Excitatory signaling
Recent articles
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
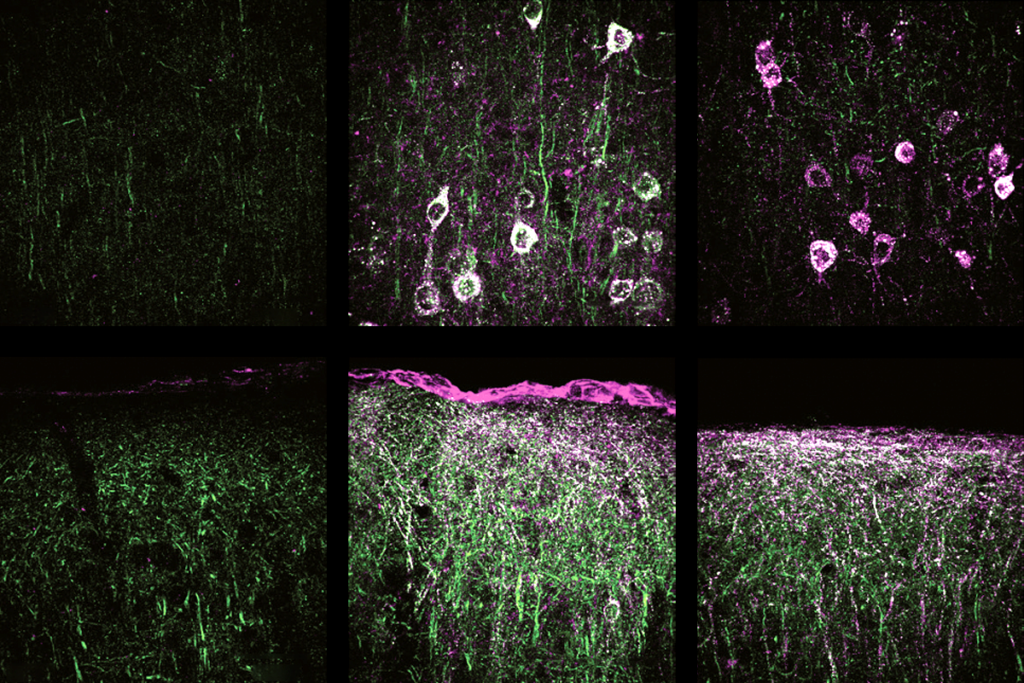
Gene replacement therapy normalizes some traits in SYNGAP1 model mice
The first published virus-based gene therapy for SYNGAP1 deletion yields benefits despite the gene’s long length and complexity.
Ramping up cortical activity in early life sparks autism-like behaviors in mice
The findings add fuel to the long-running debate over how an imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory signaling contributes to the autism.
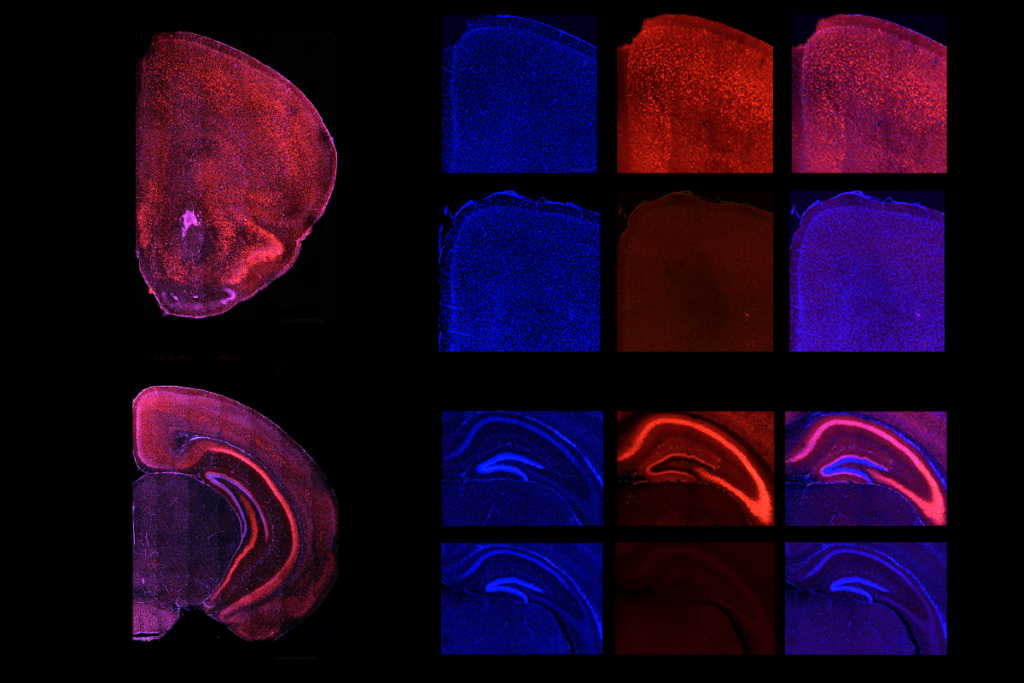
Ramping up cortical activity in early life sparks autism-like behaviors in mice
The findings add fuel to the long-running debate over how an imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory signaling contributes to the autism.
