Addiction
Recent articles
‘Understudied secret’ in brain dampens nicotine drive in mice
The interpeduncular nucleus produces an aversion to nicotine, even at low doses, and helps moderate how rewarding mice find the drug.
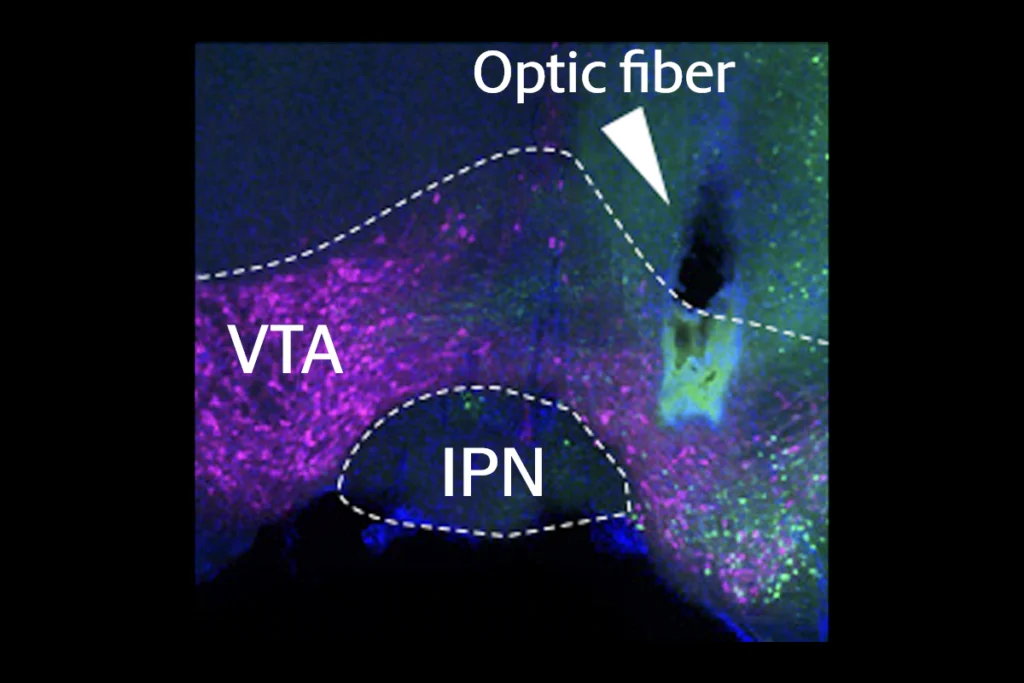
‘Understudied secret’ in brain dampens nicotine drive in mice
The interpeduncular nucleus produces an aversion to nicotine, even at low doses, and helps moderate how rewarding mice find the drug.
Neuroscientists need to do better at explaining basic mental health research
The knowledge gap between scientists, health-care professionals, policymakers and people with mental health conditions is growing, slowing the translation of basic science to new treatments. Like lawyers learning to present a case to the court, scientists should learn to educate nonscientists about their findings.

Neuroscientists need to do better at explaining basic mental health research
The knowledge gap between scientists, health-care professionals, policymakers and people with mental health conditions is growing, slowing the translation of basic science to new treatments. Like lawyers learning to present a case to the court, scientists should learn to educate nonscientists about their findings.
Striking a pose with Aya Osman
The neuroscientist and part-time fashion model opens up about the people who inspire her; her interest in science communication; and how she once ended up on a stage with Channing Tatum.
