Hyperactivity
Recent articles
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
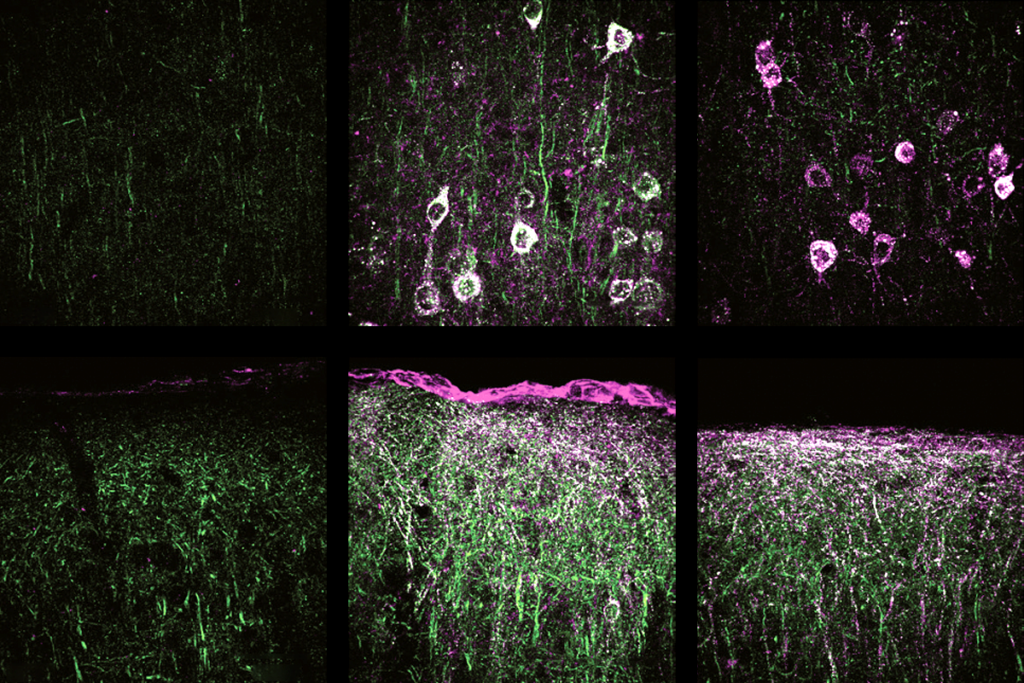
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Ketamine targets lateral habenula, setting off cascade of antidepressant effects
The drug’s affinity for overactive cells in the “anti-reward” region may help explain its rapid and long-lasting results.
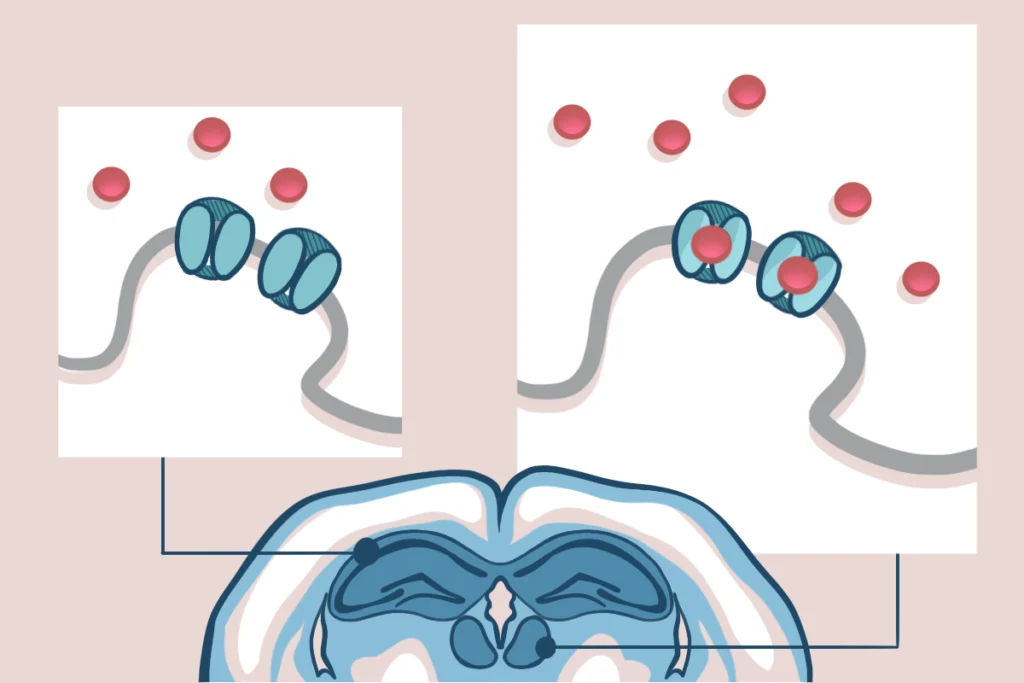
Ketamine targets lateral habenula, setting off cascade of antidepressant effects
The drug’s affinity for overactive cells in the “anti-reward” region may help explain its rapid and long-lasting results.
