Perspectives
Recent articles
Expert opinions on trends and controversies in neuroscience
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
Neuroscience needs single-synapse studies
Studying individual synapses has the potential to help neuroscientists develop new theories, better understand brain disorders and reevaluate 70 years of work on synaptic transmission plasticity.
Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.

Neuroscience has a species problem
If our field is serious about building general principles of brain function, cross-species dialogue must become a core organizing principle rather than an afterthought.
This paper changed my life: Ishmail Abdus-Saboor on balancing the study of pain and pleasure
A 2013 Nature paper from David Anderson’s lab revealed a group of sensory neurons involved in pleasurable touch and led Abdus-Saboor down a new research path.
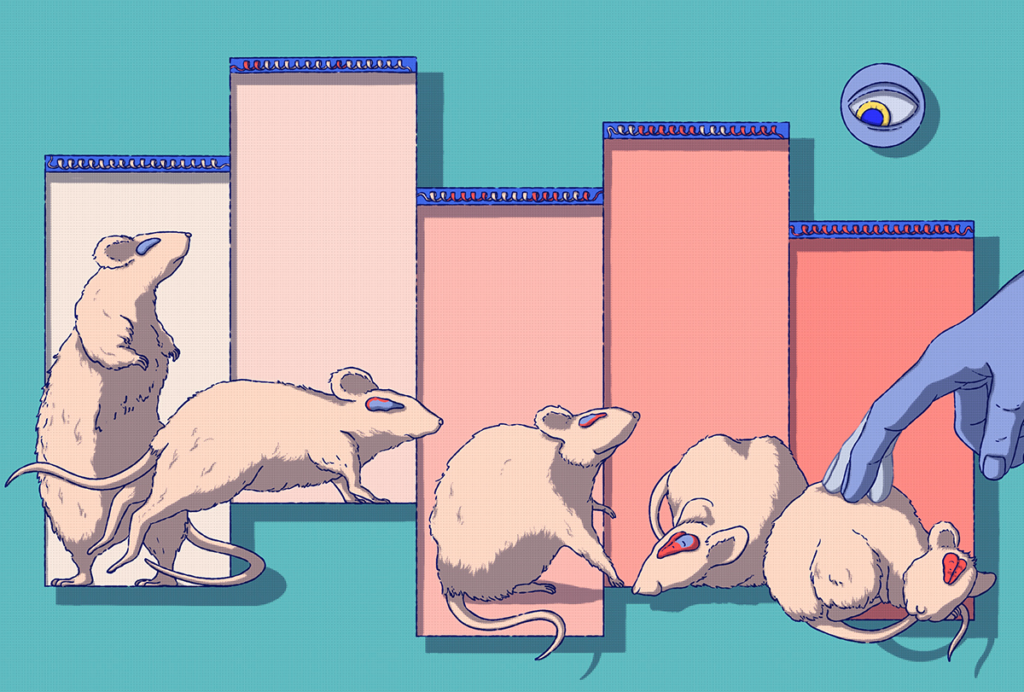
This paper changed my life: Ishmail Abdus-Saboor on balancing the study of pain and pleasure
A 2013 Nature paper from David Anderson’s lab revealed a group of sensory neurons involved in pleasurable touch and led Abdus-Saboor down a new research path.
From genes to dynamics: Examining brain cell types in action may reveal the logic of brain function
Defining brain cell types is no longer a matter of classification alone, but of embedding their genetic identities within the dynamical organization of population activity.

From genes to dynamics: Examining brain cell types in action may reveal the logic of brain function
Defining brain cell types is no longer a matter of classification alone, but of embedding their genetic identities within the dynamical organization of population activity.
Betting blind on AI and the scientific mind
If the struggle to articulate an idea is part of how you come to understand it, then tools that bypass that struggle might degrade your capacity for the kind of thinking that matters most for actual discovery.

Betting blind on AI and the scientific mind
If the struggle to articulate an idea is part of how you come to understand it, then tools that bypass that struggle might degrade your capacity for the kind of thinking that matters most for actual discovery.
Why emotion research is stuck—and how to move it forward
Studying how organisms infer indirect threats and understand changing contexts can establish a common framework that bridges species and levels of analysis.
Why emotion research is stuck—and how to move it forward
Studying how organisms infer indirect threats and understand changing contexts can establish a common framework that bridges species and levels of analysis.
How to collaborate with AI
To make the best use of LLMs in research, turn your scientific question into a set of concrete, checkable proposals, wire up an automatic scoring loop, and let the AI iterate.

How to collaborate with AI
To make the best use of LLMs in research, turn your scientific question into a set of concrete, checkable proposals, wire up an automatic scoring loop, and let the AI iterate.
Computational psychiatry needs systems neuroscience
Dissecting different parallel processing streams may help us understand the mechanisms underlying psychiatric symptoms, such as delusions, and unite human and animal research.

Computational psychiatry needs systems neuroscience
Dissecting different parallel processing streams may help us understand the mechanisms underlying psychiatric symptoms, such as delusions, and unite human and animal research.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
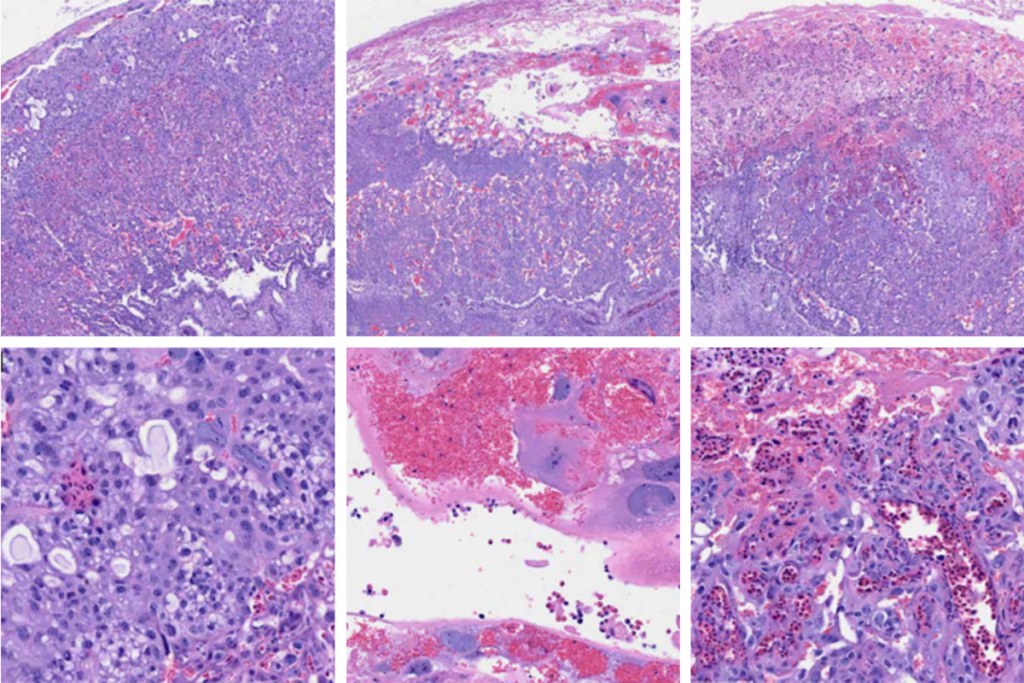
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.
Three ecological psychologists on the right and wrong ways to use the field’s principles in neuroscience
Matthieu de Wit, Luis H. Favela and Vicente Raja weigh in on the recent trend of neuroscientists importing concepts from ecological psychology, the study of how an organism’s interactions with its environment explain perception and action.