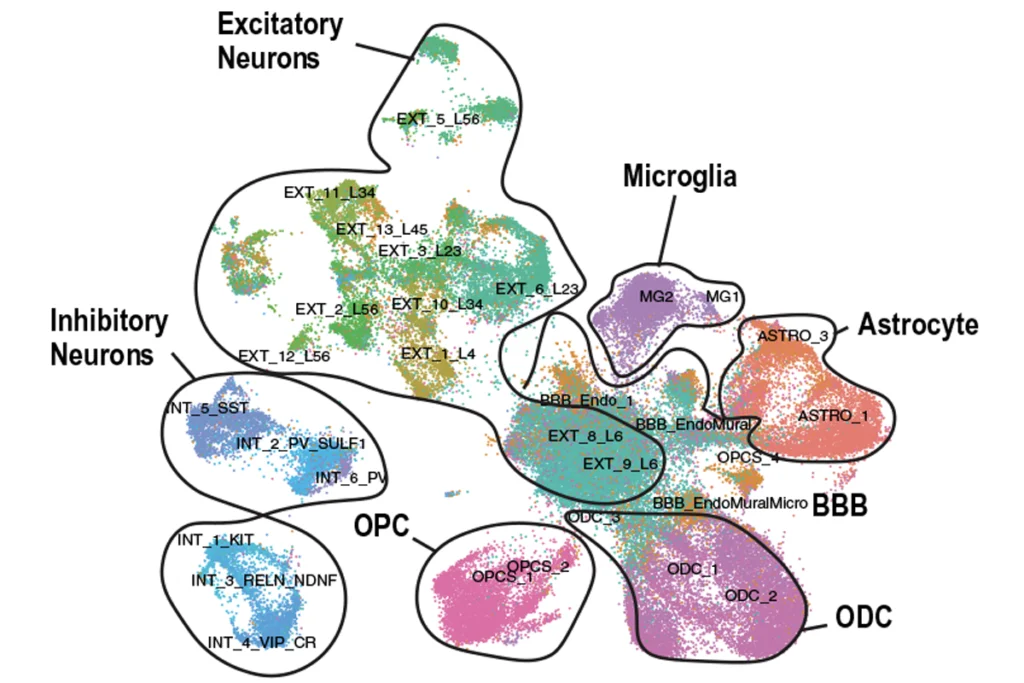
Giant analysis reveals how autism-linked genes affect brain cell types
Genes that predispose people to autism account for a large portion of the neuronal and glial cell changes seen in those with the condition.
‘SNAP’ dance of astrocytes and neurons falls out of step with age, disease
The findings add to growing evidence that astrocytes are star players in cognition.
‘SNAP’ dance of astrocytes and neurons falls out of step with age, disease
The findings add to growing evidence that astrocytes are star players in cognition.
Cortical interneurons derive differently in human brains
Excitatory neurons and some inhibitory neurons in the adult human cortex share parents, challenging the longstanding idea that the two cell types have different origins.
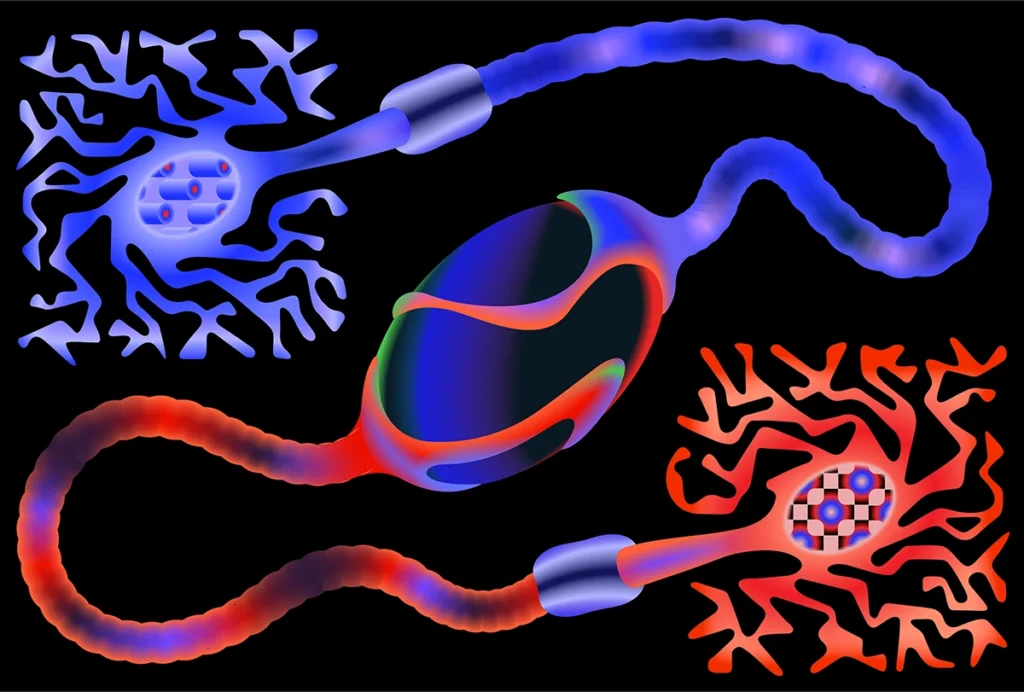
Cortical interneurons derive differently in human brains
Excitatory neurons and some inhibitory neurons in the adult human cortex share parents, challenging the longstanding idea that the two cell types have different origins.