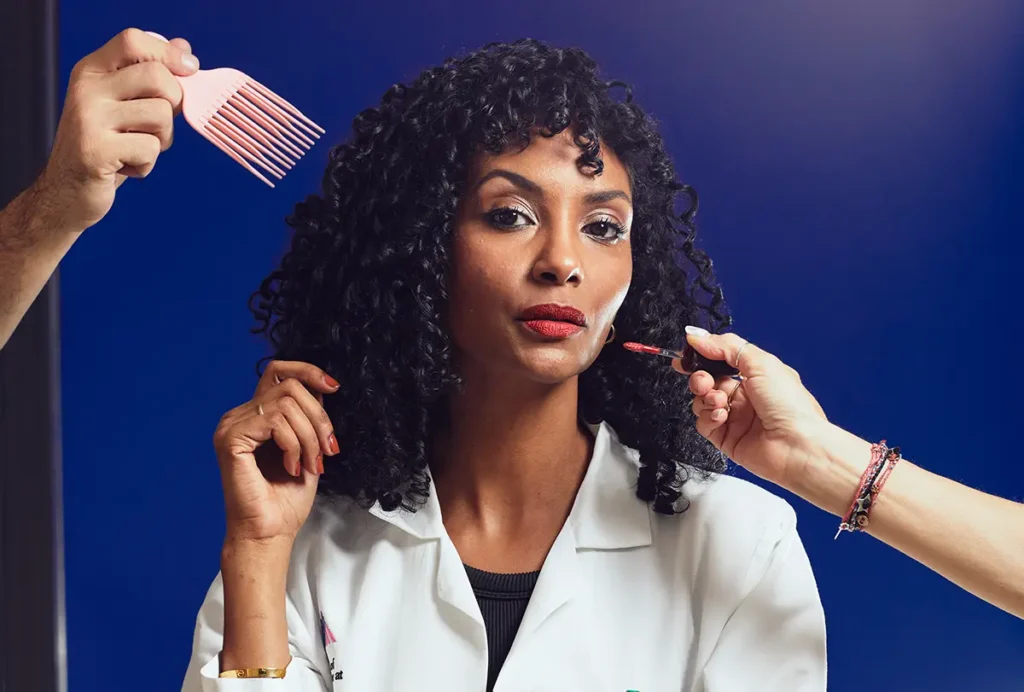

Striking a pose with Aya Osman
The neuroscientist and part-time fashion model opens up about the people who inspire her; her interest in science communication; and how she once ended up on a stage with Channing Tatum.
Cocaine, morphine commandeer neurons normally activated by food, water in mice
Confirming a long-held hypothesis, repeated exposure to the drugs alters neurons in the nucleus accumbens, the brain’s reward center, and curbs an animal’s urge for sustenance.
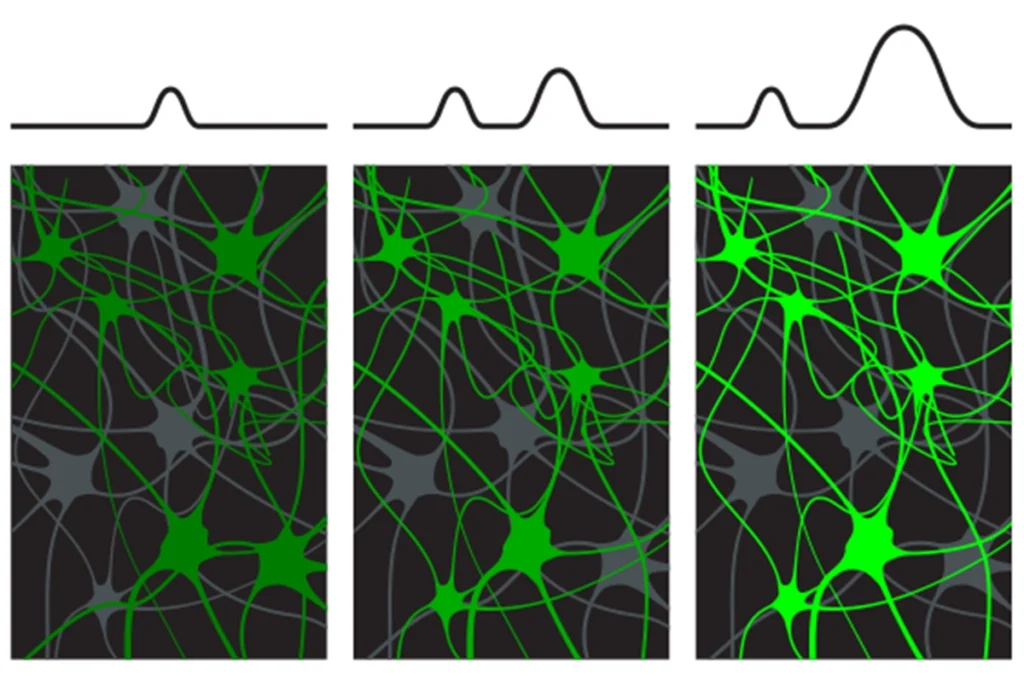
Cocaine, morphine commandeer neurons normally activated by food, water in mice
Confirming a long-held hypothesis, repeated exposure to the drugs alters neurons in the nucleus accumbens, the brain’s reward center, and curbs an animal’s urge for sustenance.
