Social reward
Recent articles
Oxytocin prompts prairie voles to oust outsiders, fortifying their friendships
The “love hormone” drives the neurobiology behind platonic bonds in animals usually studied for their romantic attachments.

Oxytocin prompts prairie voles to oust outsiders, fortifying their friendships
The “love hormone” drives the neurobiology behind platonic bonds in animals usually studied for their romantic attachments.
New test taps nose pokes as a proxy for social motivation in mice
Over one hour, a particularly motivated mouse poked its nose 350 times into a hole in the test chamber in the hopes of meeting a playmate.
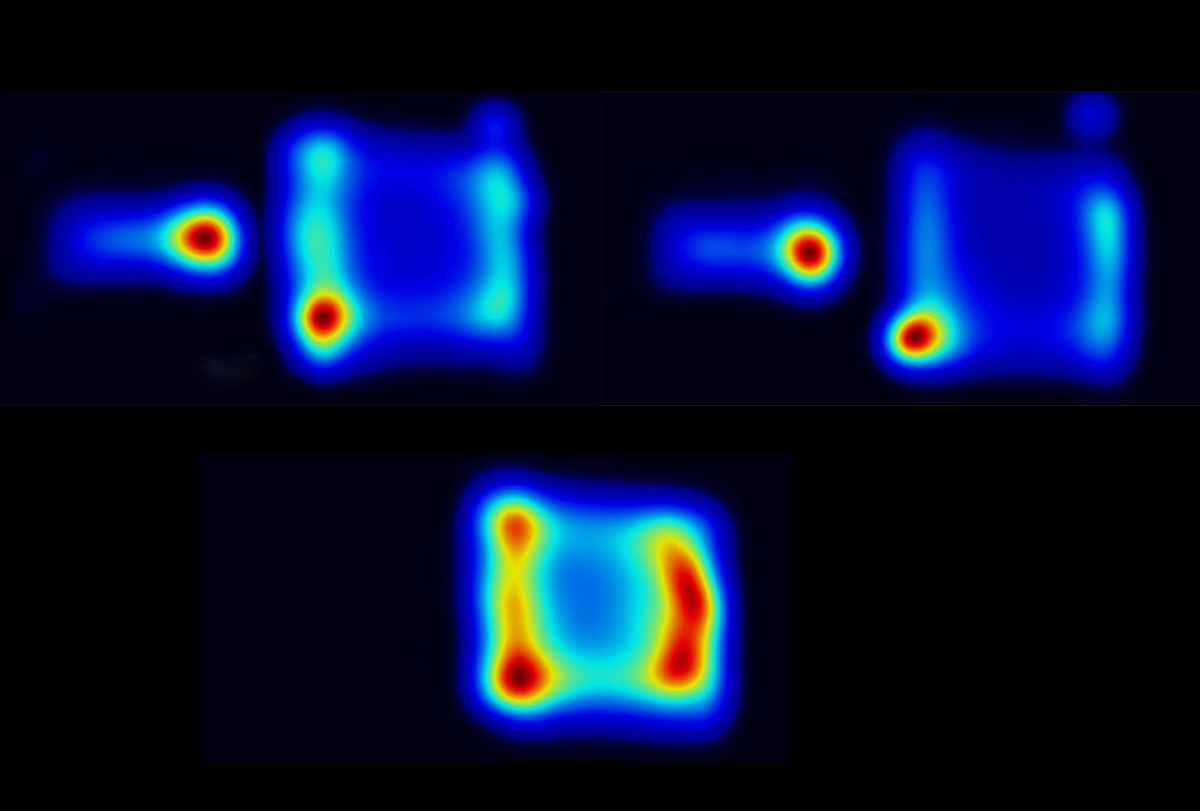
New test taps nose pokes as a proxy for social motivation in mice
Over one hour, a particularly motivated mouse poked its nose 350 times into a hole in the test chamber in the hopes of meeting a playmate.
Psychedelics give mice second chance to learn social rewards
The drugs may reopen a critical window during development in which the brain can more easily adjust its connections.

Psychedelics give mice second chance to learn social rewards
The drugs may reopen a critical window during development in which the brain can more easily adjust its connections.
Getting eight arms around autism
Octopuses can solve some of the same problems as people but do so in unusual ways.

Getting eight arms around autism
Octopuses can solve some of the same problems as people but do so in unusual ways.
Drugs boost serotonin, socialization in multiple autism mouse models
The finding that MDMA and an experimental serotonin agonist increase sociability across six different model mice suggests that disparate autism-linked mutations converge on the same underlying pathways.

