De novo mutations
Recent articles
PTEN problems underscore autism connection to excess brain fluid
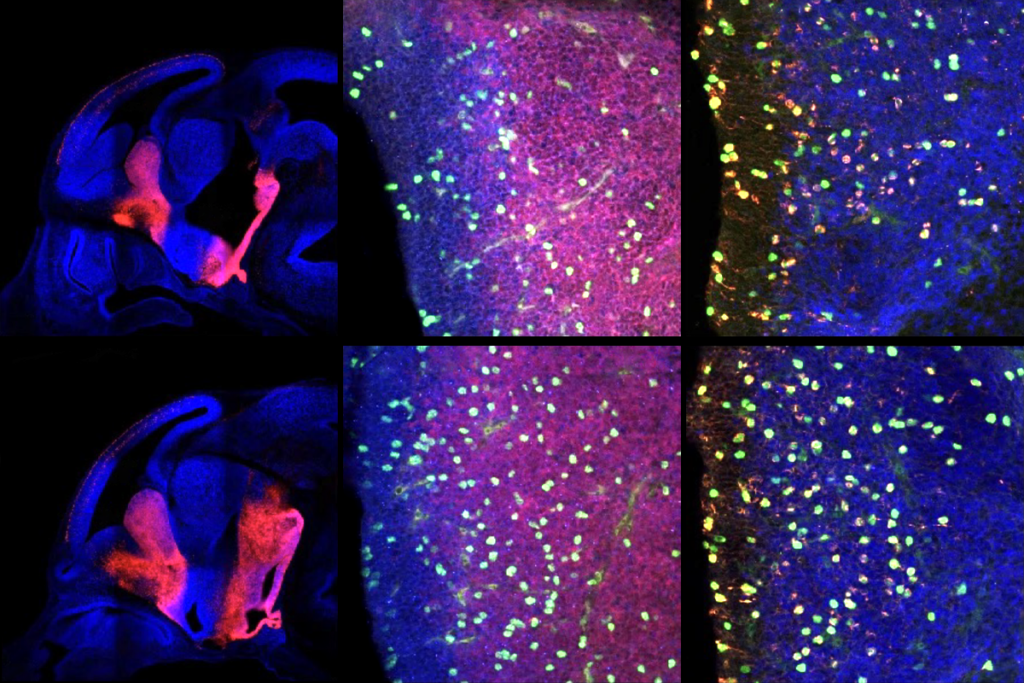
Damaging variants in the autism-linked gene cause congenital hydrocephalus—a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain—by turbocharging a downstream signaling pathway that promotes the growth of cells, according to a new study.
PTEN problems underscore autism connection to excess brain fluid
Damaging variants in the autism-linked gene cause congenital hydrocephalus—a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain—by turbocharging a downstream signaling pathway that promotes the growth of cells, according to a new study.
Genome structure could be key factor in some forms of autism
Variants in DNA stretches that do not code for proteins may alter the genome’s 3D architecture, influencing the expression of distant genes linked to autism.

Genome structure could be key factor in some forms of autism
Variants in DNA stretches that do not code for proteins may alter the genome’s 3D architecture, influencing the expression of distant genes linked to autism.
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Some who lack autism diagnosis carry variants tied to the condition
The variants are associated with slight differences in measures of intelligence, income and employment, but the relationship may not be causal.

Some who lack autism diagnosis carry variants tied to the condition
The variants are associated with slight differences in measures of intelligence, income and employment, but the relationship may not be causal.
Partner selection may amplify rare variants in children
Nonrandom mating — the propensity for people to partner with others who share their traits — can increase the likelihood of autism or other conditions across generations.

Partner selection may amplify rare variants in children
Nonrandom mating — the propensity for people to partner with others who share their traits — can increase the likelihood of autism or other conditions across generations.
Cortical differences in autism vary by sex
Compared with their non-autistic peers, young autistic girls have a thicker cortex that thins more quickly with age.

Cortical differences in autism vary by sex
Compared with their non-autistic peers, young autistic girls have a thicker cortex that thins more quickly with age.
The future of autism therapies: A conversation with Lilia Iakoucheva and Derek Hong
If a therapy for autism’s core traits makes it to market, it will likely take one of three forms, the researchers say.
The future of autism therapies: A conversation with Lilia Iakoucheva and Derek Hong
If a therapy for autism’s core traits makes it to market, it will likely take one of three forms, the researchers say.
Whole-genome trove ties new genes, variants to autism
A massive update to the MSSNG dataset gives qualified researchers ready access to explore autism’s genetic architecture on a cloud-based platform.
Whole-genome trove ties new genes, variants to autism
A massive update to the MSSNG dataset gives qualified researchers ready access to explore autism’s genetic architecture on a cloud-based platform.
Common and rare autism-linked variants share functional effects
Within the 16p region of the genome, the two types of variants similarly decrease neuronal gene expression — an effect that may reflect their spatial relationship.
Common and rare autism-linked variants share functional effects
Within the 16p region of the genome, the two types of variants similarly decrease neuronal gene expression — an effect that may reflect their spatial relationship.
Tying PPFIA3 to autism: A quick take at SfN with Tuan Chao and Maimuna Paul
Work in fruit flies has helped Paul decode a neurodevelopmental syndrome in children caused by rare de novo variants in the gene PPFIA3.
Tying PPFIA3 to autism: A quick take at SfN with Tuan Chao and Maimuna Paul
Work in fruit flies has helped Paul decode a neurodevelopmental syndrome in children caused by rare de novo variants in the gene PPFIA3.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.