Language
Recent articles
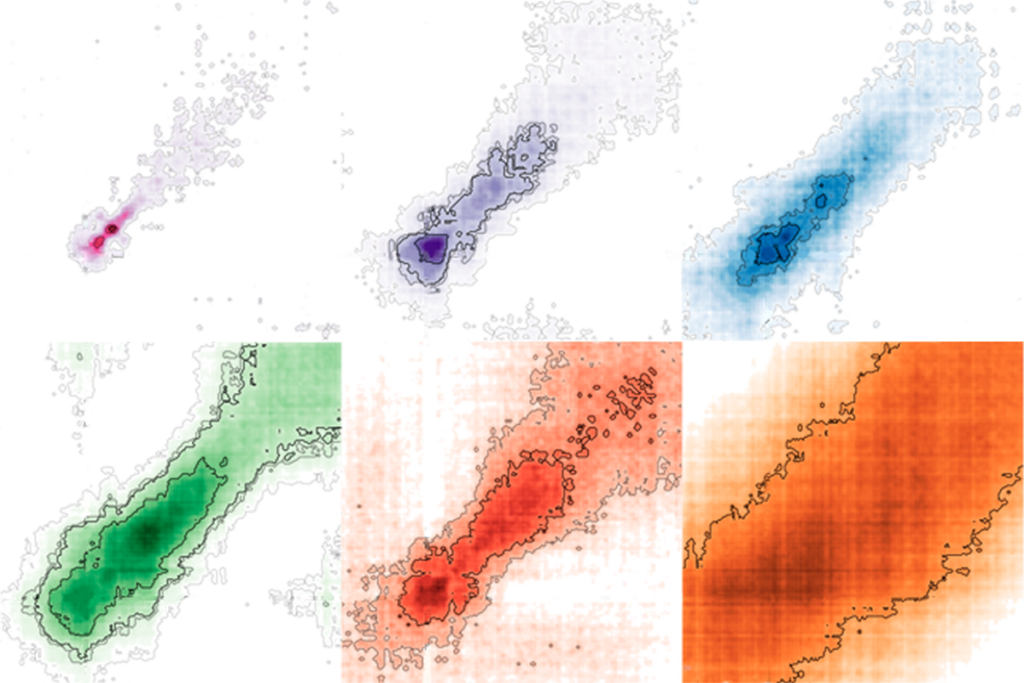
Shifting neural code powers speech comprehension
Dynamic coding helps explain how the brain processes multiple features of speech—from the smallest units of sounds to full sentences—simultaneously.
Shifting neural code powers speech comprehension
Dynamic coding helps explain how the brain processes multiple features of speech—from the smallest units of sounds to full sentences—simultaneously.
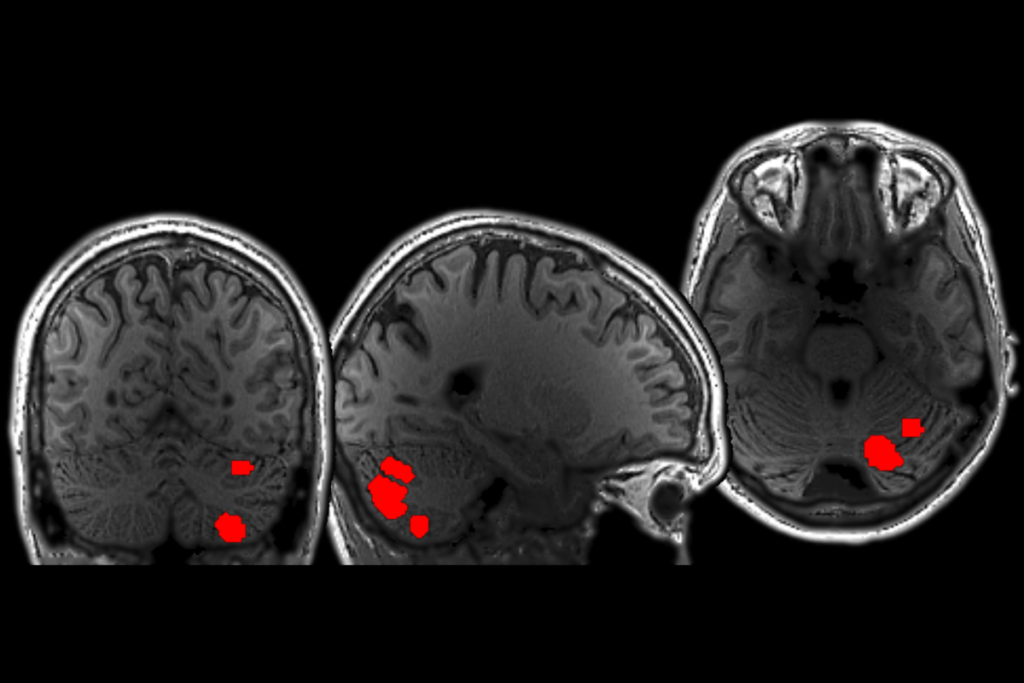
Cerebellum responds to language like cortical areas
One of four language-responsive cerebellar regions may encode meaningful information, much like the cortical language network in the left hemisphere, according to a new study.
Cerebellum responds to language like cortical areas
One of four language-responsive cerebellar regions may encode meaningful information, much like the cortical language network in the left hemisphere, according to a new study.
‘Wired for Words: The Neural Architecture of Language,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Hickok provides a detailed overview of the research into the circuits that control speech and language. In this excerpt from Chapter 5, he shares how meeting his colleague David Poeppel led to them developing the theory for bilateral speech perception.