Mental health issues emerge with shifts in autism traits across childhood
Anxiety and other challenges autistic children experience may stem from an increase in social-communication issues and a decrease in repetitive behaviors from ages 6 to 11.

Mental health issues emerge with shifts in autism traits across childhood
Anxiety and other challenges autistic children experience may stem from an increase in social-communication issues and a decrease in repetitive behaviors from ages 6 to 11.
Serotonin powers pruning of developing brain circuits in mice
Mice with microglia missing receptors for the neurotransmitter serotonin since birth have too many synapses and show social difficulties in adulthood.
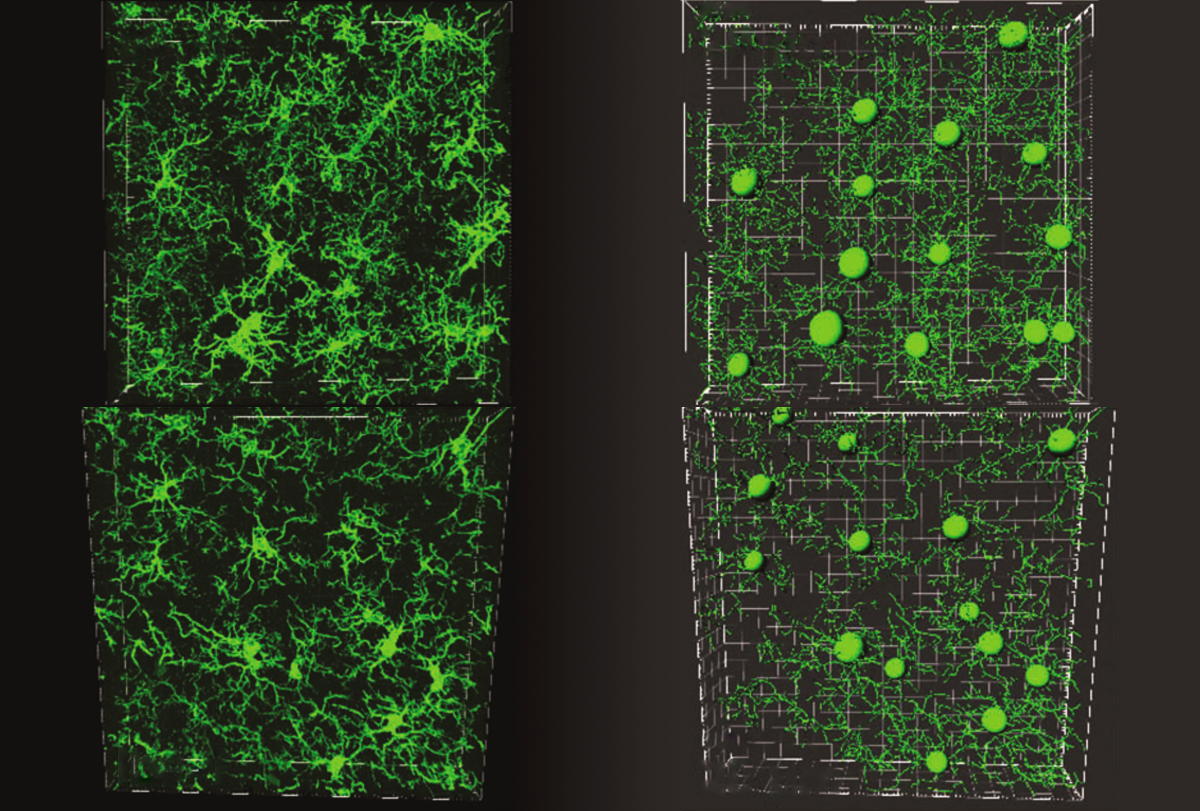
Serotonin powers pruning of developing brain circuits in mice
Mice with microglia missing receptors for the neurotransmitter serotonin since birth have too many synapses and show social difficulties in adulthood.
