Neurodegeneration
Recent articles
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
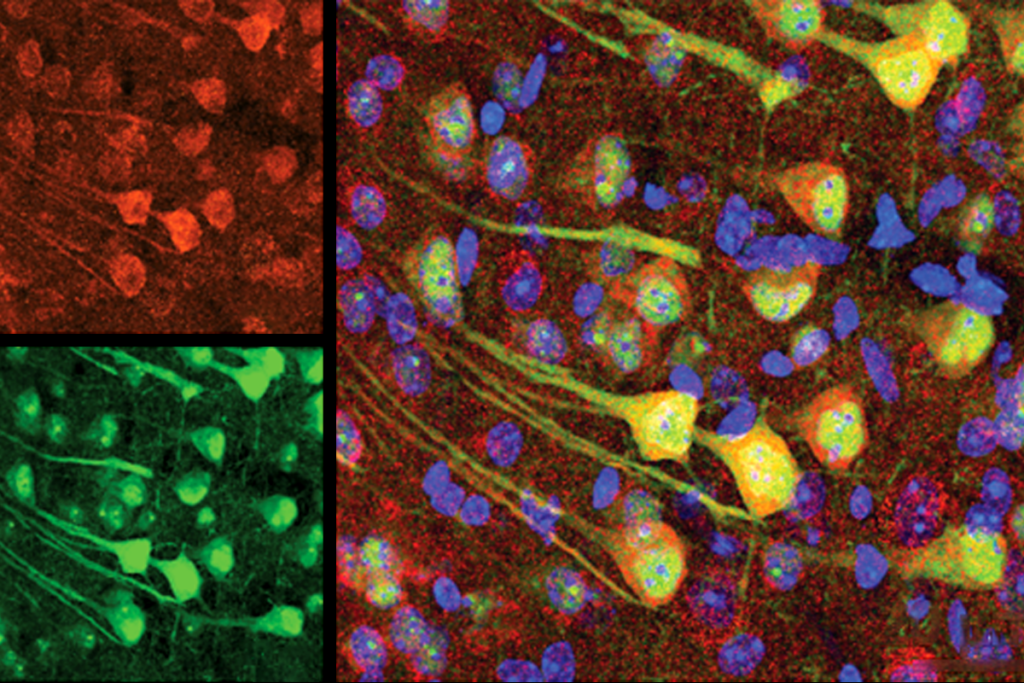
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
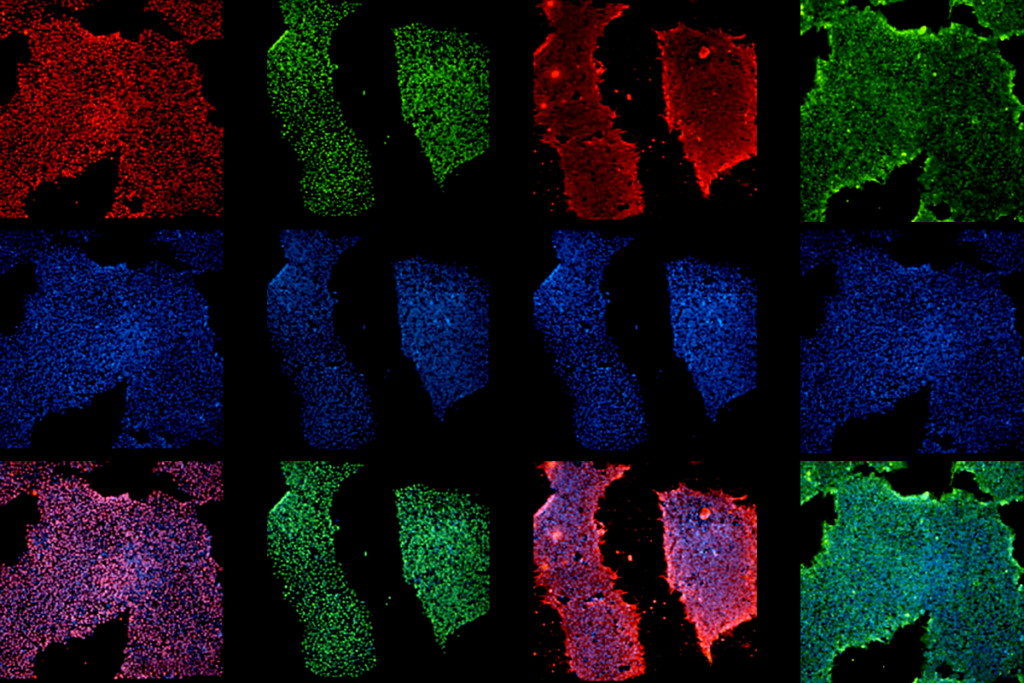
Bringing African ancestry into cellular neuroscience
Two independent teams in Africa are developing stem cell lines and organoids from local populations to explore neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions.