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
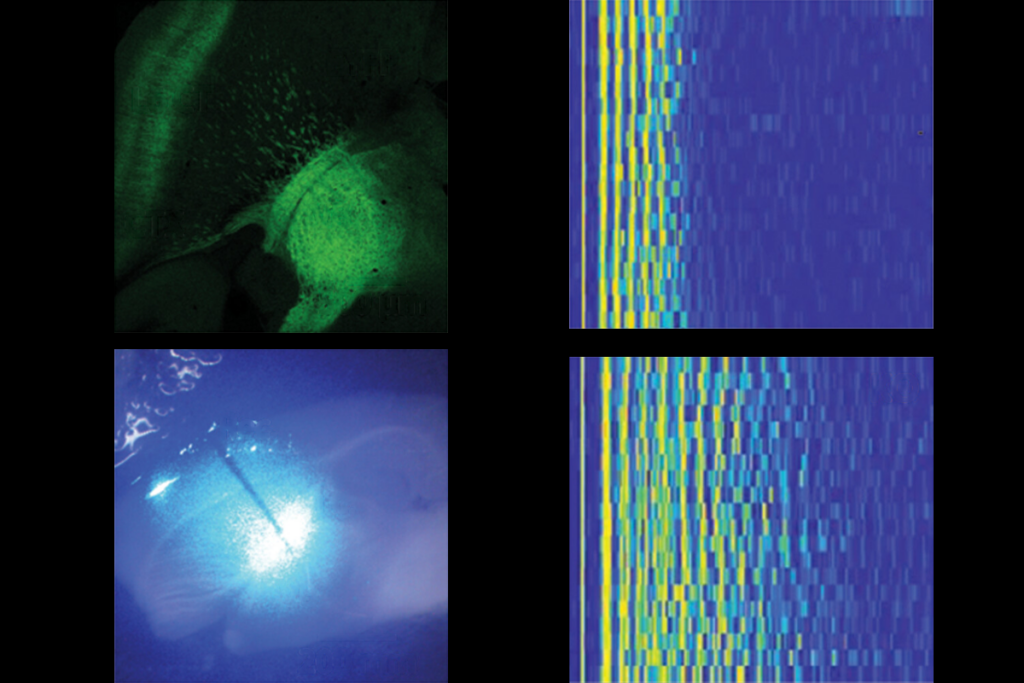
Sensory gatekeeper drives seizures, autism-like behaviors in mouse model
The new work, in mice missing the autism-linked gene CNTNAP2, suggests a mechanism to help explain the overlap between epilepsy and autism.
‘Understudied secret’ in brain dampens nicotine drive in mice
The interpeduncular nucleus produces an aversion to nicotine, even at low doses, and helps moderate how rewarding mice find the drug.
