Microglia
Recent articles
Microglia implicated in infantile amnesia
The glial cells could explain the link between maternal immune activation and autism-like behaviors in mice.
Microglia implicated in infantile amnesia
The glial cells could explain the link between maternal immune activation and autism-like behaviors in mice.
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
Aging neurons outsource garbage disposal, clog microglia
Degradation-resistant proteins pass from neurons to glial cells in a process that may spread protein clumps around the brain, according to a study in mice.
Astrocytes stabilize circuits in adult mouse brain
The glial cells secrete a protein that suppresses plasticity post-development.
Astrocytes stabilize circuits in adult mouse brain
The glial cells secrete a protein that suppresses plasticity post-development.
How to teach this paper: ‘Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia,’ by Liddelow et al. (2017)
Shane Liddelow and his collaborators identified the factors that transform astrocytes from their helpful to harmful form. Their work is a great choice if you want to teach students about glial cell types, cell culture, gene expression or protein measurement.
How to teach this paper: ‘Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia,’ by Liddelow et al. (2017)
Shane Liddelow and his collaborators identified the factors that transform astrocytes from their helpful to harmful form. Their work is a great choice if you want to teach students about glial cell types, cell culture, gene expression or protein measurement.
This paper changed my life: Shane Liddelow on two papers that upended astrocyte research
A game-changing cell culture method developed in Ben Barres’ lab completely transformed the way we study astrocytes and helped me build a career studying their reactive substates.
This paper changed my life: Shane Liddelow on two papers that upended astrocyte research
A game-changing cell culture method developed in Ben Barres’ lab completely transformed the way we study astrocytes and helped me build a career studying their reactive substates.
Video catches microglia in the act of synaptic pruning
Live cell imaging reveals the clearest picture yet of this elusive process. Whether it’s something these cells do regularly remains up for debate.
Video catches microglia in the act of synaptic pruning
Live cell imaging reveals the clearest picture yet of this elusive process. Whether it’s something these cells do regularly remains up for debate.
Age-related brain changes in mice strike hypothalamus ‘hot spot’
Neuronal and non-neuronal cells throughout the brain also express genes—particularly those related to neuronal structure and immune function—differently in aged mice, according to a new atlas.
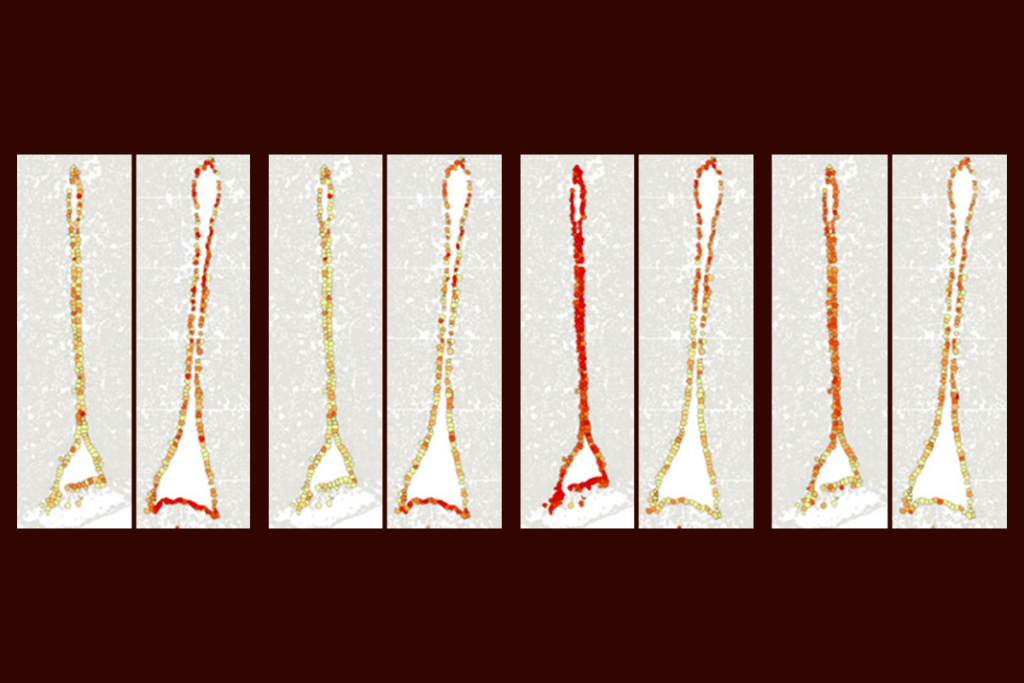
Age-related brain changes in mice strike hypothalamus ‘hot spot’
Neuronal and non-neuronal cells throughout the brain also express genes—particularly those related to neuronal structure and immune function—differently in aged mice, according to a new atlas.