Neuro’s ark: How goats can model neurodegeneration
Since debunking an urban legend that headbutting animals don’t damage their brain, Nicole Ackermans has been investigating how the behavior correlates with neurodegeneration.

Neuro’s ark: How goats can model neurodegeneration
Since debunking an urban legend that headbutting animals don’t damage their brain, Nicole Ackermans has been investigating how the behavior correlates with neurodegeneration.
What are the most-cited neuroscience papers from the past 30 years?
Highly cited papers reflect the surge in artificial-intelligence research in the field and other technical advances, plus prizewinning work on analgesics, the fusiform face area and ion channels.

What are the most-cited neuroscience papers from the past 30 years?
Highly cited papers reflect the surge in artificial-intelligence research in the field and other technical advances, plus prizewinning work on analgesics, the fusiform face area and ion channels.
New questions around motor neurons and plasticity
A researcher’s theory hangs muscle degeneration on a broken neural circuit.
New questions around motor neurons and plasticity
A researcher’s theory hangs muscle degeneration on a broken neural circuit.
Paper by memory institute director garners expression of concern over image integrity
The notice, posted last week in Nature, follows a recent string of corrections to at least three other articles by Li-Huei Tsai’s lab.
Paper by memory institute director garners expression of concern over image integrity
The notice, posted last week in Nature, follows a recent string of corrections to at least three other articles by Li-Huei Tsai’s lab.
How to teach this paper: ‘Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia,’ by Liddelow et al. (2017)
Shane Liddelow and his collaborators identified the factors that transform astrocytes from their helpful to harmful form. Their work is a great choice if you want to teach students about glial cell types, cell culture, gene expression or protein measurement.
How to teach this paper: ‘Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia,’ by Liddelow et al. (2017)
Shane Liddelow and his collaborators identified the factors that transform astrocytes from their helpful to harmful form. Their work is a great choice if you want to teach students about glial cell types, cell culture, gene expression or protein measurement.
Single-cell genomics technologies and cell atlases have ushered in a new era of human neurobiology
Single-cell approaches are already shedding light on the human brain, identifying cell types that are most vulnerable in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, for example.
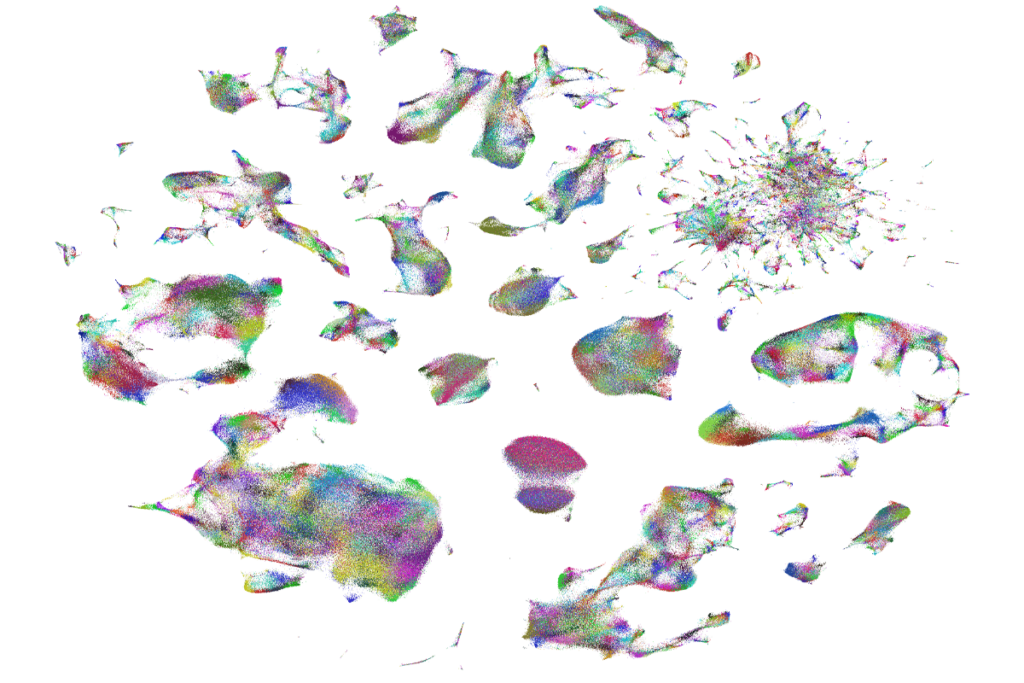
Single-cell genomics technologies and cell atlases have ushered in a new era of human neurobiology
Single-cell approaches are already shedding light on the human brain, identifying cell types that are most vulnerable in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, for example.
Huntington’s disease gene variants past a certain size poison select cells
The findings—providing “the next step in the whole pathway”—help explain the disease’s late onset and offer hope that it has an extended therapeutic window.