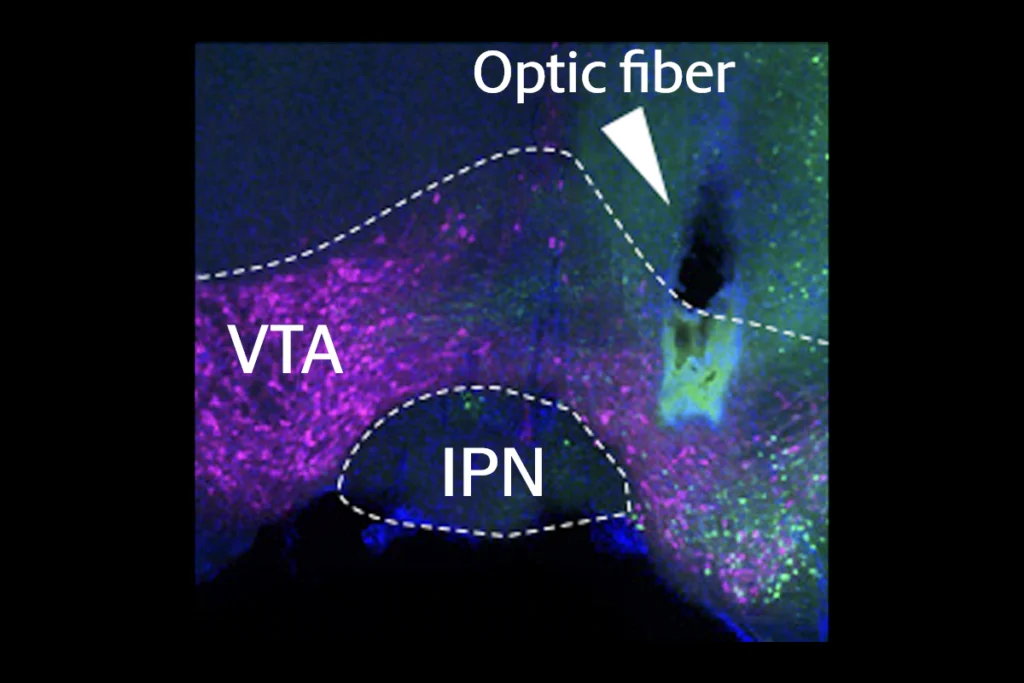
‘Understudied secret’ in brain dampens nicotine drive in mice
The interpeduncular nucleus produces an aversion to nicotine, even at low doses, and helps moderate how rewarding mice find the drug.
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
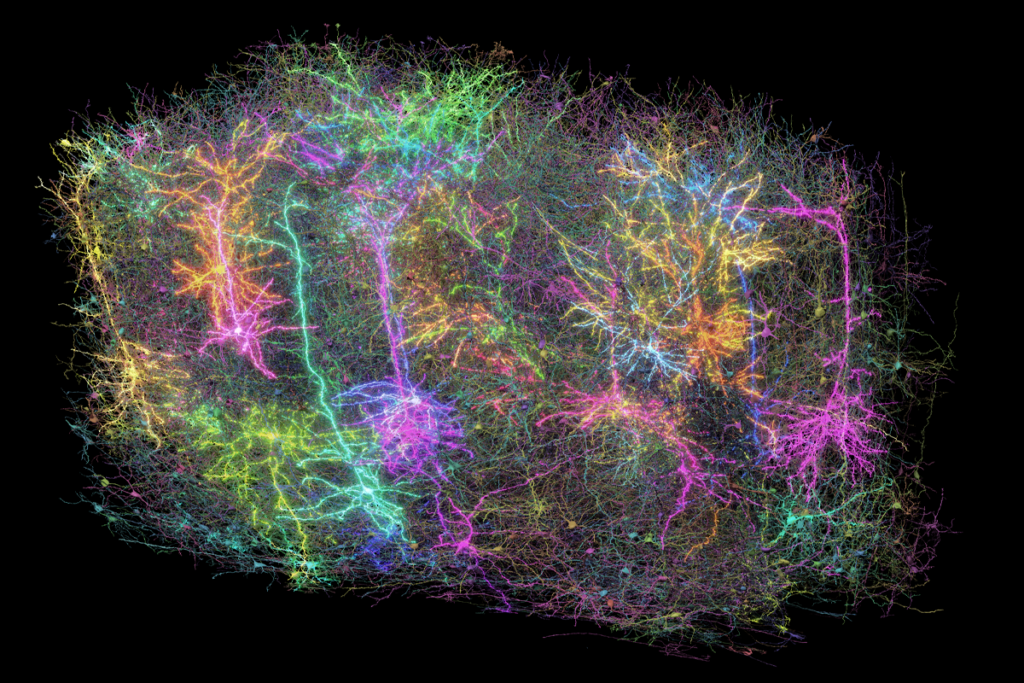
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
Bespoke photometry system captures variety of dopamine signals in mice
The tool tracks the excitation of an engineered protein that senses dopamine’s absolute levels, including fast and slow fluctuations in real time, and offers new insights into how the signals change across the brain.
