Hearing
Recent articles
Neuroscience’s leaders, legacies and rising stars of 2025
Here are seven stories from the past year about some of the field’s most engaging figures.

Neuroscience’s leaders, legacies and rising stars of 2025
Here are seven stories from the past year about some of the field’s most engaging figures.
Remembering A. James Hudspeth, hair cell explorer
Hudspeth, who died 16 August at age 79, devoted his 50-year career to untangling how the ear converts sound into electrical signals.

Remembering A. James Hudspeth, hair cell explorer
Hudspeth, who died 16 August at age 79, devoted his 50-year career to untangling how the ear converts sound into electrical signals.
Touch sensors detect subtle environmental vibrations, send information to auditory midbrain
Pacinian corpuscles sense high-frequency vibrations from meters away and send the information to a different circuit than other touch signals, according to a pair of new studies.
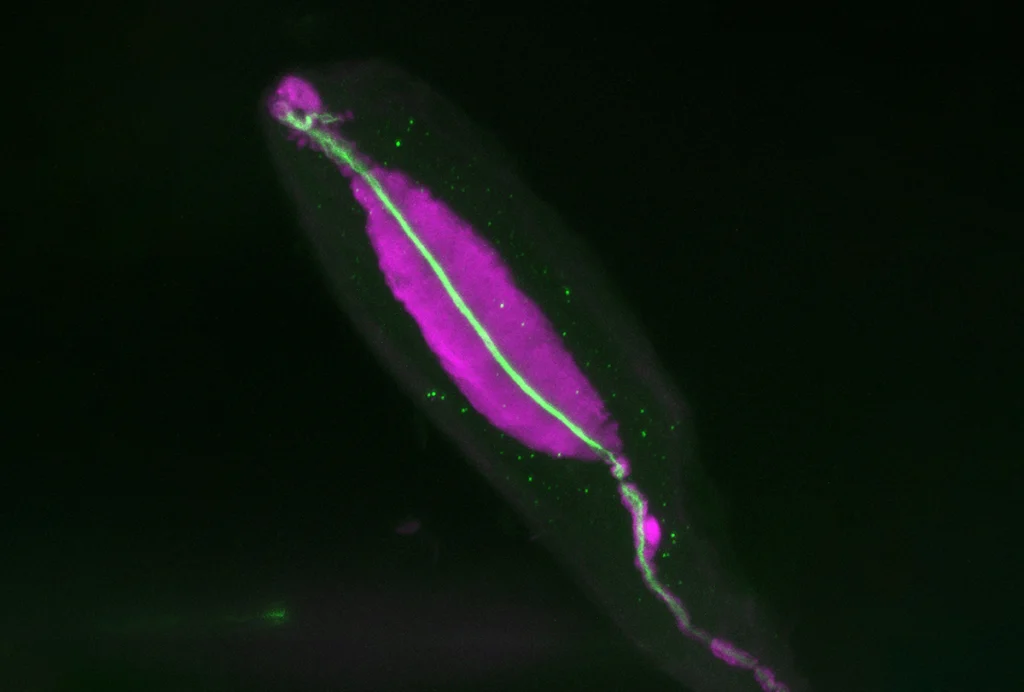
Touch sensors detect subtle environmental vibrations, send information to auditory midbrain
Pacinian corpuscles sense high-frequency vibrations from meters away and send the information to a different circuit than other touch signals, according to a pair of new studies.
New technique details brainstem’s response to sounds
By revealing differences between autistic and non-autistic children, it could help identify autism in babies.

New technique details brainstem’s response to sounds
By revealing differences between autistic and non-autistic children, it could help identify autism in babies.
Mouse studies cast astrocytes as stars of sensory perception
Data from two separate research teams suggest the cells are key to sensory hypersensitivity in fragile X syndrome.
Mouse studies cast astrocytes as stars of sensory perception
Data from two separate research teams suggest the cells are key to sensory hypersensitivity in fragile X syndrome.
Auditory cortex may develop early in autism
A well-studied brain response to sound appears earlier than usual in young children with autism.
Auditory cortex may develop early in autism
A well-studied brain response to sound appears earlier than usual in young children with autism.
Top autism candidate gene tied to newly identified syndrome
Mutations in the autism-linked gene PAX5 underlie a range of traits, including developmental delay, intellectual disability, seizures and autism.

Top autism candidate gene tied to newly identified syndrome
Mutations in the autism-linked gene PAX5 underlie a range of traits, including developmental delay, intellectual disability, seizures and autism.
Loss of autism-linked gene alters synapse development in mice
Mice missing a copy of the gene ASH1L have excess synapses and autism-like behavioral differences, some of which are reversed by boosting an ASH1L-regulated gene.
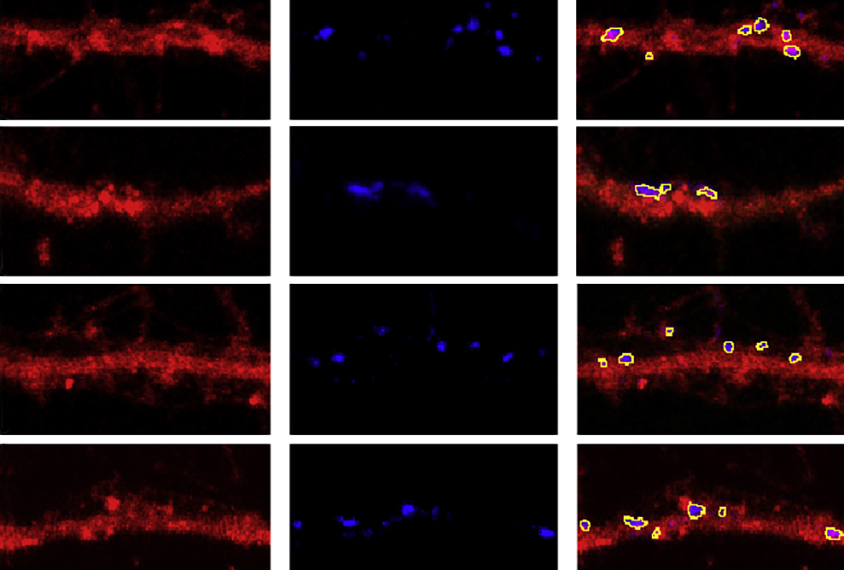
Loss of autism-linked gene alters synapse development in mice
Mice missing a copy of the gene ASH1L have excess synapses and autism-like behavioral differences, some of which are reversed by boosting an ASH1L-regulated gene.
Sensory issues linked to heart-rate differences in autistic youth
Autistic children with sensory issues show more intense physiological reactions to unpleasant sounds and other sensations than their non-autistic peers do, a new study shows.

Sensory issues linked to heart-rate differences in autistic youth
Autistic children with sensory issues show more intense physiological reactions to unpleasant sounds and other sensations than their non-autistic peers do, a new study shows.
Malfunctioning neurons mute sound processing in mouse model of Rett syndrome
Female mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene MECP2 in a specific set of inhibitory neurons have a hard time heeding pups’ calls and herding litters.

Malfunctioning neurons mute sound processing in mouse model of Rett syndrome
Female mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene MECP2 in a specific set of inhibitory neurons have a hard time heeding pups’ calls and herding litters.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.