‘Wired for Words: The Neural Architecture of Language,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Hickok provides a detailed overview of the research into the circuits that control speech and language. In this excerpt from Chapter 5, he shares how meeting his colleague David Poeppel led to them developing the theory for bilateral speech perception.
The buzziest neuroscience papers of 2023, 2024
The field took note of work on brain-computer interfaces for speech, the mechanism of psychedelics, a broader definition of hippocampal representations, and more.

The buzziest neuroscience papers of 2023, 2024
The field took note of work on brain-computer interfaces for speech, the mechanism of psychedelics, a broader definition of hippocampal representations, and more.
Robots marry natural neuroscience, experimental control to probe animal interactions
Faux fish and birds are helping researchers decipher some of the rules that govern schooling and squawking, among other social behaviors.

Robots marry natural neuroscience, experimental control to probe animal interactions
Faux fish and birds are helping researchers decipher some of the rules that govern schooling and squawking, among other social behaviors.
The BabyLM Challenge: In search of more efficient learning algorithms, researchers look to infants
A competition that trains language models on relatively small datasets of words, closer in size to what a child hears up to age 13, seeks solutions to some of the major challenges of today’s large language models.

The BabyLM Challenge: In search of more efficient learning algorithms, researchers look to infants
A competition that trains language models on relatively small datasets of words, closer in size to what a child hears up to age 13, seeks solutions to some of the major challenges of today’s large language models.
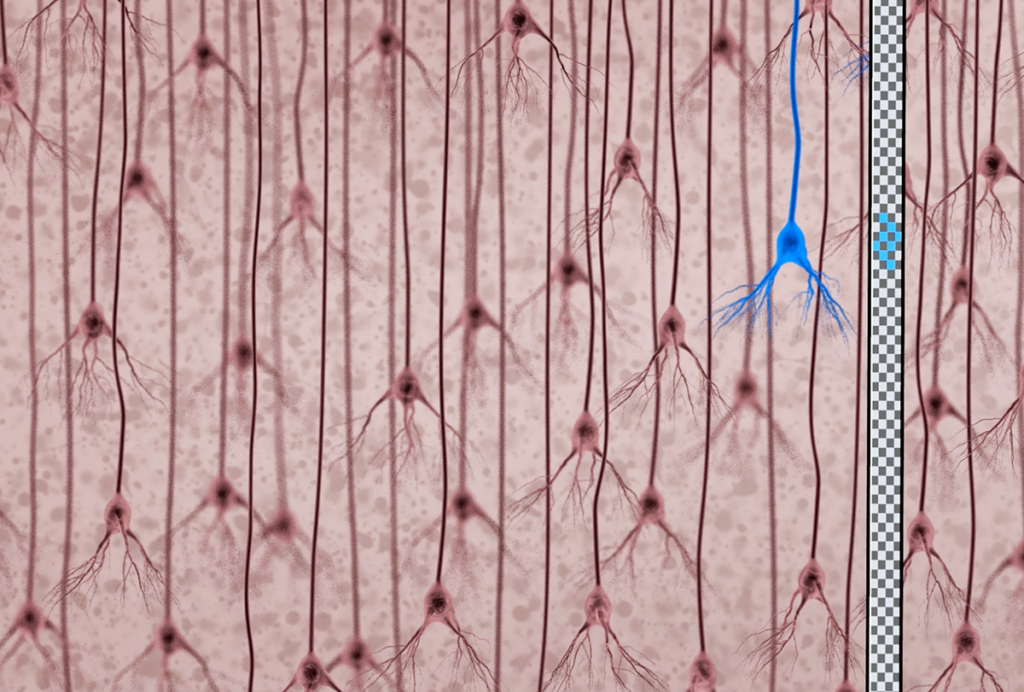
Tracking single neurons in the human brain reveals new insight into language and other human-specific functions
Better technologies to stably monitor cell populations over long periods of time make it possible to study neural coding and dynamics in the human brain.
Tracking single neurons in the human brain reveals new insight into language and other human-specific functions
Better technologies to stably monitor cell populations over long periods of time make it possible to study neural coding and dynamics in the human brain.
Gabriele Scheler reflects on the interplay between language, thought and AI
She discusses how verbal thought shapes cognition, why inner speech is foundational to human intelligence and what current artificial-intelligence models get wrong about language.
Gabriele Scheler reflects on the interplay between language, thought and AI
She discusses how verbal thought shapes cognition, why inner speech is foundational to human intelligence and what current artificial-intelligence models get wrong about language.
The last two-author neuroscience paper?
Author lists on papers have ballooned, and it’s getting hard to discern contribution.

The last two-author neuroscience paper?
Author lists on papers have ballooned, and it’s getting hard to discern contribution.
‘Digital humans’ in a virtual world
By combining large language models with modular cognitive control architecture, Robert Yang and his collaborators have built agents that are capable of grounded reasoning at a linguistic level. Striking collective behaviors have emerged.
‘Digital humans’ in a virtual world
By combining large language models with modular cognitive control architecture, Robert Yang and his collaborators have built agents that are capable of grounded reasoning at a linguistic level. Striking collective behaviors have emerged.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.
Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.

Two neurobiologists win 2026 Brain Prize for discovering mechanics of touch
Research by Patrik Ernfors and David Ginty has delineated the diverse cell types of the somatosensory system and revealed how they detect and discriminate among different types of tactile information.