Autism-related genes converge on microglia and dopamine in zebrafish
The findings add to the growing evidence that genes with disparate functions can play similar roles in brain development.
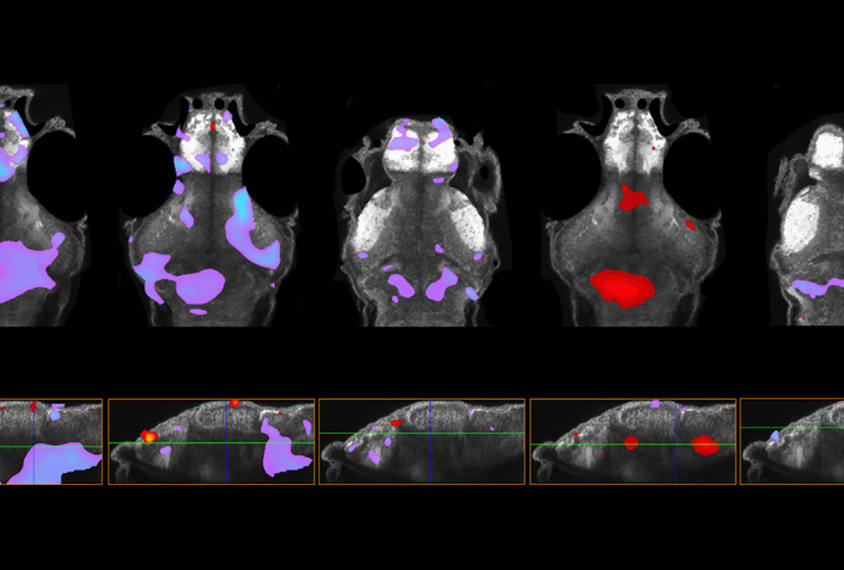
Autism-related genes converge on microglia and dopamine in zebrafish
The findings add to the growing evidence that genes with disparate functions can play similar roles in brain development.
Autism-linked MYT1L mutations prompt ‘identity crisis’ in budding brain cells
Both human and mouse progenitor cells with the alterations struggle to become neurons and instead express genes that are typically active only in muscle or the heart.
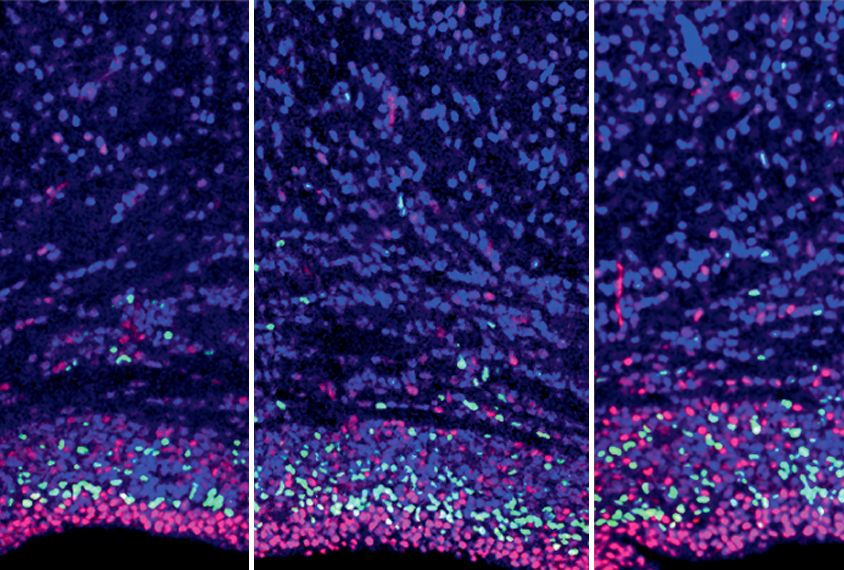
Autism-linked MYT1L mutations prompt ‘identity crisis’ in budding brain cells
Both human and mouse progenitor cells with the alterations struggle to become neurons and instead express genes that are typically active only in muscle or the heart.