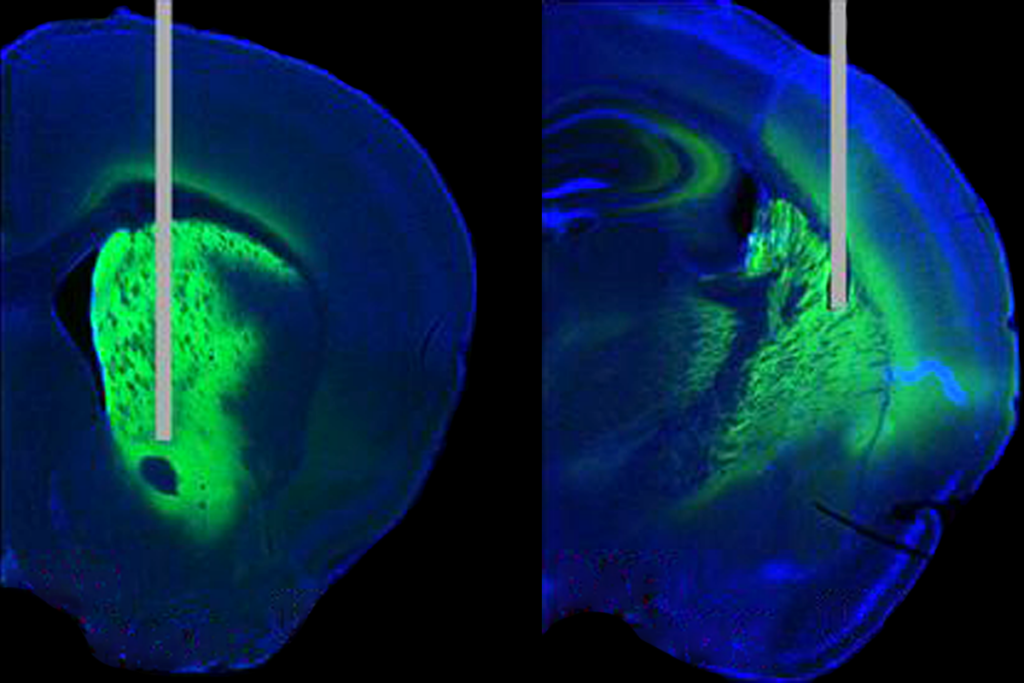
Bespoke photometry system captures variety of dopamine signals in mice
The tool tracks the excitation of an engineered protein that senses dopamine’s absolute levels, including fast and slow fluctuations in real time, and offers new insights into how the signals change across the brain.
What are recurrent networks doing in the brain?
The cortex is filled with excitatory local synapses, but we know little about their role in brain function. New experimental tools, along with ideas from artificial intelligence, are poised to change that.