Spectrum 2024: Year in review
We round up our most notable autism stories of the past 12 months.

Spectrum 2024: Year in review
We round up our most notable autism stories of the past 12 months.
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
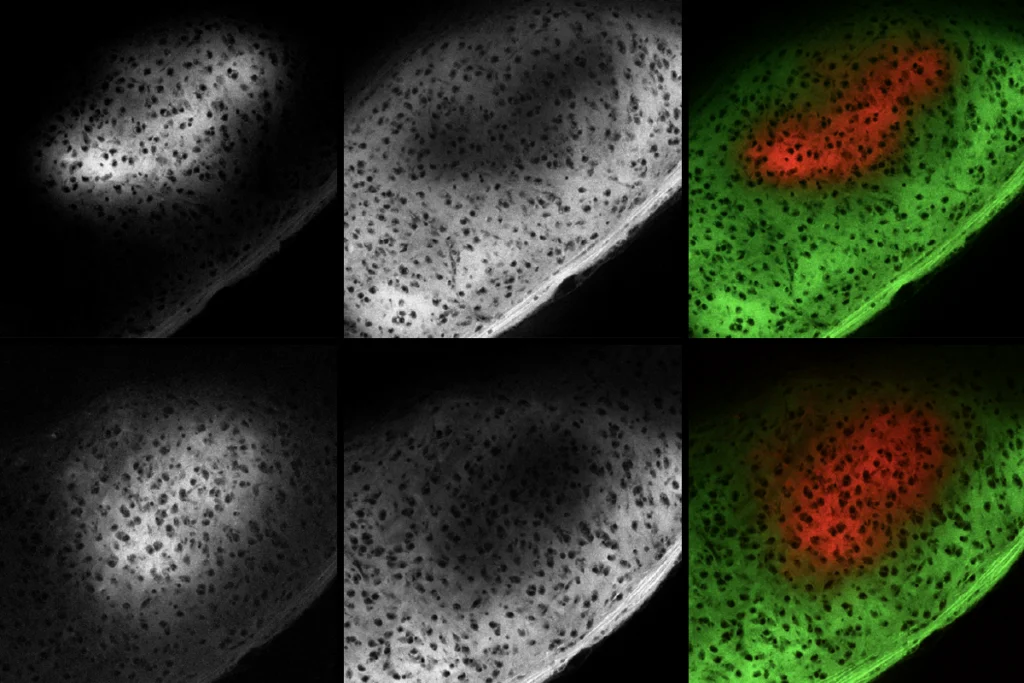
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
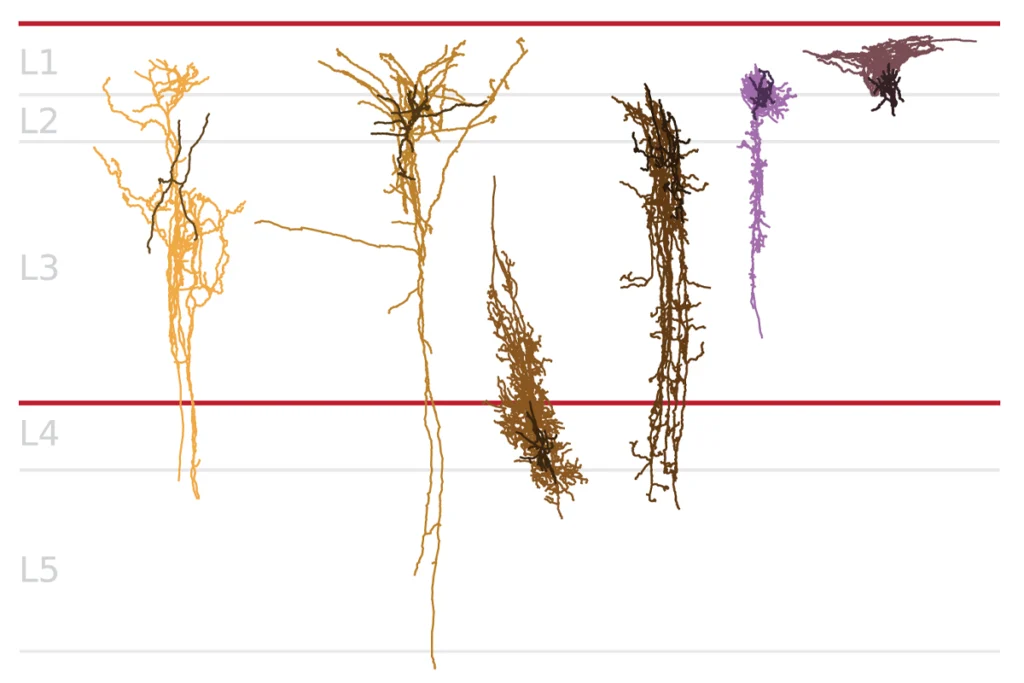

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
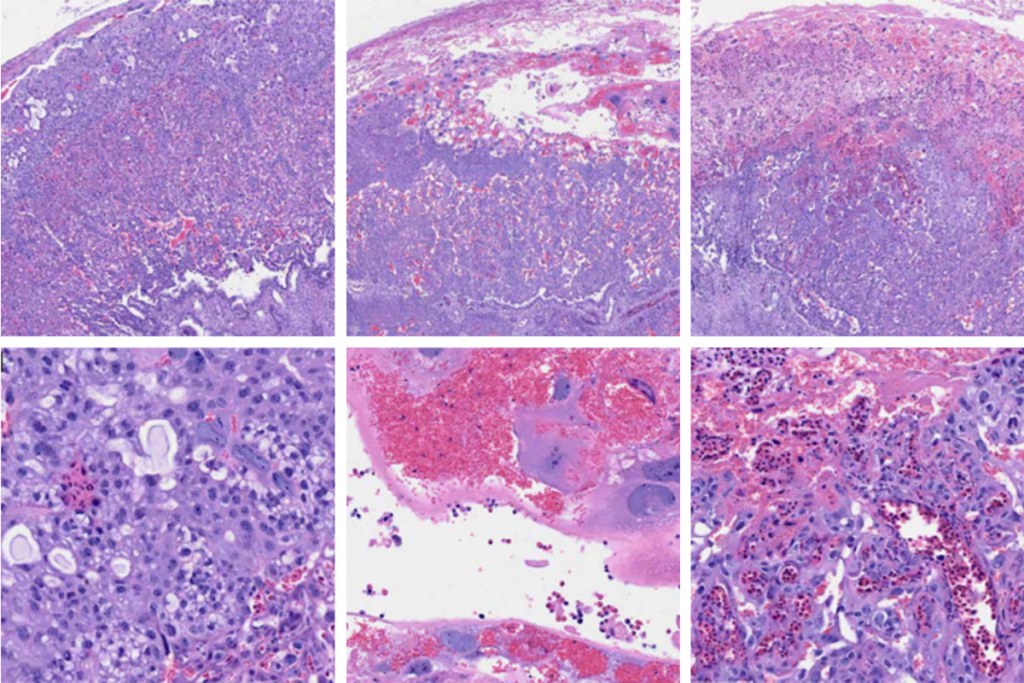
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.