Mouse model reveals root of breathing issues in rare form of autism
Dysfunctional circuits and a rogue sodium channel in the brainstem may explain the disordered breathing pattern seen in children with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a form of autism.
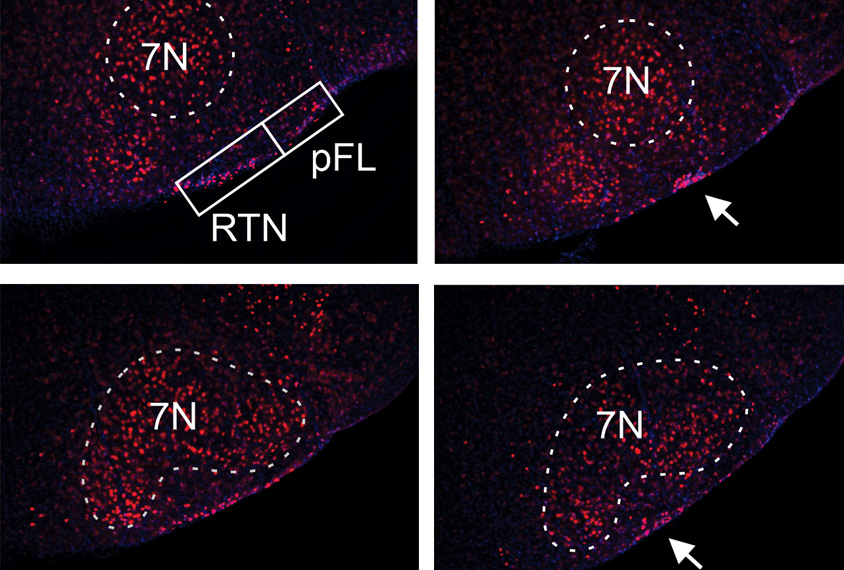
Mouse model reveals root of breathing issues in rare form of autism
Dysfunctional circuits and a rogue sodium channel in the brainstem may explain the disordered breathing pattern seen in children with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a form of autism.
Precocious neurons may stunt brain growth in rare form of autism
The first animal model of MYT1L syndrome suggests that fast-maturing neurons lead to the unusually small brains, social deficits and other traits seen in people with the condition.
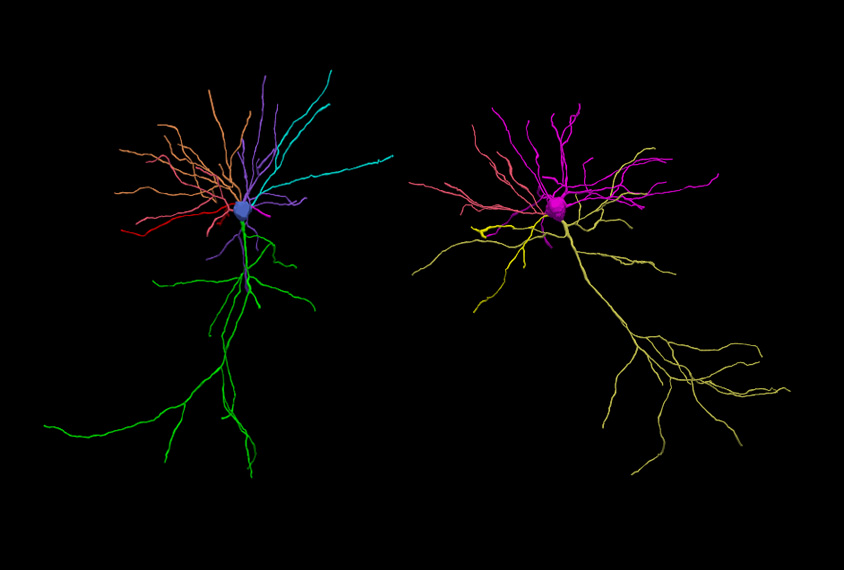
Precocious neurons may stunt brain growth in rare form of autism
The first animal model of MYT1L syndrome suggests that fast-maturing neurons lead to the unusually small brains, social deficits and other traits seen in people with the condition.
Stimulant restores cell signaling, eases behavior issues in animals missing autism gene
Worms and zebrafish missing both copies of the gene CHD7 have disrupted cellular signaling, a dearth of inhibitory neurons and behavior changes — all of which are reversed by the stimulant drug ephedrine.