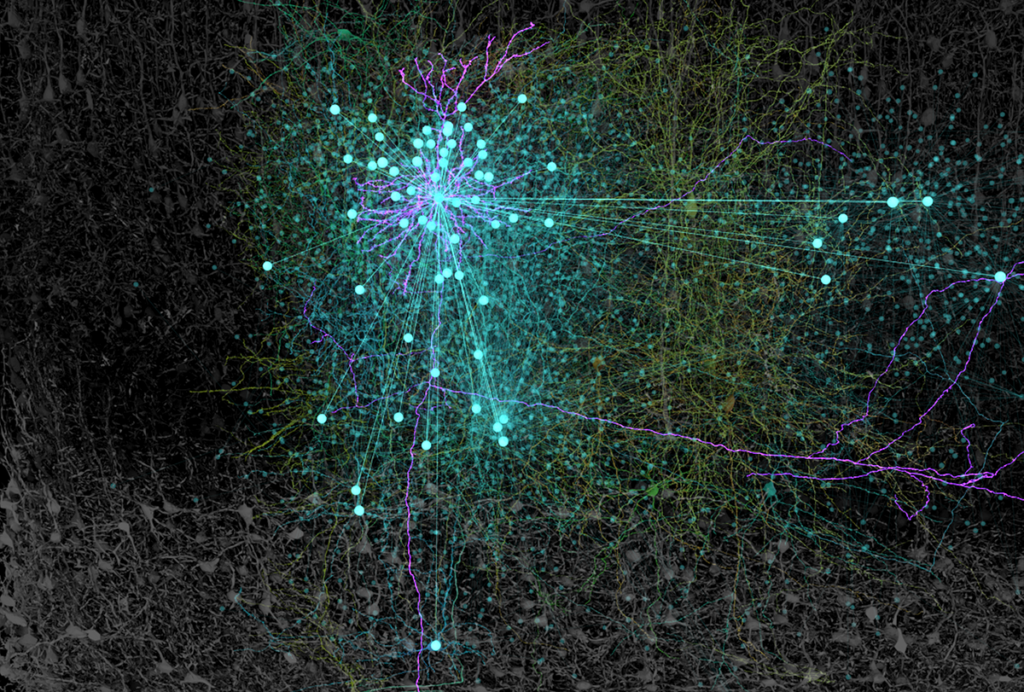

What are recurrent networks doing in the brain?
The cortex is filled with excitatory local synapses, but we know little about their role in brain function. New experimental tools, along with ideas from artificial intelligence, are poised to change that.
Newfound gene network controls long-range connections between emotional, cognitive brain areas
The finding could help unravel gene regulatory networks and explain how genetic and environmental factors interact in neurodevelopmental conditions.
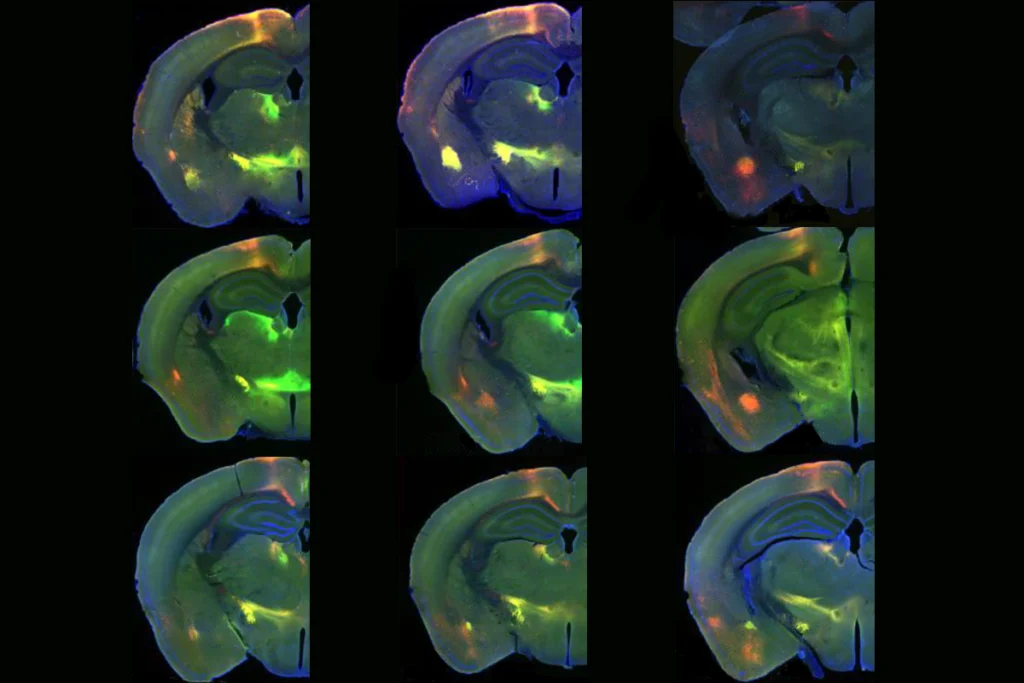
Newfound gene network controls long-range connections between emotional, cognitive brain areas
The finding could help unravel gene regulatory networks and explain how genetic and environmental factors interact in neurodevelopmental conditions.