Huntington’s disease gene variants past a certain size poison select cells
The findings—providing “the next step in the whole pathway”—help explain the disease’s late onset and offer hope that it has an extended therapeutic window.
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
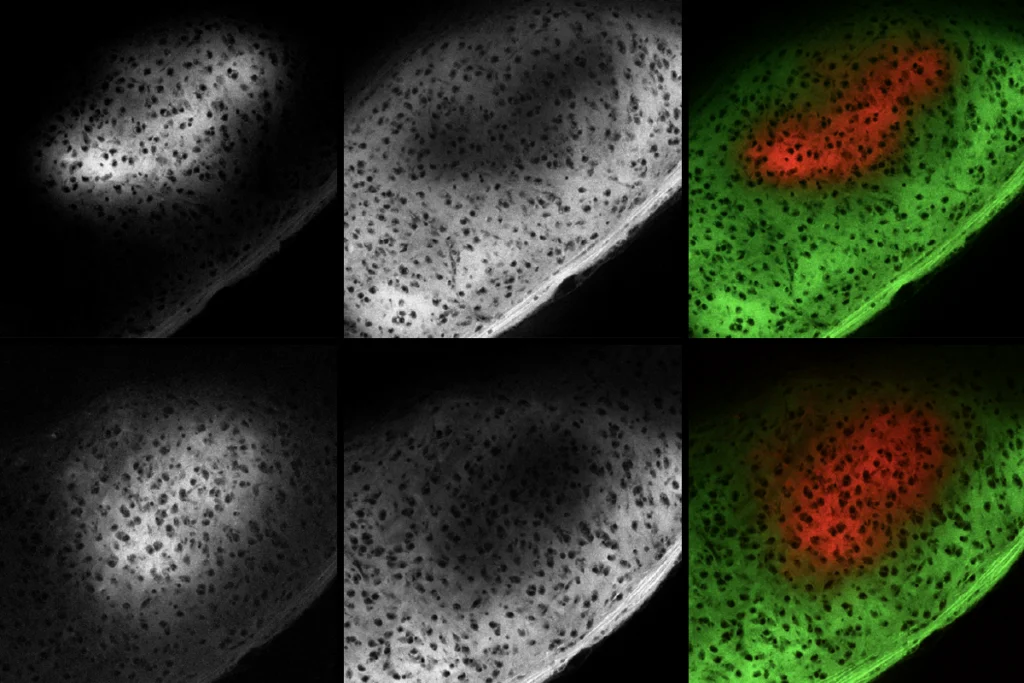
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
New insights on sex bias in autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 16 February.
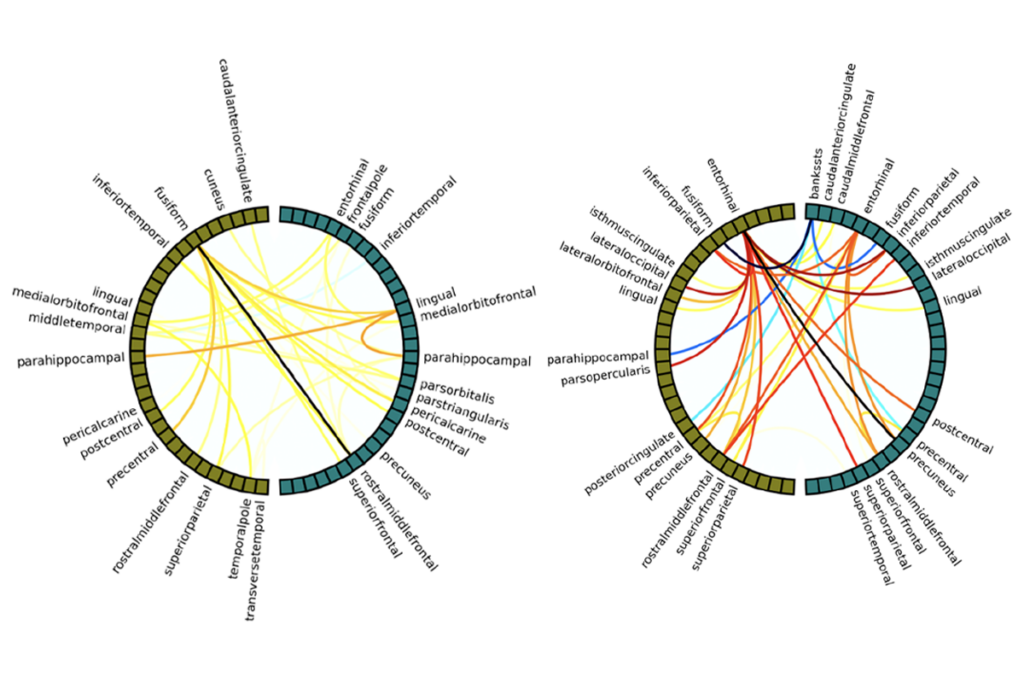
New insights on sex bias in autism, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 16 February.
Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.

Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.