NeuroAI
Recent articles
Advances and insights on the intersection between neuroscience and artificial intelligence
The Transmitter’s favorite essays of 2025
Throughout a tumultuous year in science, researchers opined on policy changes and funding uncertainty, as well as scientific trends and the impact of artificial-intelligence tools on the field.

The Transmitter’s favorite essays of 2025
Throughout a tumultuous year in science, researchers opined on policy changes and funding uncertainty, as well as scientific trends and the impact of artificial-intelligence tools on the field.
The Transmitter’s reading list: Six upcoming neuroscience books, plus notable titles in 2025
Dig into an exploration of the fundamental aspects of intelligence, a new textbook about theoretical neuroscience and a memoir about memory research, among other new releases.

The Transmitter’s reading list: Six upcoming neuroscience books, plus notable titles in 2025
Dig into an exploration of the fundamental aspects of intelligence, a new textbook about theoretical neuroscience and a memoir about memory research, among other new releases.
Breaking the jar: Why NeuroAI needs embodiment
Brain function is inexorably shaped by the body. Embracing this fact will benefit computational models of real brain function, as well as the design of artificial neural networks.

Breaking the jar: Why NeuroAI needs embodiment
Brain function is inexorably shaped by the body. Embracing this fact will benefit computational models of real brain function, as well as the design of artificial neural networks.
The BabyLM Challenge: In search of more efficient learning algorithms, researchers look to infants
A competition that trains language models on relatively small datasets of words, closer in size to what a child hears up to age 13, seeks solutions to some of the major challenges of today’s large language models.

The BabyLM Challenge: In search of more efficient learning algorithms, researchers look to infants
A competition that trains language models on relatively small datasets of words, closer in size to what a child hears up to age 13, seeks solutions to some of the major challenges of today’s large language models.
Dean Buonomano explores the concept of time in neuroscience and physics
He outlines why he thinks integrated information theory is unscientific and discusses how timing is a fundamental computation in brains.
Dean Buonomano explores the concept of time in neuroscience and physics
He outlines why he thinks integrated information theory is unscientific and discusses how timing is a fundamental computation in brains.
Aran Nayebi discusses a NeuroAI update to the Turing test
And he highlights the need to match neural representations across machines and organisms to build better autonomous agents.
Aran Nayebi discusses a NeuroAI update to the Turing test
And he highlights the need to match neural representations across machines and organisms to build better autonomous agents.
Accepting “the bitter lesson” and embracing the brain’s complexity
To gain insight into complex neural data, we must move toward a data-driven regime, training large models on vast amounts of information. We asked nine experts on computational neuroscience and neural data analysis to weigh in.
Accepting “the bitter lesson” and embracing the brain’s complexity
To gain insight into complex neural data, we must move toward a data-driven regime, training large models on vast amounts of information. We asked nine experts on computational neuroscience and neural data analysis to weigh in.
Does the solution to building safe artificial intelligence lie in the brain?
Now is the time to decipher what makes the brain both flexible and dependable—and to apply those lessons to AI—before an unaligned agentic system wreaks havoc.
Does the solution to building safe artificial intelligence lie in the brain?
Now is the time to decipher what makes the brain both flexible and dependable—and to apply those lessons to AI—before an unaligned agentic system wreaks havoc.
Dmitri Chklovskii outlines how single neurons may act as their own optimal feedback controllers
From logical gates to grandmother cells, neuroscientists have employed many metaphors to explain single neuron function. Chklovskii makes the case that neurons are actually trying to control how their outputs affect the rest of the brain.
Dmitri Chklovskii outlines how single neurons may act as their own optimal feedback controllers
From logical gates to grandmother cells, neuroscientists have employed many metaphors to explain single neuron function. Chklovskii makes the case that neurons are actually trying to control how their outputs affect the rest of the brain.
‘Digital humans’ in a virtual world
By combining large language models with modular cognitive control architecture, Robert Yang and his collaborators have built agents that are capable of grounded reasoning at a linguistic level. Striking collective behaviors have emerged.
‘Digital humans’ in a virtual world
By combining large language models with modular cognitive control architecture, Robert Yang and his collaborators have built agents that are capable of grounded reasoning at a linguistic level. Striking collective behaviors have emerged.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
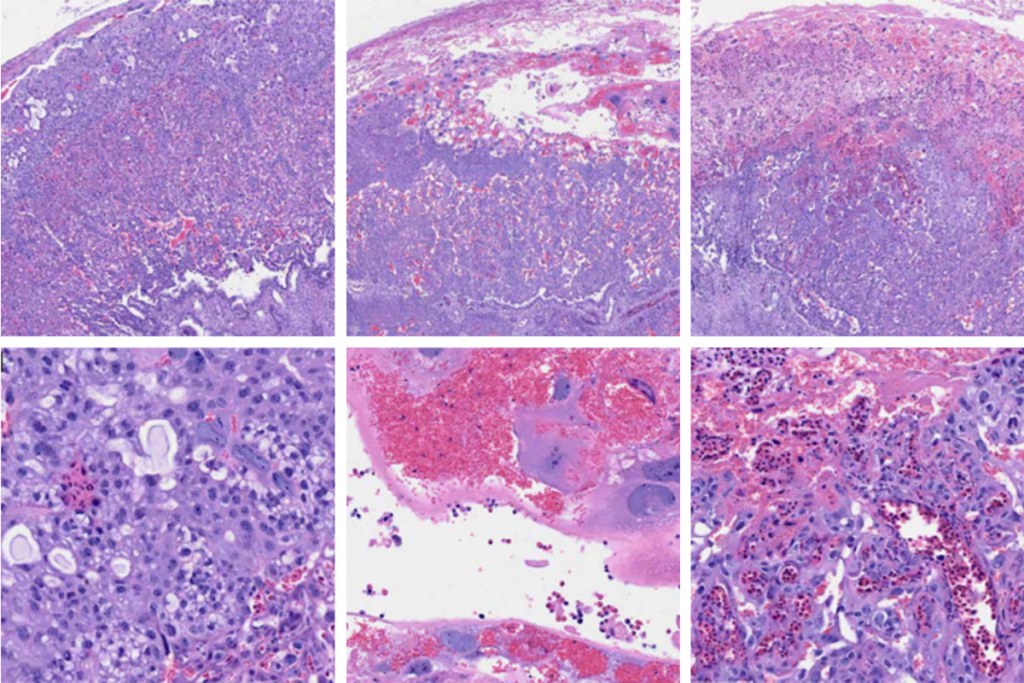
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.