As circuits wire up, interneurons take cues from surrounding cells
The inhibitory cells’ development, diversity and abundance in the cortex is directed in part by pyramidal cells, a new preprint suggests.
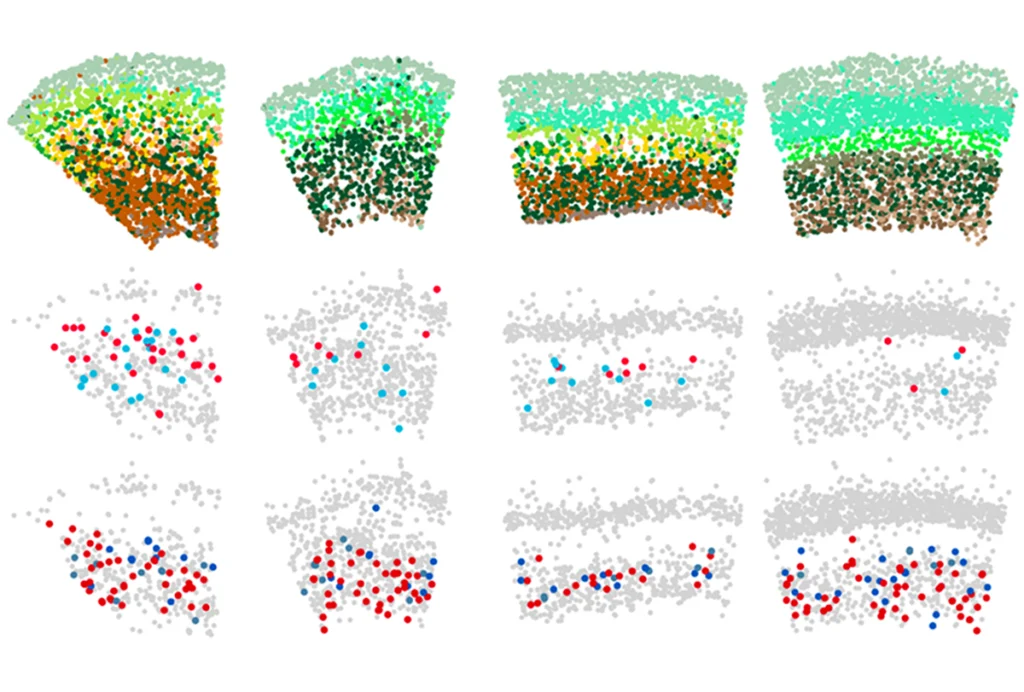
As circuits wire up, interneurons take cues from surrounding cells