Temperament is innate but hackable, animal studies suggest
Emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stress are largely inherited in rodents — but can be modified in early life by targeting inflammation-related cells or even just adjusting an animal’s environment.
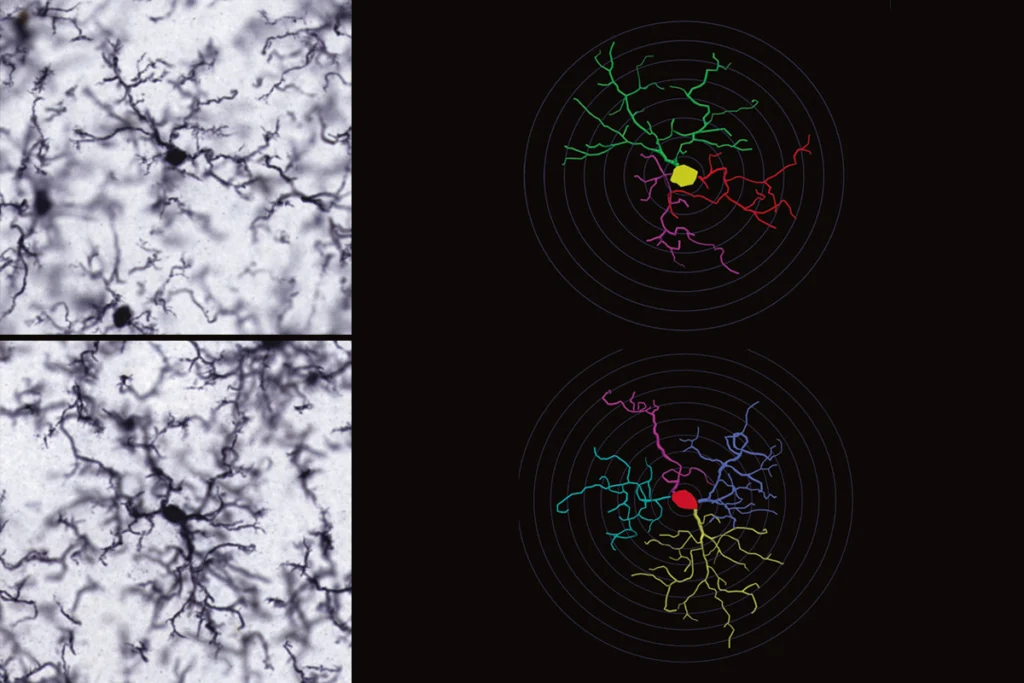
Temperament is innate but hackable, animal studies suggest
Emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stress are largely inherited in rodents — but can be modified in early life by targeting inflammation-related cells or even just adjusting an animal’s environment.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
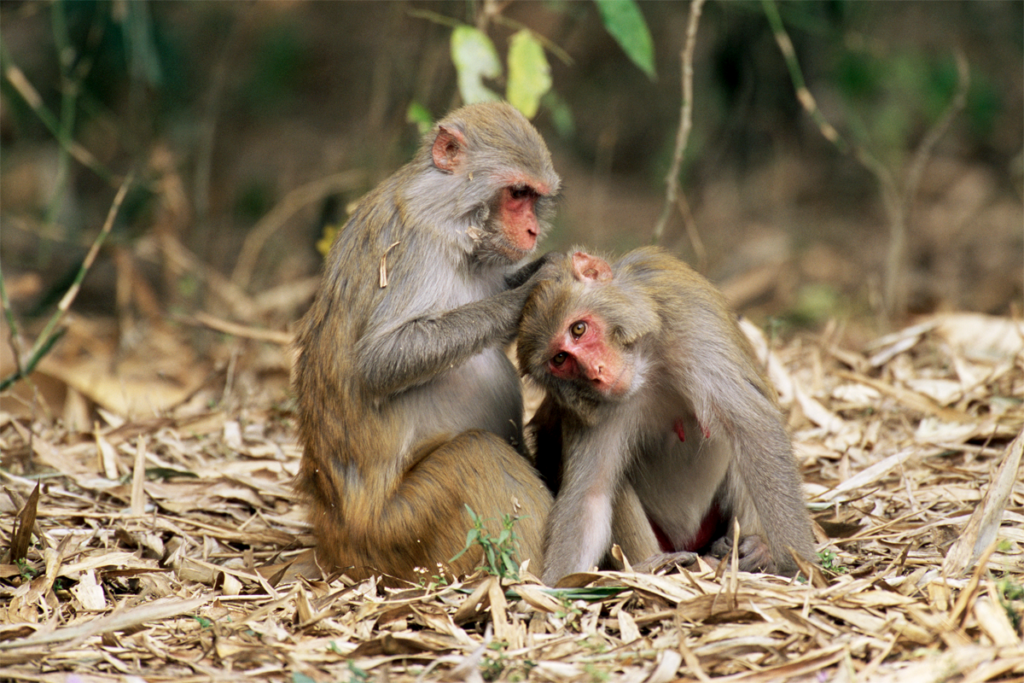

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
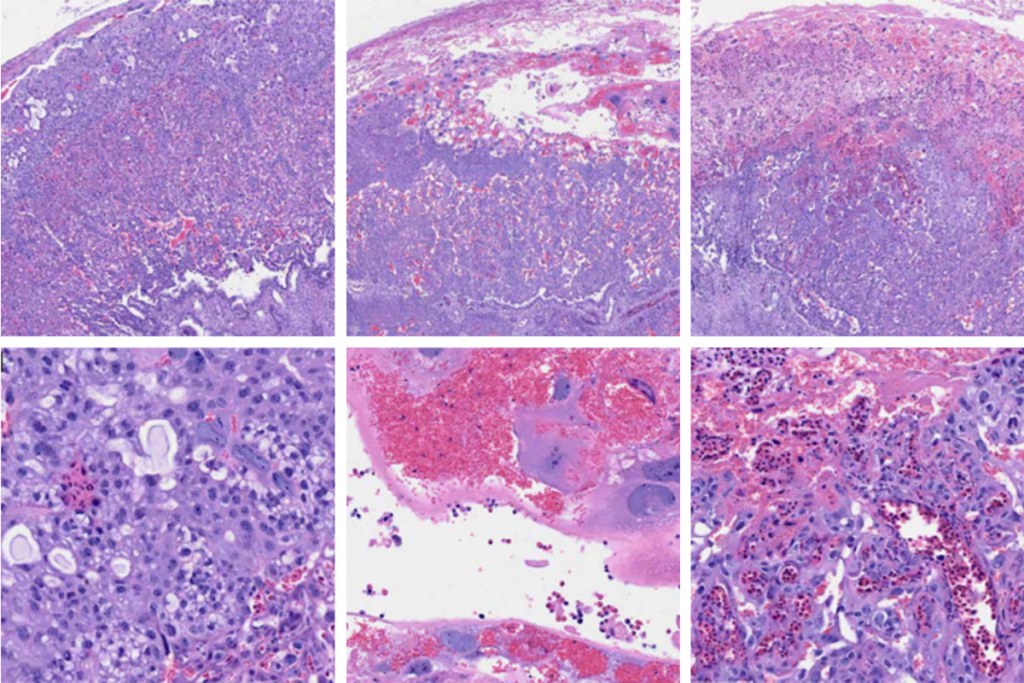
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.