Drugs boost serotonin, socialization in multiple autism mouse models
The finding that MDMA and an experimental serotonin agonist increase sociability across six different model mice suggests that disparate autism-linked mutations converge on the same underlying pathways.
The benefits of special interests in autism
Researchers are studying how the intense passions of autistic people shape the brain, improve well-being and enhance learning.

The benefits of special interests in autism
Researchers are studying how the intense passions of autistic people shape the brain, improve well-being and enhance learning.
Brain circuit makes social interactions rewarding, may be altered in autism
Blocking connections between the amygdala and hypothalamus prevents mice from finding social interactions as rewarding as they would otherwise.
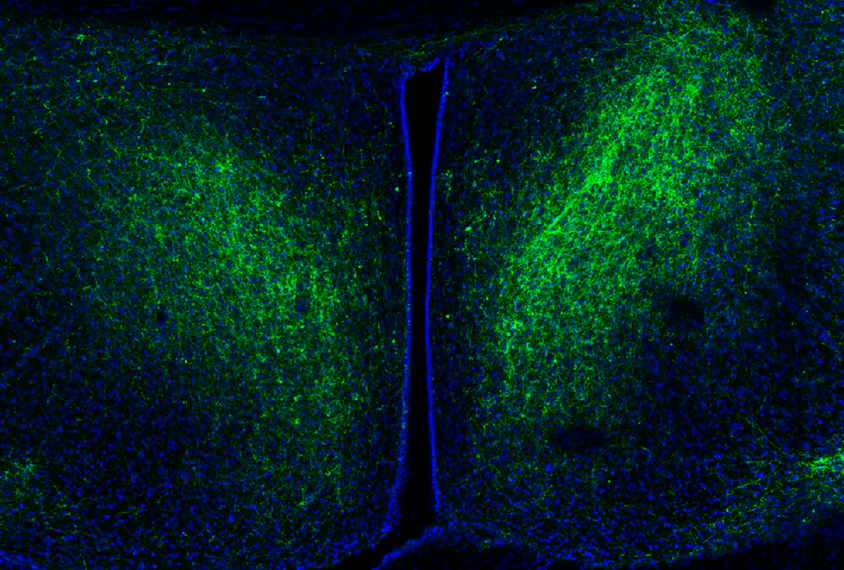
Brain circuit makes social interactions rewarding, may be altered in autism
Blocking connections between the amygdala and hypothalamus prevents mice from finding social interactions as rewarding as they would otherwise.
Dopamine neurons may dampen social behavior in mouse model of autism
Mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene PTEN show a reduced preference for social interaction, possibly due to atypically large, overconnected dopamine neurons. Easing the overconnection may alleviate this trait.
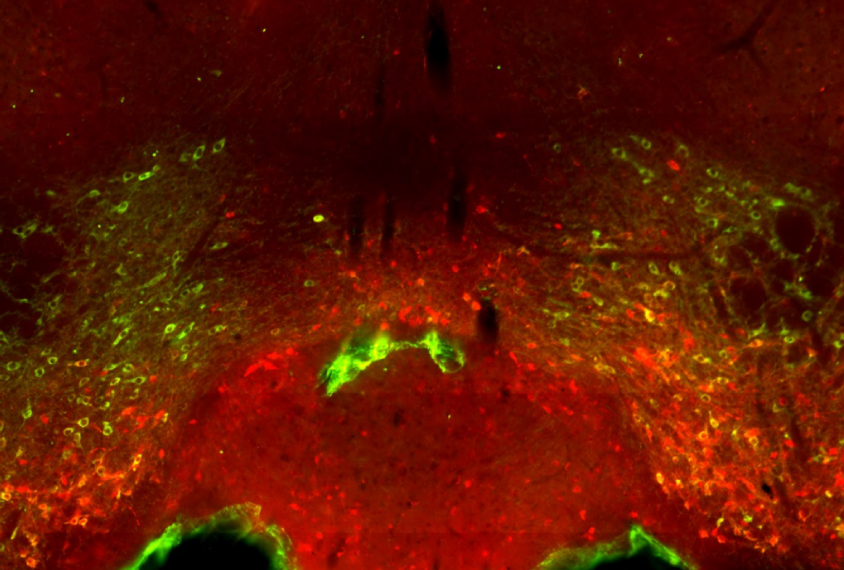
Dopamine neurons may dampen social behavior in mouse model of autism
Mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene PTEN show a reduced preference for social interaction, possibly due to atypically large, overconnected dopamine neurons. Easing the overconnection may alleviate this trait.
Autism-linked gene exerts varied effects on oxytocin circuits in mice
Two types of neurons process social information, a new mouse study suggests, but only one is disrupted in mice missing the autism-linked gene FMR1.
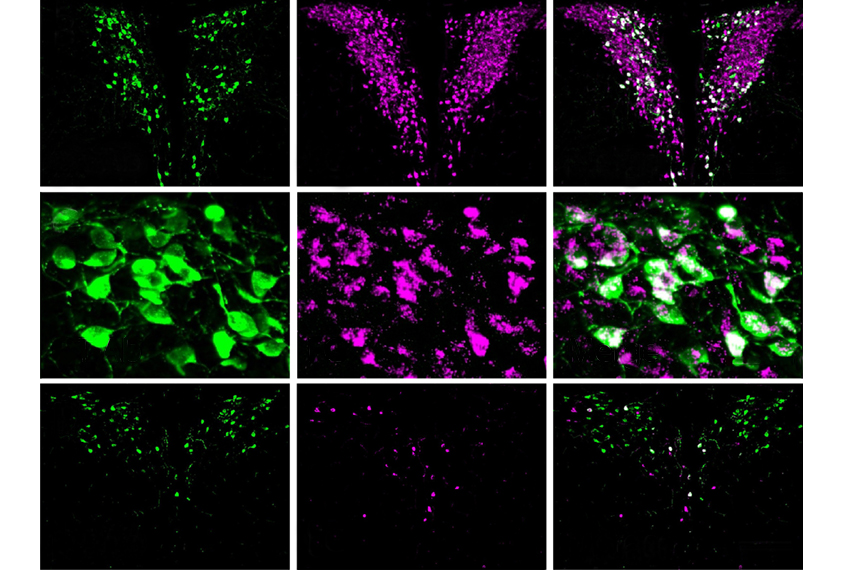
Autism-linked gene exerts varied effects on oxytocin circuits in mice
Two types of neurons process social information, a new mouse study suggests, but only one is disrupted in mice missing the autism-linked gene FMR1.
Social motivation predicts language skills in autistic children
The more children with autism tune in to and communicate with others as toddlers, the stronger their conversation skills are later in childhood.