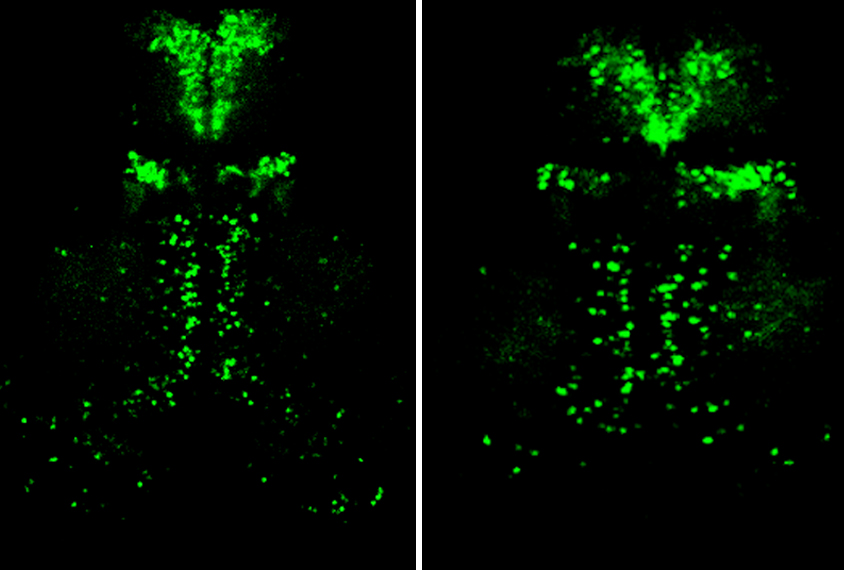
Stimulant restores cell signaling, eases behavior issues in animals missing autism gene
Worms and zebrafish missing both copies of the gene CHD7 have disrupted cellular signaling, a dearth of inhibitory neurons and behavior changes — all of which are reversed by the stimulant drug ephedrine.
Virus-based method manipulates inhibitory neurons in brains
A new viral tool can selectively control different types of neurons that dampen brain activity in rodents, monkeys and people.
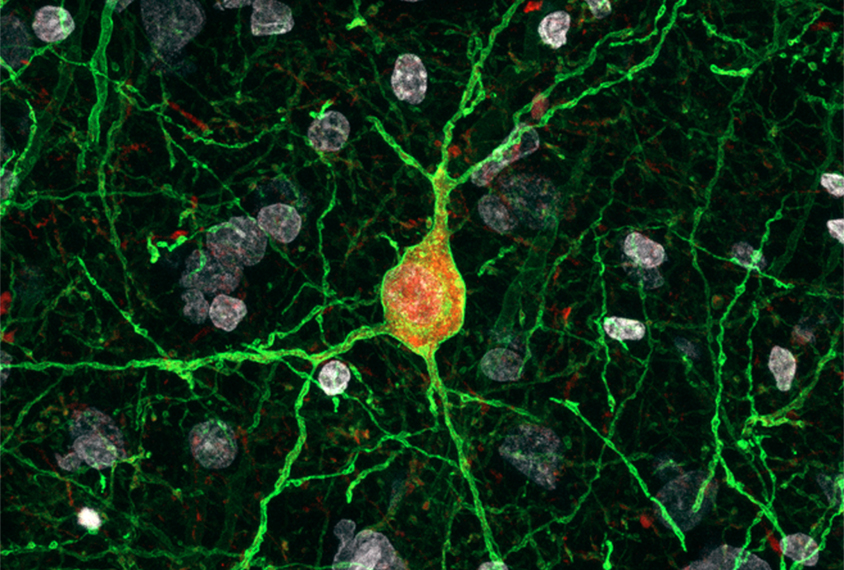
Virus-based method manipulates inhibitory neurons in brains
A new viral tool can selectively control different types of neurons that dampen brain activity in rodents, monkeys and people.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.

Is there a neuroscientist in the House?
Sam Wang, a neuroscientist running for the U.S. House of Representatives, has been considering American democracy for decades.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.
Marcelle Lapicque: A forgotten pioneer in neuroscience
Lapicque was the first Black woman neuroscientist in Europe, new research suggests.