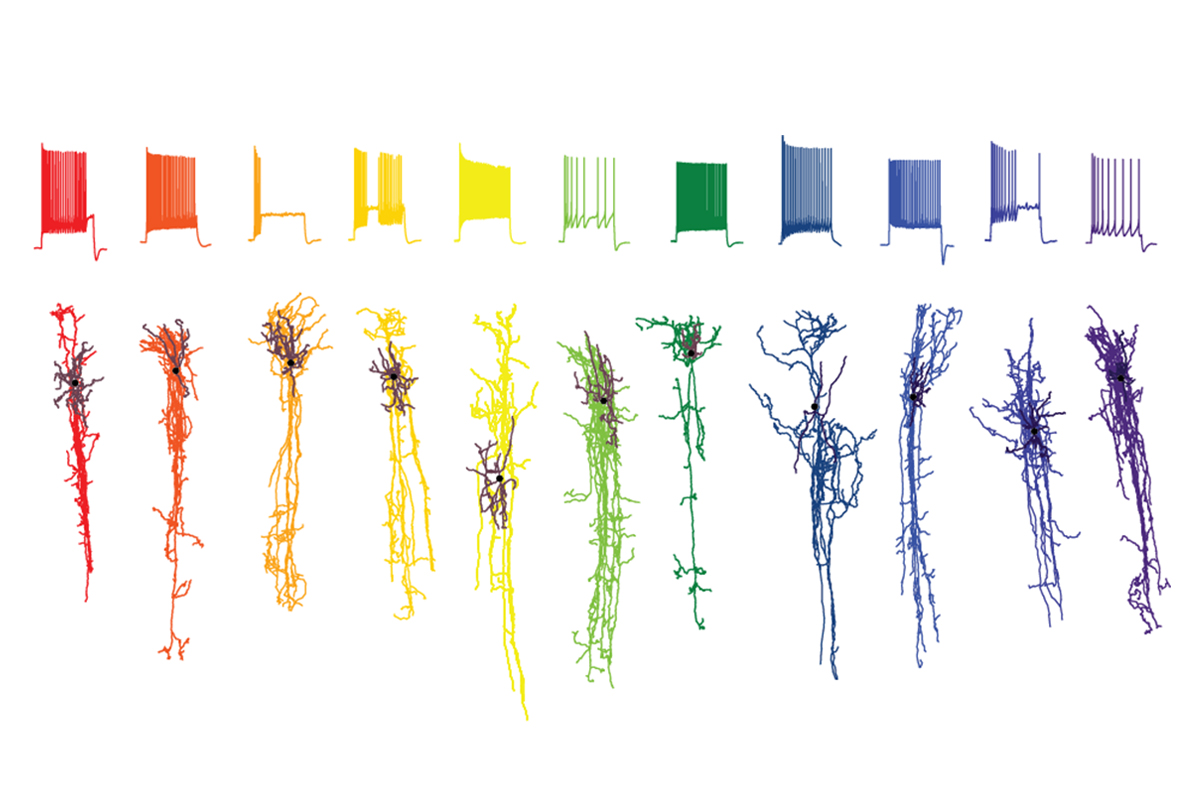
Vast diversity of human brain cell types revealed in trove of new datasets
The collection offers a glimpse into differences in cell composition — across people and brain regions — that may shape neural function.

Vast diversity of human brain cell types revealed in trove of new datasets
The collection offers a glimpse into differences in cell composition — across people and brain regions — that may shape neural function.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
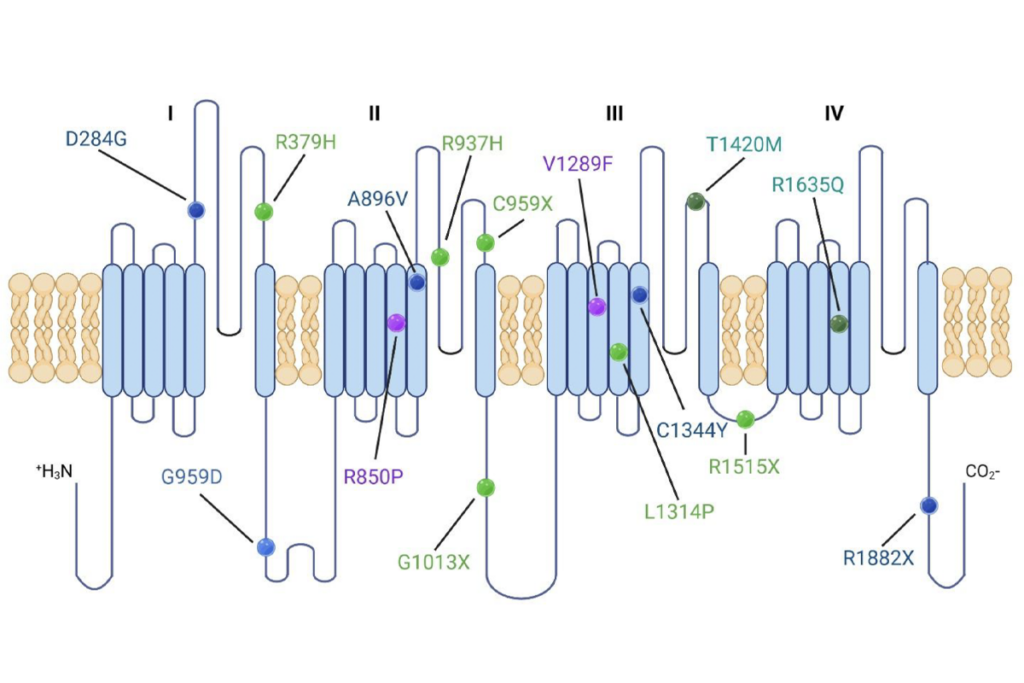
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.