Social motivation predicts language skills in autistic children
The more children with autism tune in to and communicate with others as toddlers, the stronger their conversation skills are later in childhood.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.
Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.
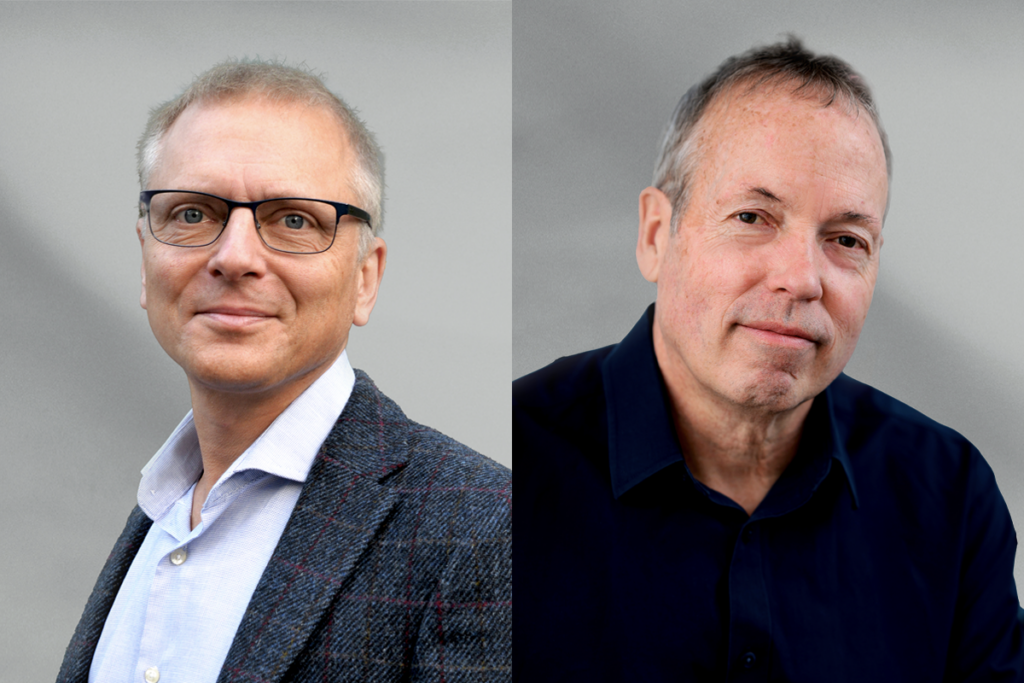

Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.