The inhibitory cells’ development, diversity and abundance in the cortex is directed in part by pyramidal cells, a new preprint suggests.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
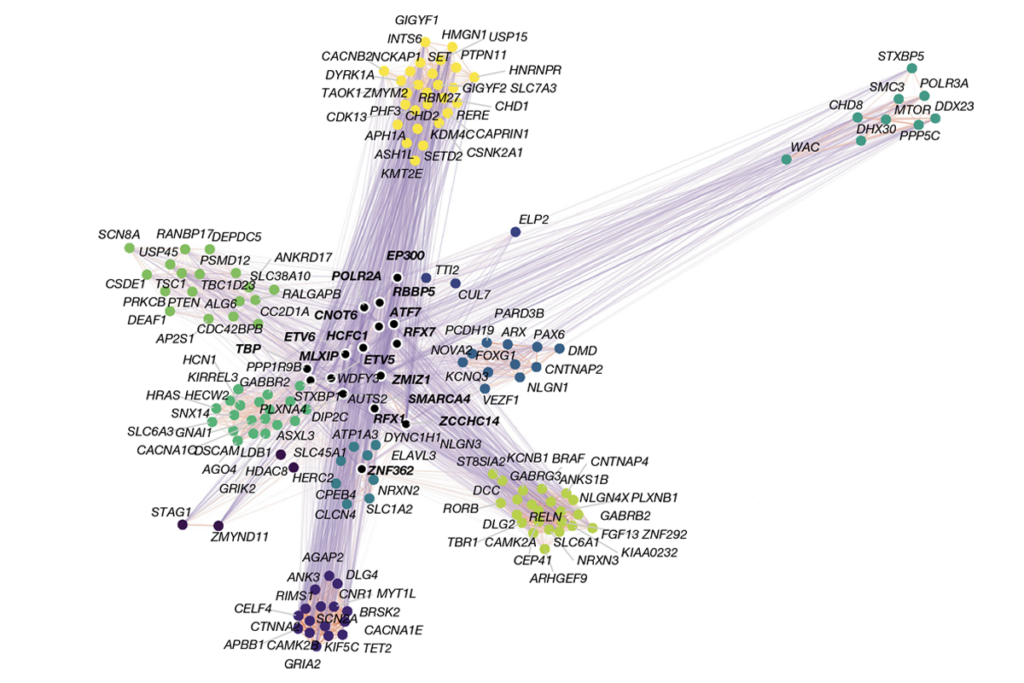
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
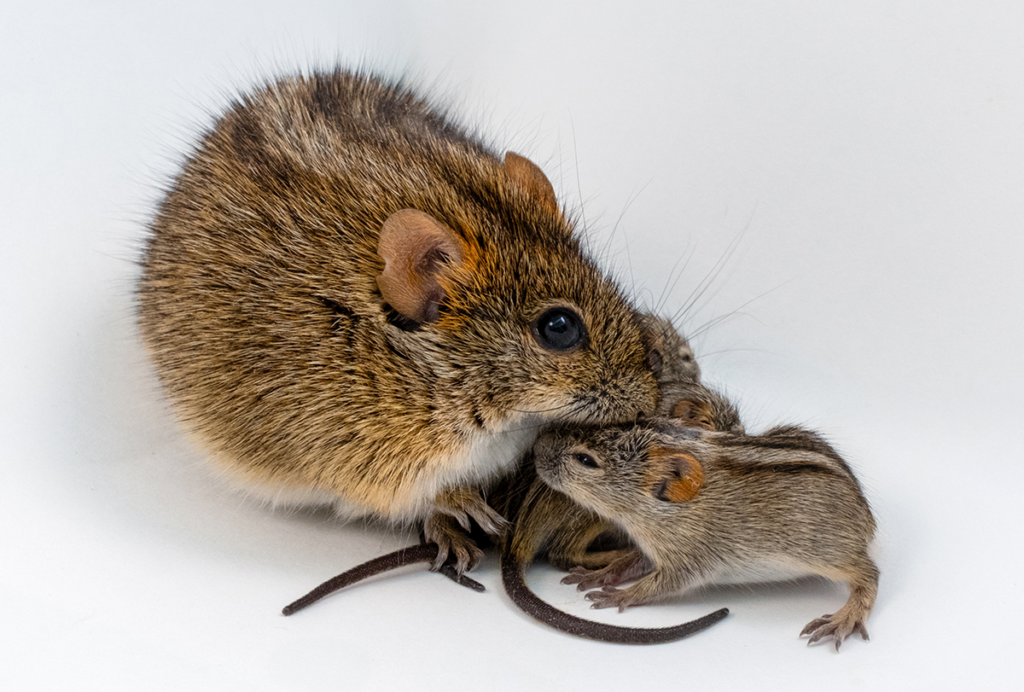

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.